 2 citations,
July 1988 in “JAMA”
2 citations,
July 1988 in “JAMA” Amphetamines may not directly cause hair loss, as the type of thinning seen with their use differs from severe alopecia.
22 citations,
February 2002 in “European Neuropsychopharmacology” Hair analysis for drugs in psychosis patients is unreliable due to varying hair growth rates.
[object Object] 
Amphetamine use may not cause hair loss, "geezer" traits are normal aging, not all educated older people are stereotypes, and metronidazole can rarely cause lung disease.

Amphetamines may not directly cause hair loss.
 30 citations,
May 1991 in “Psychosomatics”
30 citations,
May 1991 in “Psychosomatics” Some psychiatric medications can cause reversible hair loss.

Forensic hair analysis for drugs is now more reliable and accurate.

research Hair
1 citations,
April 2023 in “Elsevier eBooks” Hair analysis can detect drug use but is costly and interpretation is complex.
 1 citations,
July 1988 in “JAMA”
1 citations,
July 1988 in “JAMA” Metronidazole can cause lung disease.
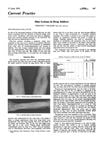 56 citations,
June 1970 in “The BMJ”
56 citations,
June 1970 in “The BMJ” Drug addicts often have scars, skin color changes, blocked veins, and bruising, with severe ulcers from barbiturate injections.
 1 citations,
August 2006 in “International forensic science and investigation series”
1 citations,
August 2006 in “International forensic science and investigation series” Hair testing is a reliable method for detecting workplace drug use when done with proper sample preparation and confirmation.
 August 1994 in “Drugs & Therapy Perspectives”
August 1994 in “Drugs & Therapy Perspectives” Some drugs can cause hair loss or growth, but hair usually returns to normal after stopping the drug.
 63 citations,
October 1972 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
63 citations,
October 1972 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Women with thinning hair have thinner hair strands than women without hair loss.
 39 citations,
October 1967 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
39 citations,
October 1967 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss in women often doesn't follow a pattern, isn't linked to age, may be genetic, and can be related to thyroid issues or other health factors.
 36 citations,
March 2002 in “Journal of Biological Chemistry”
36 citations,
March 2002 in “Journal of Biological Chemistry” Food deprivation increases MST enzyme in the brain, possibly affecting energy balance.
 32 citations,
December 1969 in “The Lancet”
32 citations,
December 1969 in “The Lancet” Children with marasmus have more resting hair follicles and thinner, less pigmented hair, showing long-term malnutrition.
 28 citations,
May 2015 in “Addiction Biology”
28 citations,
May 2015 in “Addiction Biology” Prenatal stress changes how male and female rats enjoy rewards differently, linked to sex hormones.
 22 citations,
February 2008 in “Journal of Neurochemistry”
22 citations,
February 2008 in “Journal of Neurochemistry” Minoxidil prevents serotonin loss from MDMA by affecting potassium channels and increasing Akt phosphorylation.
 17 citations,
March 1985 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
17 citations,
March 1985 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Minoxidil can lower blood pressure in some people.
 8 citations,
October 2014 in “Journal of analytical toxicology.”
8 citations,
October 2014 in “Journal of analytical toxicology.” Chemical hair straightening significantly reduces detectable drug levels in hair.
 3 citations,
January 2002 in “Transgenic Research”
3 citations,
January 2002 in “Transgenic Research” Scientists made a mouse that can be made to lose hair and then grow it back.
 1 citations,
December 2018 in “IntechOpen eBooks”
1 citations,
December 2018 in “IntechOpen eBooks” Human hair shows promise for non-invasive medical testing, but more research is needed to standardize its use.
 February 2020 in “Scholars academic journal of pharmacy”
February 2020 in “Scholars academic journal of pharmacy” The weight loss drug Orlistat can cause liver damage and should be used with caution, especially in those with liver or kidney issues.
 July 2003 in “Pediatrics in review”
July 2003 in “Pediatrics in review” In 2001, the FDA approved 12 new drugs for children to treat allergies, asthma, ADHD, birth control, and other conditions.
 January 2021 in “Journal of Allergy and Therapy”
January 2021 in “Journal of Allergy and Therapy” Electric Follicle Stimulation may promote hair growth and density with no known side effects.
 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Telogen effluvium is a common hair loss condition where many hairs enter the resting phase, often not noticeable until significant loss occurs, and treatment focuses on the underlying cause.
 January 2003 in “Postgraduate medicine”
January 2003 in “Postgraduate medicine” The article concludes that hair loss has many causes and treatments, with medication options like finasteride and minoxidil for men, and minoxidil, hormones, or iron for women, while warning against unproven remedies.
 501 citations,
October 2008 in “Psychoneuroendocrinology”
501 citations,
October 2008 in “Psychoneuroendocrinology” Hair cortisol levels can show increased stress during late pregnancy but only for up to six months.
 417 citations,
March 1991 in “American Journal of Psychiatry”
417 citations,
March 1991 in “American Journal of Psychiatry” Most adult chronic hair pullers are women who started in their early teens, often have other mental health issues, and may pull hair due to underlying psychiatric conditions.
[object Object]  233 citations,
November 2002 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
233 citations,
November 2002 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Creating stronger blockers for skin enzymes might lead to better treatment for conditions like acne and excessive hair growth.
 214 citations,
March 1993 in “Archives of Dermatology”
214 citations,
March 1993 in “Archives of Dermatology” Telogen effluvium is a reversible hair loss condition that requires a detailed diagnosis and often resolves on its own.





























