 126 citations,
January 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
126 citations,
January 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The document concludes that understanding hair structure is key to diagnosing hair abnormalities and recommends gentle hair care for management.
16 citations,
October 1992 in “Journal of cutaneous pathology” Bubble hair deformity may be caused by hair shaft trauma and can improve with gentle hair care.
 3 citations,
April 1990 in “Archives of dermatology”
3 citations,
April 1990 in “Archives of dermatology” The book reveals diverse patterns of hair growth in different species and advancements in hair and alopecia research.
 July 2007 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature”
July 2007 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature” The BASP classification is a detailed system for categorizing hair loss in both men and women, but it may be complex for beginners and not fully suitable for grading female hair loss.
 May 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
May 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The meeting covered advances in understanding hair growth, causes of hair loss, and potential treatments.
 76 citations,
November 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
76 citations,
November 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Some African American women's central scalp hair loss is linked to genetics and past fungal scalp infections, with more research needed on other causes.
 215 citations,
November 2006 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
215 citations,
November 2006 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Dutasteride more effective for hair growth, but has more side effects than finasteride.
 203 citations,
December 2004 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
203 citations,
December 2004 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Early diagnosis and treatment, using finasteride, minoxidil, or hair transplantation, improves hair loss outcomes.
 145 citations,
December 1999 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
145 citations,
December 1999 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Finasteride 1mg helps reverse hair miniaturization in men and postmenopausal women.
 116 citations,
September 2001 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
116 citations,
September 2001 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Hair loss occurs due to fewer papillary cells, smaller follicles, and shorter growth phases.
 23 citations,
January 2002 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
23 citations,
January 2002 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Finasteride helps hair growth by decreasing cell death in hair follicles.
 22 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology”
22 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology” Miniaturized hairs stay connected to muscle in alopecia areata, allowing possible regrowth, but not in androgenetic alopecia.
22 citations,
April 2003 in “PubMed” Finasteride 1 mg significantly improves hair growth in men aged 41 to 60 with male pattern hair loss.
 21 citations,
January 2002 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
21 citations,
January 2002 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Finasteride affects hair growth by changing caspase and XIAP levels, potentially treating hair diseases.
 2 citations,
October 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
2 citations,
October 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Focal atrichia helps diagnose female pattern hair loss.
 April 2006 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature”
April 2006 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature” Oral finasteride, combined with drospirenone, improved hair loss in 62% of premenopausal women, with no reported side effects.
 129 citations,
October 2000 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
129 citations,
October 2000 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Finasteride helps increase hair growth in men with hair loss.
 35 citations,
February 2012 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
35 citations,
February 2012 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Finasteride significantly improves hair growth but may cause sexual side effects.
 46 citations,
October 1999 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
46 citations,
October 1999 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Finasteride effectively treats male pattern hair loss with a 1 mg daily dose.
 30 citations,
October 2002 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
30 citations,
October 2002 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Use "female pattern hair loss" term, finasteride may help, more research needed.
5 citations,
October 1999 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”  100 citations,
September 1999 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
100 citations,
September 1999 in “British Journal of Dermatology” The study found that two enzymes linked to hair loss are located in different parts of the scalp, supporting a common treatment's effectiveness.
 75 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
75 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Chronic Telogen Effluvium is a hair loss condition in middle-aged women that usually doesn't lead to complete baldness.
54 citations,
September 2012 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Vitamin A affects hair loss and immune response in alopecia areata.
 46 citations,
July 2008 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
46 citations,
July 2008 in “Dermatologic Therapy” A scale was made to measure hair loss severity in African American women.
 39 citations,
November 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
39 citations,
November 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The document suggests using standardized methods to track and measure hair loss in alopecia areata, including patient self-assessment and a 50% improvement in specific scores as a treatment goal.
 June 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
June 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Advancements in hair biology include new treatments and tools for hair growth and alopecia.
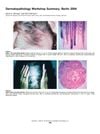 November 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
November 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” The workshop aimed to improve hair loss disorder diagnosis and understanding.
71 citations,
January 1998 in “Pathobiology” The document concludes that certain rats and mice are useful for studying hair loss in humans and testing treatments.
 98 citations,
May 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
98 citations,
May 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology” There are many treatments for permanent hair loss disorders, but their effectiveness varies and there's no clear best option.

























