 11 citations,
September 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
11 citations,
September 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology” New ABCA12 gene mutations were linked to a skin condition with scaling and hair loss, and a treatment helped with hair loss in a related case.
 January 2008 in “US endocrinology”
January 2008 in “US endocrinology” Mutations in the glucocorticoid receptor gene cause reduced sensitivity to glucocorticoids and may lead to poor response to treatment.
 April 2023 in “Biomedical Journal of Scientific and Technical Research”
April 2023 in “Biomedical Journal of Scientific and Technical Research” Indian head cactus extract may help hair grow by boosting important cell activity and gene expression.
 June 2012 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
June 2012 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Japanese researchers created new hair follicles from human cells that grew hair when put into mice, and other findings showed a link between eye disease severity and corneal thickness, gene mutations affecting hearing and touch, and the safety of the shingles vaccine for adults over 50.
 1 citations,
May 2019 in “Journal of pediatric endocrinology & metabolism/Journal of pediatric endocrinology and metabolism”
1 citations,
May 2019 in “Journal of pediatric endocrinology & metabolism/Journal of pediatric endocrinology and metabolism” Intravenous calcium therapy is a safe and effective treatment for a rare type of rickets.
 June 2022 in “Biomedical reports”
June 2022 in “Biomedical reports” STK11 gene variations do not predict how well metformin will work for PCOS, but may affect hair loss and excess hair growth.
 November 2021 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
November 2021 in “Research Square (Research Square)” A 532 nm laser at 15 J/cm2 speeds up tendon healing by increasing tendon stem cell growth and tendon-related gene activity.
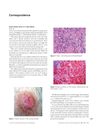 October 2010 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
October 2010 in “International Journal of Dermatology” An 86-year-old man with prostate cancer was diagnosed with a rare, low-grade breast cancer and underwent surgery but declined additional hormone therapy.
 14 citations,
September 2018 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology”
14 citations,
September 2018 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology” A boy's growth and immune problems were caused by a new mutation in the STAT5B gene.
 2 citations,
May 2017 in “International journal of pharmacy and pharmaceutical sciences/International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences”
2 citations,
May 2017 in “International journal of pharmacy and pharmaceutical sciences/International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences” Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder caused by a specific gene mutation, characterized by aging symptoms and managed by monitoring heart health and using low-dose aspirin.
 July 2019 in “Journal of the Formosan Medical Association”
July 2019 in “Journal of the Formosan Medical Association” Melatonin may help with nerve pain, a hepatitis C drug is effective but has side effects, a treatment for mouth sores works but can cause blood issues, ear reconstruction with an implant is safe, HIV transmission from mother to child in Taiwan is now 0% with treatment, certain blood problems are more common in people with a tongue condition, a gene and being overweight are linked to hair loss in some women, a new technique could reduce radiation for lung nodule patients, a hepatitis treatment may lower cancer recurrence after a procedure, and adding extra screening improves tuberculosis detection in patients with lung infections.
 December 2024 in “Medical Review”
December 2024 in “Medical Review” Organoids help study and treat genetic diseases, offering personalized medicine and therapy testing.
 7 citations,
November 2020 in “Experimental Dermatology”
7 citations,
November 2020 in “Experimental Dermatology” Different cell types work together to repair skin, and targeting them may improve healing and reduce scarring.
 June 2024 in “IP Indian journal of clinical and experimental dermatology”
June 2024 in “IP Indian journal of clinical and experimental dermatology” Hair loss has many causes and treatments, but future research aims for better solutions.
151 citations,
June 2010 in “Endocrinology and metabolism clinics of North America” Two rare genetic diseases cause severe rickets in children due to defects in vitamin D metabolism.
 129 citations,
January 2019 in “Clinical medicine insights”
129 citations,
January 2019 in “Clinical medicine insights” Obesity worsens PCOS symptoms, and PCOS may lead to more weight gain; managing both requires a holistic approach that includes mental health.
 125 citations,
September 2019 in “Journal of Clinical Immunology”
125 citations,
September 2019 in “Journal of Clinical Immunology” Foxp3 is crucial for regulatory T cell function, and targeting these cells may help treat immune disorders.
 11 citations,
May 2021 in “Journal of Medical Virology”
11 citations,
May 2021 in “Journal of Medical Virology” Men are more likely to have severe respiratory viral infections like COVID-19 due to hormonal and genetic differences, while women generally have stronger immune responses.
 1 citations,
July 2022 in “Movement disorders clinical practice”
1 citations,
July 2022 in “Movement disorders clinical practice” A patient with Wilson's disease showed hair-pulling behavior as an initial symptom.
 1 citations,
August 2021 in “Canadian journal of neurological sciences”
1 citations,
August 2021 in “Canadian journal of neurological sciences” Woodhouse-Sakati syndrome can cause writer's cramp and other varied symptoms, highlighting the importance of genetic testing for diagnosis.
 December 2022 in “Scientific Reports”
December 2022 in “Scientific Reports” Stem cells from whiskers can be transplanted to stimulate hair growth.
 June 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
June 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Researchers discovered potential origins and new treatments for skin cancer, including biomarkers for melanoma and therapies that reduce tumor growth.
 January 2009 in “Hair transplant forum international”
January 2009 in “Hair transplant forum international” Dr. Rodney Sinclair uses a detailed grading system to diagnose female pattern hair loss, recommends daily spironolactone and minoxidil for treatment, and believes genetics play a role in the condition.
 51 citations,
May 2019 in “Biomaterials”
51 citations,
May 2019 in “Biomaterials” Researchers developed a method to grow hair follicles using special beads that could help with hair loss treatment.
 1 citations,
July 2023 in “Cureus”
1 citations,
July 2023 in “Cureus” Some treatments for hereditary hair loss are effective but vary in results and side effects; new therapies show promise but need more research.
 May 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
May 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Wnt-3a helps grow more skin stem cells, which could lead to new hair loss treatments.
 January 2015 in “Dermatology”
January 2015 in “Dermatology” The document covers various dermatological treatments and conditions.
 11 citations,
December 2018 in “Bone”
11 citations,
December 2018 in “Bone” Removing a methyl group from the ITGAV gene speeds up bone formation in a specific type of bone disease model.
September 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” A new mutation in the STING protein causes a disease with lupus-like symptoms and responds well to a specific inhibitor treatment.
98 citations,
March 2019 in “Frontiers in immunology” Damaging mutations in NFKB2 cause a severe and distinct form of primary immunodeficiency with early-onset and often ACTH-deficiency.


























