 34 citations,
December 1995 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
34 citations,
December 1995 in “Pediatric Dermatology” Congenital Triangular Alopecia is a rare, non-scarring hair loss that can be surgically treated in females for cosmetic reasons.
14 citations,
January 2010 in “Dermatology” Some people with congenital triangular alopecia have a central tuft of hair in the bald patch, but the cause is unknown.
 13 citations,
January 2011 in “International Journal of Trichology”
13 citations,
January 2011 in “International Journal of Trichology” CTA is often mistaken for AA but doesn't respond to steroids and may require hair transplantation.
 5 citations,
October 2018 in “Dermatologic therapy”
5 citations,
October 2018 in “Dermatologic therapy” Recognizing congenital triangular alopecia is crucial to avoid unnecessary treatments.
 4 citations,
May 2015 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
4 citations,
May 2015 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” Congenital triangular alopecia can occur outside the typical fronto-temporal region.
 4 citations,
February 1988 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
4 citations,
February 1988 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Congenital triangular alopecia is more common than thought and some treatments can be beneficial for appearance concerns.
3 citations,
January 2020 in “International journal of trichology” Congenital triangular alopecia is a hair loss condition present from birth or early childhood with no effective treatment needed.
 May 2024 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology”
May 2024 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology” 5% topical minoxidil effectively treated a boy's congenital triangular alopecia without side effects.
 April 2024 in “Indian Journal of Paediatric Dermatology”
April 2024 in “Indian Journal of Paediatric Dermatology” Congenital triangular alopecia and vitiligo can occur together, but treatment for one may not affect the other.
 January 2021 in “Skin appendage disorders”
January 2021 in “Skin appendage disorders” The report concludes that atypical Brauer nevus is more common in males, present at birth, and often misdiagnosed due to its unusual scalp locations.
 January 2020 in “Przegla̧d dermatologiczny”
January 2020 in “Przegla̧d dermatologiczny” A 5-year-old boy was diagnosed with congenital triangular alopecia, a type of hair loss without skin changes, usually starting between ages 2-5, with no specific treatment.
 January 2018 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2018 in “Springer eBooks” Congenital triangular alopecia is a harmless, non-spreading hair loss condition often seen in young children.
January 2023 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Sublingual minoxidil helped regrow hair in a person with congenital triangular alopecia.
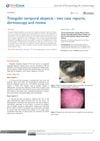 2 citations,
February 2018 in “Journal of dermatology & cosmetology”
2 citations,
February 2018 in “Journal of dermatology & cosmetology” Triangular temporal alopecia is a benign hair loss pattern best diagnosed with dermoscopy, with limited treatment options like surgery and hair transplantation.
 July 2024 in “Dermatology Practical & Conceptual”
July 2024 in “Dermatology Practical & Conceptual” LC-OCT helps accurately diagnose different types of infant hair loss without invasive methods.
January 2023 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal” A 23-year-old man has a benign, non-progressive hair loss patch that doesn't respond to treatment but can be cosmetically treated.
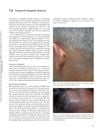 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Temporal triangular alopecia is a lifelong condition with hairless patches on the side of the head that may be present from birth.
 January 2011 in “International Journal of Trichology”
January 2011 in “International Journal of Trichology” The document concludes that doctors should recognize congenital triangular alopecia to avoid unnecessary treatments, as it does not respond to steroids like alopecia areata does.
 December 2020 in “TURKDERM”
December 2020 in “TURKDERM” A 3-year-old boy was diagnosed with a rare, non-scarring hair loss condition called temporal triangular alopecia.
 56 citations,
March 2010 in “Journal of Dermatology”
56 citations,
March 2010 in “Journal of Dermatology” Most cases of Temporal Triangular Alopecia are found in early childhood and may be related to genetic conditions.
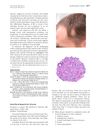
The man has Temporal Triangular Alopecia, a stable, non-scarring hair loss condition best treated with hair transplantation.
January 2022 in “Clinical Cases in Dermatology” A 12-year-old boy has a rare, harmless hair loss on his chin with no need for treatment.
 36 citations,
June 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
36 citations,
June 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Dermoscopy is useful for diagnosing various skin, hair, and nail disorders and can reduce the need for biopsies.
 30 citations,
May 2004 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
30 citations,
May 2004 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” The document concludes that early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for children with hair loss to prevent permanent damage, although not all conditions can be effectively treated.
 24 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology”
24 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology” The document concludes that accurate diagnosis of hair loss in children is crucial due to limited treatment options and the condition's psychological impact.
 3 citations,
January 2020 in “Clinical dermatology review”
3 citations,
January 2020 in “Clinical dermatology review” Trichoscopy is useful for diagnosing hair and scalp disorders in people with darker skin.
 1 citations,
July 2016 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
July 2016 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Men with a certain type of hair loss often use facial moisturizers, and a specific antibiotic treatment may help another hair condition.
 July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” The most common cause of hair loss in children is tinea capitis, followed by alopecia areata and telogen effluvium.
 7 citations,
December 2008 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
7 citations,
December 2008 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” The document concludes that various childhood hair and nail disorders exist, some may improve on their own, and advances in genetics and immunology could enhance treatment and counseling.
 16 citations,
June 2009 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
16 citations,
June 2009 in “Dermatologic Surgery” A 17-year-old boy with Temporal Triangular Alopecia successfully grew new hair after a hair restoration surgery using follicular unit transplantation.

























