 August 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
August 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” A 54-year-old man with painful skin blisters and fever was diagnosed with Sweet syndrome and successfully treated with corticosteroids.
 April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” IL-17C is important in inflammatory skin diseases and could be a target for treatment.
 November 2013 in “John Wiley & Sons, Ltd eBooks”
November 2013 in “John Wiley & Sons, Ltd eBooks” Skin symptoms can indicate endocrine disorders and have various treatments.
 March 2013 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
March 2013 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” The document concludes that there have been significant improvements in diagnosing and treating skin diseases, including melanoma, with new techniques and therapies.
 November 2012 in “South African Family Practice”
November 2012 in “South African Family Practice” The article concludes that early treatment of alopecia is crucial to prevent permanent hair loss.
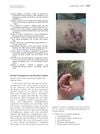
A 72-year-old man was diagnosed with a rare skin form of Rosai-Dorfman disease after years of misdiagnosis.
 August 2010 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
August 2010 in “The Journal of Dermatology” The document concludes that low-dose acne treatment is most suitable for moderate acne, with high patient satisfaction and low relapse rates.
 March 2006 in “Drug Discovery Today: Therapeutic Strategies”
March 2006 in “Drug Discovery Today: Therapeutic Strategies” The 2006 editorial concluded that immunotherapy was advancing with new drugs, focusing on specific biological therapies and convenient oral treatments, and highlighted the importance of partnerships and new regulations in the field.
 30 citations,
September 2017 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
30 citations,
September 2017 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Men with common hair loss may have a higher risk of heart disease and diabetes, and should be checked for these conditions.
 7 citations,
May 1978 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
May 1978 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Recent hair loss research shows some progress, especially in understanding male pattern baldness, but effective treatments for many types of hair loss are still lacking.
 4 citations,
July 2019 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
4 citations,
July 2019 in “Clinics in Dermatology” The document concludes that while white skin, nail, and mucosa diseases increase skin cancer risk, they are generally harmless, especially compared to darker pigmentation conditions.
 July 2024 in “Biomolecular and Health Science Journal”
July 2024 in “Biomolecular and Health Science Journal” Mycophenolic acid effectively improved hair and nail growth in a lupus patient.
May 2018 in “The Journal of Immunology” A(1-7) treatment reduces symptoms of lupus in mice.
 19 citations,
November 2011
19 citations,
November 2011 Using systemic drugs as creams for skin conditions shows promise, but more research is needed to confirm their effectiveness and safety.
 3 citations,
June 2020 in “Cutis”
3 citations,
June 2020 in “Cutis” Poor nutrition can lead to skin diseases in hospitalized patients and should be quickly identified and treated.
 2 citations,
February 2023 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
2 citations,
February 2023 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” People with autism are more likely to develop alopecia areata than those without autism.
 1 citations,
August 2022 in “JAAD Case Reports”
1 citations,
August 2022 in “JAAD Case Reports” A woman's complete hair loss condition improved after recovering from COVID-19.
 January 2023 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal”
January 2023 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal” No single ideal JAK inhibitor for alopecia areata has been determined; JAK3 inhibitors may be promising with fewer side effects.
 August 2021 in “Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine”
August 2021 in “Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine” The article concludes that understanding Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia (FFA) is crucial for effective treatment, which includes medication like 5α-reductase inhibitors and hydroxychloroquine.
2 citations,
January 2015 in “Indian dermatology online journal” A woman with vitiligo had a rare fungal infection around her vitiligo patch and it improved with antifungal cream.
1 citations,
August 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Vδ1+ T-cells in the skin contribute to hair loss in alopecia areata and could be targeted for treatment.
12 citations,
January 2014 in “Dermatology online journal” White hair regrowth in alopecia areata may be more common than thought.
 7 citations,
February 2022 in “JAAD International”
7 citations,
February 2022 in “JAAD International” COVID-19 may be linked to hair loss or worsening of hair loss in some people.
 7 citations,
December 2011 in “Elsevier eBooks”
7 citations,
December 2011 in “Elsevier eBooks” The document concludes that early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing skin diseases in ferrets.
 4 citations,
October 2022 in “Genes”
4 citations,
October 2022 in “Genes” Our microbiome may affect the development of the hair loss condition Alopecia Areata, but more research is needed to understand this relationship.
 3 citations,
June 2020 in “Cureus”
3 citations,
June 2020 in “Cureus” A woman's hair loss led to discovering she had lupus.
 3 citations,
June 2006 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
3 citations,
June 2006 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” The document concludes that hair loss is complex, affects many people, has limited treatments, and requires more research on its causes and psychological impact.
 July 2024 in “Indonesian Journal of Case Reports”
July 2024 in “Indonesian Journal of Case Reports” Effective treatment improved skin and overall symptoms in a lupus patient.
 May 2023 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
May 2023 in “British Journal of Dermatology” COVID-19 can cause long-term skin problems and has changed how skin doctors work.
 November 2022 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
November 2022 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” The study suggests a link between varicella-zoster virus and segmental vitiligo, with evidence of the virus disrupting skin pigment cells.


























