 April 2024 in “Journal of endocrinological investigation”
April 2024 in “Journal of endocrinological investigation” Topical minoxidil helps transgender individuals assigned female at birth grow more facial hair.
 1 citations,
July 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine”
1 citations,
July 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” Different causes of beard hair loss have various treatments, including medications, lifestyle changes, and procedures to stimulate hair growth.
 7 citations,
November 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
7 citations,
November 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Low-dose oral minoxidil may cause side effects like hypertrichosis and is not suitable for everyone.
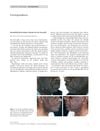 6 citations,
May 2012 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology”
6 citations,
May 2012 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology” Oral minoxidil can cause inflamed, ingrown hairs in the beard area.
 January 2015 in “Przegla̧d dermatologiczny”
January 2015 in “Przegla̧d dermatologiczny” Intralesional triamcinolone is the most effective treatment for alopecia areata, followed by excimer light therapy, and then topical minoxidil. The scalp responds better to treatment than the beard area.
 43 citations,
November 2007 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
43 citations,
November 2007 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Hair and nail changes can indicate health issues, including cancer and side effects from cancer treatments.
 14 citations,
May 2011 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America”
14 citations,
May 2011 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America” Laser hair removal is effective for dark hair but needs improvement for nonpigmented or fine hairs.

Different scalp and hair disorders are more common in certain ethnic groups, with the most common being androgenetic alopecia, which is treated with medications like minoxidil and finasteride.
 77 citations,
March 2001 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
77 citations,
March 2001 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Androgenetic alopecia involves genetics, hormones, and can be treated with medications or surgery.
 38 citations,
March 2010 in “Medicine”
38 citations,
March 2010 in “Medicine” Most patients with Porphyria Cutanea Tarda had skin blisters and were often affected by hepatitis C and alcohol abuse, with differences between familial and sporadic cases.
 24 citations,
September 2019 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
24 citations,
September 2019 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Low-dose oral minoxidil improved or stabilized hair loss in some patients, but higher doses may be needed for significant effects.
 6 citations,
October 1997 in “CNS Drugs”
6 citations,
October 1997 in “CNS Drugs” Psychotropic drugs can cause hair loss or excessive hair growth.
 2 citations,
December 2004 in “Medicine”
2 citations,
December 2004 in “Medicine” Different hair and scalp disorders cause hair loss or excess hair growth, with various treatments available depending on the specific condition.
 October 2018 in “Springer eBooks”
October 2018 in “Springer eBooks” The document concludes that various hair disorders have different treatments, including medication, surgery, and addressing underlying causes.
 147 citations,
April 1994 in “Drug Safety”
147 citations,
April 1994 in “Drug Safety” Some drugs can cause hair loss or increase hair growth, but these effects are usually reversible when the drug is stopped.
 20 citations,
July 2009 in “Journal of Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology”
20 citations,
July 2009 in “Journal of Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology” Quick treatment of hair disorders in teenage girls is important because of the emotional effects.
 2 citations,
January 1908 in “Journal of the American Medical Association”
2 citations,
January 1908 in “Journal of the American Medical Association” Fear of hair-related issues causes significant mental distress, especially in high-stress women.
 1 citations,
October 1984 in “Clinics in dermatology”
1 citations,
October 1984 in “Clinics in dermatology” People distressed by minor skin changes should consult dermatologists with cosmetic expertise, and a public Cosmetic Dermatology Service with mental health support is recommended.
 157 citations,
April 1994 in “Clinical endocrinology”
157 citations,
April 1994 in “Clinical endocrinology” Androgens can cause hair growth in some areas and hair loss on the scalp.
 21 citations,
April 2019 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology”
21 citations,
April 2019 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology” The document concludes that stopping shaving or removing affected hair can alleviate Pseudofolliculitis barbae (PFB).
 January 2015 in “Our Dermatology Online”
January 2015 in “Our Dermatology Online” Intralesional triamcinolone is the most effective treatment for hair regrowth in alopecia areata patients.
 January 2024 in “SAGE Open Medical Case Reports”
January 2024 in “SAGE Open Medical Case Reports” Minoxidil can help increase facial hair growth.
 December 2022 in “Cureus”
December 2022 in “Cureus” Hormones significantly influence hair growth, with conditions like hirsutism and patterned hair loss linked to hormone levels; more research is needed for full understanding.
 August 2019 in “DOAJ (DOAJ: Directory of Open Access Journals)”
August 2019 in “DOAJ (DOAJ: Directory of Open Access Journals)” Minoxidil is a primary treatment for hair loss but its exact working method is unknown.
March 2025 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” Low-dose oral minoxidil effectively treats alopecia but can cause side effects like excess hair growth and fluid retention.
 January 2023 in “Skin appendage disorders”
January 2023 in “Skin appendage disorders” Low-dose oral minoxidil may help treat hair loss but is not FDA-approved and can cause side effects like unwanted hair growth and heart issues.
 November 2024 in “Skin Health and Disease”
November 2024 in “Skin Health and Disease” Minoxidil is effective for promoting hair growth and has various dermatological uses.
 27 citations,
December 2001 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology”
27 citations,
December 2001 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology” Different hair removal methods have pros and cons, and more evidence is needed to prove laser treatments work.
 26 citations,
April 1999 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
26 citations,
April 1999 in “Dermatologic Clinics” The long-pulsed alexandrite laser is effective for hair reduction, particularly for light-skinned individuals with dark hair, but caution is needed for darker skin.
 August 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
August 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Obesity is linked to more severe hair loss in adult men and to excess hair growth, but its effects on hair conditions are complex and need more research.





























