 10 citations,
January 2016 in “Dermatology online journal”
10 citations,
January 2016 in “Dermatology online journal” Adults with persistent scalp issues unresponsive to typical treatments should be tested for the fungal infection tinea capitis to start the right antifungal medication.
 1 citations,
January 2021 in “Our Dermatology Online”
1 citations,
January 2021 in “Our Dermatology Online” A scalp infection can look like alopecia areata and get worse if treated incorrectly.
 January 2019 in “Open access journal of mycology & mycological sciences”
January 2019 in “Open access journal of mycology & mycological sciences” The article concludes that proper antifungal treatment is essential for treating scalp fungal infections in children, and trichoscopy is useful for diagnosis and monitoring.
[object Object] 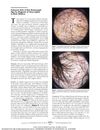 108 citations,
March 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology”
108 citations,
March 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology” Corkscrew hair may be a new sign for quickly diagnosing scalp fungus in black children.
 April 2012 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
April 2012 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Dermoscopy can help diagnose tinea capitis in children by looking for comma hairs, black dots, and broken hairs with white bands.
 1 citations,
October 2022 in “Asian journal of medical sciences”
1 citations,
October 2022 in “Asian journal of medical sciences” Trichoscopy is a valuable, quick, and non-invasive tool for diagnosing tinea capitis in children.
 32 citations,
August 2003 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
32 citations,
August 2003 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Tinea capitis can be misdiagnosed as bacterial infection in adult women but is treatable with antifungal medication.
 2 citations,
January 2022 in “Eduvest”
2 citations,
January 2022 in “Eduvest” A teenage girl with a fungal scalp infection got better with antifungal and allergy medication, and special shampoo.
1 citations,
November 2020 in “International journal of infectious diseases” A baby girl's severe scalp infection caused by a fungus was cured with oral and topical antifungal medications.

A Moroccan athlete got a rare scalp infection, stressing the need for better hygiene in sports.
[object Object]  38 citations,
July 2010 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology”
38 citations,
July 2010 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology” To treat tinea capitis in children, oral antifungal medication is necessary, with newer drugs offering shorter treatment times than the traditional griseofulvin.
 24 citations,
January 2011 in “International Journal of Trichology”
24 citations,
January 2011 in “International Journal of Trichology” Light microscopy is useful for diagnosing different hair disorders.
 8 citations,
January 2007 in “Mycoses”
8 citations,
January 2007 in “Mycoses” A man's scalp infection, mistaken for bacterial, was actually a rare fungal infection treated successfully with antifungal medication.
 May 2017 in “InTech eBooks”
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks” Trichoscopy and trichogram are useful for diagnosing hair and scalp conditions.
 3 citations,
January 2020 in “Clinical dermatology review”
3 citations,
January 2020 in “Clinical dermatology review” Trichoscopy is useful for diagnosing hair and scalp disorders in people with darker skin.
 35 citations,
January 1996 in “Dermatologic clinics”
35 citations,
January 1996 in “Dermatologic clinics” Tinea capitis is a common scalp infection causing hair loss, mostly in young children.
 May 2017 in “InTech eBooks”
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks” Early treatment of children's hair loss, which can be caused by various factors, is important due to its emotional impact.
 15 citations,
August 2015 in “Scanning”
15 citations,
August 2015 in “Scanning” Corkscrew and cigarette-ash-shaped hairs in tinea capitis are caused by internal hair degradation and external resistance.
 7 citations,
November 2000 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
7 citations,
November 2000 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Most hair loss in children is caused by a few common conditions and is easy to diagnose, but rare types require careful evaluation.
May 2024 in “Journal of Fungi” Tinea capitis in adults, especially postmenopausal Black women, needs prompt treatment with oral antifungals to avoid scarring.
 2 citations,
January 2019 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal”
2 citations,
January 2019 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal” The congress concluded that misuse of antifungal drugs in South Asia has led to widespread treatment failure, and new approaches and regional cooperation are needed.
3 citations,
January 2021 in “Therapeutic advances in infectious disease” A 9-year-old girl with a healthy immune system was successfully treated for a severe fungal scalp infection caused by Microsporum audouinii.
 February 2014 in “Medicine - Programa De Formación Médica Continuada Acreditado”
February 2014 in “Medicine - Programa De Formación Médica Continuada Acreditado” The document concludes that non-scarring alopecias can be reversed, but scarring alopecias cause permanent hair loss.

The document is a detailed guide on skin conditions and treatments for dermatologists.
 73 citations,
April 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology”
73 citations,
April 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology” The scalp's microorganisms significantly affect hair health and disease.
 1 citations,
January 2021 in “Advances in animal and veterinary sciences”
1 citations,
January 2021 in “Advances in animal and veterinary sciences” Pets in Egypt can pass skin fungus, especially Microsporum canis, to humans, with outdoor and young pets being more at risk.
1 citations,
October 2020 in “Cermin Dunia Kedokteran” A boy's scalp rash and baldness were cured using oral medication and medicated shampoo.
January 2022 in “Clinical Cases in Dermatology” A 7-year-old girl's scalp infection was cured with oral medication and medicated shampoo.
 23 citations,
January 2005 in “Nihon Ishinkin Gakkai zasshi”
23 citations,
January 2005 in “Nihon Ishinkin Gakkai zasshi” Nested PCR can reliably identify fungal infections when traditional methods fail.
 12 citations,
June 2012 in “Revista da Sociedade Brasileira de Medicina Tropical”
12 citations,
June 2012 in “Revista da Sociedade Brasileira de Medicina Tropical” A family had a rare fungal infection called white piedra, identified as Trichosporon inkin.

























