 2 citations,
July 2012 in “InTech eBooks”
2 citations,
July 2012 in “InTech eBooks” People with alopecia areata often have thyroid autoimmunity.
 1 citations,
April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” People with allergies or high eosinophil levels have a higher chance of severe hair loss from alopecia areata, and sudden hair loss can indicate chronic graft-versus-host disease.
 1 citations,
January 2006 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2006 in “Elsevier eBooks” Cats lose fur due to various reasons, including allergies, infections, genetics, hormones, diet, cancer, stress, and some conditions are treatable while others are not.
 June 2023 in “International journal of pharmaceutical quality assurance”
June 2023 in “International journal of pharmaceutical quality assurance” Videodermoscopy is effective for diagnosing different types of non-scarring hair loss.
 May 2023 in “Sučasna pedìatrìâ. Ukraïna”
May 2023 in “Sučasna pedìatrìâ. Ukraïna” An 11-year-old child with total hair loss may have a genetic autoimmune disease, and the outlook for hair regrowth is not good.
 October 2018 in “InTech eBooks”
October 2018 in “InTech eBooks” The most effective treatments for hair loss are minoxidil, finasteride, PRP, and hair transplants, with steroids and immunosuppressants for autoimmune types.
 July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” The most common cause of hair loss in children is tinea capitis, followed by alopecia areata and telogen effluvium.
 January 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” The document concludes that alopecia has significant social and psychological effects, leading to a market for hair loss treatments.
 March 2015 in “Polish Journal of Public Health”
March 2015 in “Polish Journal of Public Health” Blood vessel patterns in skin diseases relate to certain blood markers in systemic sclerosis but not in psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis, and may indicate circulation issues in alopecia.
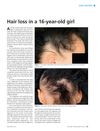 November 2014 in “Prescriber”
November 2014 in “Prescriber” The 16-year-old girl with hair loss was successfully treated for alopecia areata, leading to significant hair regrowth.
 March 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
March 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” TNF-a may not be as involved in certain types of hair loss as previously thought.
 May 2003 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America”
May 2003 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America” Hair loss can be treated with medications like minoxidil and finasteride or surgery, but treatment effectiveness varies by alopecia type and accurate diagnosis is important.
 74 citations,
April 2005 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
74 citations,
April 2005 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Minoxidil and finasteride are effective for male hair loss, minoxidil for female hair loss, and various treatments like corticosteroids work for alopecia areata; treatment should be tailored to the individual.
 49 citations,
January 2003 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
49 citations,
January 2003 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Effective management of children's hair loss involves accurate diagnosis, various treatments, and supportive care.
 34 citations,
June 2007 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
34 citations,
June 2007 in “The Journal of Dermatology” Most Korean systemic lupus erythematosus patients experienced hair loss, often as non-scarring diffuse hair loss, with non-scarring patch alopecia also common.
 32 citations,
December 2017 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
32 citations,
December 2017 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Low vitamin D might be linked to certain types of hair loss, and supplements could help, but more research is needed.
 22 citations,
June 1980 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
22 citations,
June 1980 in “International Journal of Dermatology” The document concludes that correct diagnosis of alopecia types is crucial, scalp biopsies are important, and more research is needed.
 20 citations,
July 1990 in “Pediatrics in Review”
20 citations,
July 1990 in “Pediatrics in Review” The four main causes of hair loss in children are fungal infections, pulling out hair, autoimmune hair loss, and stress-related hair shedding.
 18 citations,
March 2004 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
18 citations,
March 2004 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Lupus can cause hair loss and nail changes, with treatments available for both.
 8 citations,
May 2017 in “Singapore Medical Journal”
8 citations,
May 2017 in “Singapore Medical Journal” A Korean woman with complete hair loss regrew her hair after taking tofacitinib, with no side effects.
 8 citations,
September 2015 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
8 citations,
September 2015 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Hair loss in children is diagnosed and treated differently than in adults, with different common causes and a focus on less invasive methods.
3 citations,
April 2022 in “Biomolecules” Higher miR-34a levels and the A variant of the MIR-34A gene are linked to increased risk and severity of alopecia areata.
 3 citations,
June 2006 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
3 citations,
June 2006 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” The document concludes that hair loss is complex, affects many people, has limited treatments, and requires more research on its causes and psychological impact.
 3 citations,
January 1996 in “Pharmacotherapy: The Journal of Human Pharmacology and Drug Therapy”
3 citations,
January 1996 in “Pharmacotherapy: The Journal of Human Pharmacology and Drug Therapy” Zidovudine may cause hair loss in advanced-stage HIV patients.
 114 citations,
January 2007 in “Drug Safety”
114 citations,
January 2007 in “Drug Safety” Some drugs can cause skin, nail, and hair problems, which are important for healthcare professionals to recognize and report.
 43 citations,
November 2007 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
43 citations,
November 2007 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Hair and nail changes can indicate health issues, including cancer and side effects from cancer treatments.
 February 2018 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
February 2018 in “British Journal of Dermatology” We need better research to improve alopecia treatment and patient care.
 7 citations,
May 2014 in “Clinical practice”
7 citations,
May 2014 in “Clinical practice” Cooling the scalp may prevent hair loss from chemotherapy, hair often grows back after treatment, and nail issues usually improve after stopping the drug.
 4 citations,
August 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
4 citations,
August 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The authors agree that biotin may help certain hair disorders but lacks evidence for use in healthy people and call for more research.
 10 citations,
June 2020 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
10 citations,
June 2020 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Frontal fibrosing alopecia may be linked to genital Lichen sclerosus through an autoimmune process.





























