 6 citations,
October 2015 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology”
6 citations,
October 2015 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology” Hair aging is inevitable, but using the right hair care products can help maintain hair health.
 67 citations,
November 2002 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
67 citations,
November 2002 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The document concludes that careful evaluation is key to diagnose and treat women with hair loss, with tests for thyroid, iron, and hormones as needed.
 75 citations,
December 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
75 citations,
December 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Female pattern hair loss can be treated with medications, surgery, and cosmetic products, considering its psychological impact.
 11 citations,
August 2012 in “Canadian journal of ophthalmology”
11 citations,
August 2012 in “Canadian journal of ophthalmology” Eyelash alopecia areata often goes undiagnosed and can lead to complete eyelash regrowth, especially in younger patients.

Androgenetic alopecia, or hair loss, is caused by a mix of genetics, hormones, and environment, where testosterone affects hair growth and causes hair to become smaller and grow for a shorter time.
 3 citations,
November 1999 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
3 citations,
November 1999 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Examining scalp biopsies in different ways helps better diagnose hair loss types.
3 citations,
January 2020 in “International journal of trichology” Congenital triangular alopecia is a hair loss condition present from birth or early childhood with no effective treatment needed.
 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” The document concludes that diagnosing hair loss requires evaluating multiple histological features, as no single feature is definitive on its own.
 4 citations,
October 2012 in “Archives of Dermatology”
4 citations,
October 2012 in “Archives of Dermatology” Hair diameter diversity is a key sign for diagnosing and managing male pattern baldness.
 June 2018 in “Advances in Cosmetic Surgery”
June 2018 in “Advances in Cosmetic Surgery” Hair loss caused by genetics and hormones; more research needed for treatments.
 64 citations,
July 1997 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
64 citations,
July 1997 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Finding eosinophils near hair bulbs helps diagnose alopecia areata.
 January 2023 in “Journal of surgery and research”
January 2023 in “Journal of surgery and research” New treatment effectively reverses hair thinning in most patients with mild side effects.
 52 citations,
April 2004 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
52 citations,
April 2004 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Male pattern baldness involves three mechanisms and finasteride can help reverse it.
 1 citations,
December 2019 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
1 citations,
December 2019 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Only anti-androgenic drugs likely halt AGA progression.
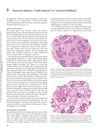 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Senescent alopecia is a type of hair loss that occurs after age 50, not caused by genetics, and involves a gradual thinning of hair without significant inflammation.
 30 citations,
August 1983 in “Pediatric Clinics of North America”
30 citations,
August 1983 in “Pediatric Clinics of North America” Most hair loss in children is caused by a few common conditions, and it's important to diagnose these properly and support the child's mental health.
 July 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine”
July 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” The document concludes that understanding hair follicle histology and the hair cycle is crucial for diagnosing alopecia.
 129 citations,
January 2009 in “International Journal of Trichology”
129 citations,
January 2009 in “International Journal of Trichology” Trichoscopy can diagnose female hair loss with high accuracy by looking for specific patterns in hair and scalp appearance.

Non-invasive methods can effectively diagnose and manage alopecia areata.
 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Telogen effluvium is a common hair loss condition where many hairs enter the resting phase, often not noticeable until significant loss occurs, and treatment focuses on the underlying cause.
 9 citations,
March 2007 in “Hair transplant forum international”
9 citations,
March 2007 in “Hair transplant forum international” Densitometry and video-microscopy are precise for evaluating hair loss and transplant success but need special equipment and training.
 2 citations,
October 2022 in “Journal of structural biology”
2 citations,
October 2022 in “Journal of structural biology” Older thin hair is not just thinner but also has different shape, structure, and stiffness.
 June 2023 in “Skin Research and Technology”
June 2023 in “Skin Research and Technology” High-resolution MRI can distinguish between tertiary androgenetic alopecia and severe alopecia areata by measuring scalp and tissue thickness and hair follicle depth.
 January 2024 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
January 2024 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Microneedling combined with other treatments significantly improves hair growth in people with hair loss and is safe.
 39 citations,
March 2018 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
39 citations,
March 2018 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Androgens may block hair growth signals, targeting this could treat hair loss.
 June 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
June 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” The new follicular unit extraction treatment effectively treats severe hair loss in Asian men, giving natural-looking results with few side effects.
 April 2024 in “Animal models and experimental medicine”
April 2024 in “Animal models and experimental medicine” PRP treatment helps hair growth and rebalances scalp bacteria in androgenetic alopecia patients.
 January 2024 in “Journal of Cosmetics, Dermatological Sciences and Applications”
January 2024 in “Journal of Cosmetics, Dermatological Sciences and Applications” Injecting a peptide-hyaluronic acid mix improved hair growth in men with hair loss and was safe.
 1 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical research in dermatology”
1 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical research in dermatology” Hair loss, known as Androgenetic Alopecia, is often caused by hormones and can be diagnosed using noninvasive techniques. Treatments include topical minoxidil and oral finasteride, with new treatments being explored. There may also be a link between this type of hair loss and heart disease risk.
 122 citations,
April 1995 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
122 citations,
April 1995 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” The document describes how to tell different types of non-scarring hair loss apart by looking at hair and scalp tissue under a microscope.





























