 5 citations,
January 2017 in “Acta Endocrinologica”
5 citations,
January 2017 in “Acta Endocrinologica” High androgen levels in postmenopausal women may suggest an ovarian tumor, and removing it can improve heart and metabolic health.
[object Object] 2 citations,
January 2022 in “Annals of Dermatology” Treatment type and patch size affect hair regrowth patterns in alopecia areata.
 2 citations,
January 1997 in “Archives of Dermatology”
2 citations,
January 1997 in “Archives of Dermatology” Alopecia areata can regrow hair in a pattern similar to androgenetic alopecia.
 30 citations,
November 2008 in “Facial Plastic Surgery”
30 citations,
November 2008 in “Facial Plastic Surgery” The conclusion is that the best approach for treating Female Pattern Hair Loss is a combination of different treatments.
 7 citations,
August 2021 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
7 citations,
August 2021 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Early treatment of fibrosing alopecia in a pattern distribution may improve outcomes.
 March 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
March 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” A woman's progressive hair loss was correctly diagnosed as a rare condition called fibrosing alopecia in a pattern distribution after initially being mistaken for a more common type.
 January 2024 in “Pan African Medical Journal”
January 2024 in “Pan African Medical Journal” Non-scarring hair loss is common in lupus patients and can be diagnosed with specific hair and tissue tests.
 15 citations,
January 1988 in “Drugs”
15 citations,
January 1988 in “Drugs” The document concludes that treatments for female hair loss and excessive hair growth are temporary and not well-studied.
 6 citations,
January 2019 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology”
6 citations,
January 2019 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology” About 12% of children in Kota, Rajasthan, experience hair loss, mainly due to fungal infections, with early treatment advised to prevent worsening.
 May 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine”
May 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” New understanding and treatments for hair loss are improving, but more research is needed.
 29 citations,
June 2013 in “Journal of the Saudi Society of Dermatology & Dermatologic Surgery”
29 citations,
June 2013 in “Journal of the Saudi Society of Dermatology & Dermatologic Surgery” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune hair loss condition treated with corticosteroids, and histologic confirmation is the best diagnosis method.
 28 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology”
28 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology” Genetics affect early female hair loss, severity depends on duration, and low ferritin levels not significant.
[object Object]  April 2020 in “IP Indian journal of clinical and experimental dermatology”
April 2020 in “IP Indian journal of clinical and experimental dermatology” Many children with alopecia areata also have other autoimmune diseases.
 1 citations,
April 2019 in “Acta Medica Philippina”
1 citations,
April 2019 in “Acta Medica Philippina” Azathioprine may help treat severe alopecia areata, but more research is needed.
 1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks”
1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks” The document concludes that alopecia areata is an unpredictable autoimmune hair loss condition with no cure, but various treatments exist that require personalized approaches.
 53 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
53 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Cancer treatments often cause hair disorders, significantly affecting patients' quality of life, and better management methods are needed.
 5 citations,
April 2015 in “HSOA journal of clinical dermatology & therapy”
5 citations,
April 2015 in “HSOA journal of clinical dermatology & therapy” Triamcinolone acetonide mesotherapy may be effective for treating patchy hair loss in alopecia areata.
 July 2024 in “Plastic and Aesthetic Research”
July 2024 in “Plastic and Aesthetic Research” Careful planning and accurate diagnosis are crucial for successful hair restoration surgery.
 28 citations,
September 1998 in “Medical Clinics of North America”
28 citations,
September 1998 in “Medical Clinics of North America” Most hair loss can be diagnosed with patient history and physical exam, and a few common types make up most cases.
 1 citations,
January 2013 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2013 in “Elsevier eBooks” The document reviews various hair and nail disorders, their causes, and treatments, emphasizing the need for proper diagnosis and the link between nail changes and systemic diseases.
 July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” Some drugs can cause reversible hair loss, but certain chemotherapy drugs may lead to permanent hair loss; drugs can also change hair color and texture.
 52 citations,
October 2012 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
52 citations,
October 2012 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” The document concludes that mouse models are crucial for studying hair biology and that all mutant mice may have hair growth abnormalities that require detailed analysis to identify.
 86 citations,
December 2001 in “Experimental dermatology”
86 citations,
December 2001 in “Experimental dermatology” Mutant mice help researchers understand hair growth and related genetic factors.
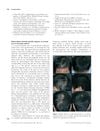 10 citations,
July 2012 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
10 citations,
July 2012 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Syphilis can cause hair loss and should be considered in unexplained cases.
 7 citations,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Syphilis can cause hair loss without other symptoms and should be considered when diagnosing unexplained hair loss.
 2 citations,
January 2017 in “Przegla̧d dermatologiczny”
2 citations,
January 2017 in “Przegla̧d dermatologiczny” Two trichoscopic patterns found in hair loss: diffuse fibrotic and androgenetic alopecia, affecting treatment choice and regrowth chances.
 3 citations,
January 2016 in “Skin appendage disorders”
3 citations,
January 2016 in “Skin appendage disorders” Possible causes of female hair loss include androgenetic alopecia, telogen effluvium, cicatricial alopecia, and alopecia areata incognita; diagnosis and treatment require dermoscopy and histopathology.
 37 citations,
December 2010 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
37 citations,
December 2010 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Aging alone rarely causes significant hair loss; hormones are a bigger factor.
35 citations,
November 2019 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” A new variant of lichen planopilaris causing diffuse hair thinning was identified.
 124 citations,
August 1990 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
124 citations,
August 1990 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Diffuse alopecia in women may be related to androgens and iron deficiency, and basic hormone and nutrient screening is useful.



























