 January 2015 in “Dermatology online journal”
January 2015 in “Dermatology online journal” A man with total hair loss also developed a rare nail condition, likely due to autoimmune issues.
 2 citations,
February 2014 in “Hair therapy & transplantation”
2 citations,
February 2014 in “Hair therapy & transplantation” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune condition causing hair loss, influenced by genetics, environment, and possibly improved by anti-MIF therapy, with many patients experiencing regrowth within a year.
 April 2024 in “International Journal of Research Publication and Reviews”
April 2024 in “International Journal of Research Publication and Reviews” Alopecia areata causes hair loss with varied treatment responses and frequent relapses.
 December 2016 in “Springer eBooks”
December 2016 in “Springer eBooks” A 45-year-old woman with autoimmune diseases experienced patchy hair loss due to alopecia areata, which has no cure but can be treated, with varying success.
 148 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of autoimmunity”
148 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of autoimmunity” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease causing patchy hair loss, often with other autoimmune disorders, but its exact causes are unknown.
 61 citations,
September 2010 in “Genomics”
61 citations,
September 2010 in “Genomics” The study found that immune responses disrupt hair growth cycles, causing hair loss in alopecia areata.
 16 citations,
August 1967 in “JAMA”
16 citations,
August 1967 in “JAMA” Oral contraceptives may cause hair loss in women.
 4 citations,
November 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology”
4 citations,
November 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology” Hamilton scale imprecise, hair shaft diameter decreases, stem cell transplant regrows hair, ECP ineffective for alopecia areata universalis.
 24 citations,
July 2011 in “PubMed”
24 citations,
July 2011 in “PubMed” Thyroid hormones affect skin texture, hair and nail growth, and can cause skin diseases related to thyroid problems.
 January 2012 in “Vitamins & trace elements”
January 2012 in “Vitamins & trace elements” Smoking and drinking can lower vitamin levels and potentially trigger early hair loss, but overall vitamin levels don't seem to affect hair loss duration.
 55 citations,
November 2018 in “American journal of human genetics”
55 citations,
November 2018 in “American journal of human genetics” Mutations in the LSS gene cause a rare type of hereditary hair loss.
 26 citations,
January 2019 in “Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs”
26 citations,
January 2019 in “Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs” New treatments for hair loss show promise, but more research is needed to confirm their safety and effectiveness.
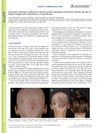 24 citations,
June 2016 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
24 citations,
June 2016 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Tofacitinib helped a young woman's severe hair loss and arthritis but not her plaque psoriasis.
 January 2007 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2007 in “Elsevier eBooks” Alopecia areata is a reversible, autoimmune-related hair loss that can have significant emotional impact and uncertain treatment effectiveness.
 7 citations,
December 2015 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
December 2015 in “International Journal of Dermatology” New and known mutations in the hairless gene cause a hair loss condition called Atrichia with papular lesions.
 1 citations,
August 2002 in “Zeitschrift für Hautkrankheiten”
1 citations,
August 2002 in “Zeitschrift für Hautkrankheiten” Male androgenetic alopecia involves hair follicle miniaturization due to DHT, with potential treatments using inhibitors and blockers.
 71 citations,
February 2006 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
71 citations,
February 2006 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Pregnancy causes skin changes like darkening, hair thickening, nail changes, and increased risk of skin growths, most of which usually resolve after birth.
 17 citations,
August 2015 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy”
17 citations,
August 2015 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy” The document concludes that oral finasteride and topical minoxidil are effective for genetic hair loss, while other treatments for different types of hair loss show promise but need more research.
 8 citations,
June 2016 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
8 citations,
June 2016 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” Two women were diagnosed with a rare melanoma that looked like hair loss but was actually a type of skin cancer.
 June 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy”
June 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy” The Middle East and Africa need better data, treatment consensus, and support for Alopecia Areata.
 21 citations,
October 2017 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
21 citations,
October 2017 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Various potential triggers may be causing the rise in frontal fibrosing alopecia, and avoiding these could help stop the disease's increase.
 August 2024 in “EMJ Dermatology”
August 2024 in “EMJ Dermatology” Non-scarring alopecia in females affects emotional well-being and requires accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment.
 37 citations,
June 2002 in “The Laryngoscope”
37 citations,
June 2002 in “The Laryngoscope” Ectodermal dysplasia causes various symptoms and early treatment is important for eye, dental, and skin issues.
48 citations,
April 2019 in “PloS one” Alopecia areata patients have more Propionibacterium acnes and less Staphylococcus epidermidis on their scalps.
 33 citations,
November 2006 in “Survey of Ophthalmology”
33 citations,
November 2006 in “Survey of Ophthalmology” Madarosis is the loss of eyelashes and eyebrows due to various health issues and requires thorough examination to diagnose and treat the underlying cause.
 8 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
8 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” The PRP-like cosmetic with biomimetic peptides is potentially effective and safe for treating alopecia areata.
 243 citations,
September 2016 in “Dermatology and Therapy”
243 citations,
September 2016 in “Dermatology and Therapy” Dermoscopy is a useful tool for identifying features of skin conditions, but more research is needed to define its role in dermatology.
 67 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
67 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” Chronic Telogen Effluvium may resolve after years and is diagnosed by examining the patient's history and clinical signs, with treatment aimed at underlying causes and possibly minoxidil.
 39 citations,
January 2019 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
39 citations,
January 2019 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Tofacitinib may help treat severe childhood alopecia areata, but risks require careful consideration.
 30 citations,
September 2020 in “Journal of Patient-Reported Outcomes”
30 citations,
September 2020 in “Journal of Patient-Reported Outcomes” Alopecia Areata (AA) causes significant emotional distress, including feelings of embarrassment, depression, and anxiety, and impacts social interactions and daily activities.





























