 6 citations,
January 2001 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
6 citations,
January 2001 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Female pattern alopecia is common, starts in late 20s, and is not androgen dependent.
 6 citations,
February 1974 in “The BMJ”
6 citations,
February 1974 in “The BMJ” The document concludes that scalp disorders can be treated with hair washing, specific shampoos, medications, and sometimes surgery or hair transplants, but hereditary baldness is untreatable.
 5 citations,
September 1998 in “Atlas of the oral and maxillofacial surgery clinics of North America”
5 citations,
September 1998 in “Atlas of the oral and maxillofacial surgery clinics of North America” Hair transplantation and micrografting, used for baldness, involve moving hair follicles from hair-rich to bald areas, requiring careful procedure and post-care for success.
 5 citations,
December 1979 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
5 citations,
December 1979 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Anti-androgens are effective for female acne but less so for male-pattern hair loss, with side effects similar to birth control pills.
 3 citations,
October 2021 in “Indian Journal of Plastic Surgery”
3 citations,
October 2021 in “Indian Journal of Plastic Surgery” Not all hair loss patients are suitable for hair transplant due to various conditions like unstable hair loss, insufficient hair loss, very young age, unrealistic expectations, certain psychological disorders, and medical unfitness.
3 citations,
June 2015 in “CRC Press eBooks” Male pattern hair loss affects up to 80% of men due to genetics and hormone sensitivity.
 3 citations,
February 1996 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
3 citations,
February 1996 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Walter P. Unger suggests using advanced hair transplant techniques for broader coverage, as they provide natural results and use donor tissue efficiently, while also recommending personalized planning due to the unpredictable progression of baldness.
 2 citations,
January 2020 in “Journal of Experimental Social Psychology”
2 citations,
January 2020 in “Journal of Experimental Social Psychology” Baldness and shaved heads change how traits are seen but don't really affect leader preferences.
 2 citations,
August 2016 in “Experimental Dermatology”
2 citations,
August 2016 in “Experimental Dermatology” Finasteride treats baldness but may cause lasting sexual side effects.
 2 citations,
January 2011 in “Lecture Notes in Computer Science”
2 citations,
January 2011 in “Lecture Notes in Computer Science” A proposed robotic system could make hair harvesting for baldness treatment faster and more precise.
 1 citations,
September 2016 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
September 2016 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Women with aging signs and heart issues have higher hair loss risk, which may predict shorter lifespan and affect attractiveness.
 1 citations,
August 2013 in “Journal of the National Cancer Institute”
1 citations,
August 2013 in “Journal of the National Cancer Institute” Early hair loss may increase the risk of prostate cancer, especially in African American men and those with frontal baldness.
 1 citations,
January 1996 in “Springer eBooks”
1 citations,
January 1996 in “Springer eBooks” Diet affects baldness; eat balanced, less animal fat, more fruits, vegetables, and cereals.
 1 citations,
February 1988 in “The BMJ”
1 citations,
February 1988 in “The BMJ” The document explains different hair and scalp conditions, including common hair loss after pregnancy or illness, drug-induced hair loss, hereditary excessive hair growth, patterned baldness, autoimmune hair loss, and permanent loss due to skin disease, with generally limited treatment options.
 March 2024 in “Cancer Research”
March 2024 in “Cancer Research” Men with baldness on the top of their head might have a small increased risk of prostate cancer.
 May 2020 in “Hair transplant forum international”
May 2020 in “Hair transplant forum international” The updated NPRT system now covers different types of hair loss in men and women.
 July 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
July 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The research found that male pattern hair loss is mostly genetic and involves hair thinning due to hormonal effects and changes in gene expression.
Researchers developed a quick and accurate method to measure hormones in urine, confirming a baldness treatment's effectiveness without altering hormone levels.
August 2017 in “Revista de la Facultad de Ciencias Médicas (Quito)/Revista de la Facultad de Ciencias Médicas” Early baldness in men may indicate a higher risk of prostate cancer.
 June 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
June 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The new treatment was safe and may effectively treat male pattern hair loss.

Botulinum toxin-A may increase hair growth and reduce hair loss in men with baldness, and injecting near blood vessels can improve pain relief and last longer.
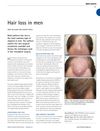 May 2013 in “Trends in Urology & Men's Health”
May 2013 in “Trends in Urology & Men's Health” Male-pattern hair loss is normal, often involves hormone effects on hair follicles, and can be treated with medication or surgery, but new treatments are being researched.

Men with both baldness and scalp psoriasis often don't have psoriasis on bald spots.
 May 2012 in “Scientific American”
May 2012 in “Scientific American” New app improves storm surge predictions; advances in baldness treatment show potential but require time.
 April 2012 in “Lab Animal”
April 2012 in “Lab Animal” Early exposure to germs may protect against autoimmune diseases, lack of sex increases alcohol preference in fruit flies, a potential baldness treatment could involve blocking a specific receptor, skin memory cells help prevent re-infection, high-fat diets can affect brain cells related to weight, and the link between social status, stress, and heart disease in primates is unclear.
 May 2009 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
May 2009 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” Mast cells play a significant role in hair loss conditions like male pattern hair loss and alopecia areata.
 March 2009 in “Journal of Biomedical Research”
March 2009 in “Journal of Biomedical Research” Herbal extract mixtures may speed up hair growth and could help treat baldness.
 March 2003 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
March 2003 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Dr. Dominic A. Brandy shared methods to fix aesthetic problems from old hair restoration techniques, using methods like follicular unit grafting and scalp removal, which helped patients look more natural after surgery. He also suggested using oral finasteride and topical minoxidil to control hair loss in most men with baldness, especially those who had flap surgery.
Micrografts and minigrafts effectively treat male hair loss with natural-looking results.
 March 1998 in “Journal of dermatological science”
March 1998 in “Journal of dermatological science” Protease Nexin-1 is found in human hair growth cells and is affected by male hormones.


























