 61 citations,
January 2019 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
61 citations,
January 2019 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” The cause of Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia is unclear, diagnosis involves clinical evaluation and various treatments exist, but their effectiveness is uncertain.
 12 citations,
February 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
12 citations,
February 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” A cancer drug caused unusual hair growth on a 100-year-old man's scalp and eyelashes.
 7 citations,
September 2008 in “Dermatologic surgery”
7 citations,
September 2008 in “Dermatologic surgery” Hair transplantation can successfully treat stubborn alopecia areata.
 28 citations,
July 2013 in “Journal of Craniofacial Surgery”
28 citations,
July 2013 in “Journal of Craniofacial Surgery” Hair follicle transplantation can hide scars but often needs more than one surgery for better results.
8 citations,
July 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Certain microRNAs might help identify and understand Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia.
 10 citations,
June 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology”
10 citations,
June 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology” Finasteride caused blisters on hands and feet.
 16 citations,
April 2009 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
16 citations,
April 2009 in “Dermatologic Surgery” The place where hair is transplanted can change its growth rate and length but not its thickness.
 5 citations,
May 2005 in “Seminars in Plastic Surgery”
5 citations,
May 2005 in “Seminars in Plastic Surgery” Hair transplantation using micrografts and minigrafts is effective and safe for facial and scalp reconstruction with natural-looking results.
 11 citations,
January 1987 in “Electrophoresis”
11 citations,
January 1987 in “Electrophoresis” Keratin proteins are consistent across different hair types from the same person.
 May 2004 in “The Journal of Laryngology & Otology”
May 2004 in “The Journal of Laryngology & Otology” The first book is highly recommended for facial surgery education, the second book is useful despite its limited focus, and the third book is not user-friendly due to dense text and poor images.
 7 citations,
January 2021 in “Dermatology and therapy”
7 citations,
January 2021 in “Dermatology and therapy” Both dermatologists and patients in Japan agree that treatment success for alopecia areata is having 20% or less scalp hair loss.
 26 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
26 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics” The document details hair transplantation techniques and innovations, highlighting Follicular Unit Transplantation as the standard and discussing the effectiveness and challenges of the procedure.
 July 2023 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine ”
July 2023 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine ” Alopecia areata is a hair loss condition caused by immune factors and can be treated with JAK inhibitors.
 January 2025 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology”
January 2025 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology” Frontal fibrosing alopecia is a challenging hair loss condition with no known cause or definitive treatment.
 41 citations,
July 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
41 citations,
July 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Men with Frontal fibrosing alopecia typically lose hair on the front scalp and sometimes on sideburns and upper lip, with treatments showing varied success.
 January 2025 in “Journal of Cutaneous Immunology and Allergy”
January 2025 in “Journal of Cutaneous Immunology and Allergy” Baricitinib is effective for treating severe alopecia areata in Japanese patients, but long-term safety needs more study.
 8 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
8 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The authors updated the criteria for diagnosing frontal fibrosing alopecia, making it easier to diagnose without a biopsy.
 7 citations,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Syphilis can cause hair loss without other symptoms and should be considered when diagnosing unexplained hair loss.
 8 citations,
September 2011 in “European Journal of Dermatology”
8 citations,
September 2011 in “European Journal of Dermatology” Most treatments for Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia are ineffective, but early anti-inflammatory therapy may help and the condition may stabilize over time.
 February 2024 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
February 2024 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Baricitinib is effective and safe for long-term use in severe alopecia areata, improving hair regrowth and quality of life with few side effects.
 January 2018 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2018 in “Springer eBooks” Men and women need different facial rejuvenation treatments due to distinct aging processes and anatomical differences.
 3 citations,
September 2017 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
3 citations,
September 2017 in “Pediatric Dermatology” Avoiding allergens can improve skin and hair conditions in adults with allergic reactions.
 63 citations,
May 2000 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
63 citations,
May 2000 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Chemotherapy and bone marrow transplant can cause permanent hair loss.
4 citations,
December 2020 Methotrexate may help stabilize frontal fibrosing alopecia.
 1 citations,
April 2016 in “The American Journal of the Medical Sciences”
1 citations,
April 2016 in “The American Journal of the Medical Sciences” The document concludes that doctors should check for frontal fibrosing alopecia in patients with acquired hyperpigmentation and that early treatment is important.
71 citations,
December 2013 in “The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings/The Journal of investigative dermatology symposium proceedings” There are no FDA-approved treatments for Alopecia Areata, and current options have varying success and relapse rates.
 7 citations,
April 1987 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
April 1987 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Stopping imipramine reduced the woman's hair loss.
 58 citations,
June 2018 in “Scientific reports”
58 citations,
June 2018 in “Scientific reports” Researchers found 15 new genetic links to skin traits in Japanese women.
 14 citations,
September 2009 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
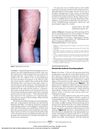
14 citations,
September 2009 in “International Journal of Dermatology” DCPA is a chronic leg infection often related to Staphylococcus aureus, affecting mostly young men in India.
 72 citations,
July 2014 in “American journal of clinical dermatology”
72 citations,
July 2014 in “American journal of clinical dermatology” Some treatments, like corticosteroids and sensitizing agents, can help with alopecia areata, but more high-quality research is needed.



























