 6 citations,
July 2022 in “Journal of health economics and outcomes research”
6 citations,
July 2022 in “Journal of health economics and outcomes research” Adolescents with severe alopecia incur significantly higher healthcare costs.
 1 citations,
January 2024 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
1 citations,
January 2024 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” COVID-19 vaccines have been linked to an increase in hair loss conditions.

The article concludes that understanding the causes of hair loss and using continuous treatments like minoxidil and finasteride can help manage it, despite potential side effects.
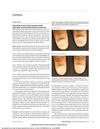 41 citations,
December 2015 in “JAMA Dermatology”
41 citations,
December 2015 in “JAMA Dermatology” Tofacitinib citrate improved nail dystrophy and pain in patients with alopecia universalis without causing side effects.
 9 citations,
August 2018 in “JAAD Case Reports”
9 citations,
August 2018 in “JAAD Case Reports” Tofacitinib can temporarily improve hair growth in alopecia universalis, but its effectiveness may decrease over time.
 9 citations,
November 2012 in “Hepatology Research”
9 citations,
November 2012 in “Hepatology Research” A man lost all his hair permanently after hepatitis C treatment, a side effect not seen before.
 7 citations,
January 2009 in “Immunological investigations”
7 citations,
January 2009 in “Immunological investigations” A 3-year-old boy lost all his hair due to a rare reaction to phenobarbital, but it grew back after steroid treatment.
 October 2021 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual”
October 2021 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual” High-dose corticosteroids can significantly regrow hair in severe alopecia areata.
 April 2020 in “Trends in Immunotherapy”
April 2020 in “Trends in Immunotherapy” Combining triamcinolone acetonide and immunotherapy can help regrow hair in some alopecia totalis patients.

Topical calcipotriol successfully treated hair loss in three patients with Alopecia Totalis.
 March 2018 in “Trends in Immunotherapy”
March 2018 in “Trends in Immunotherapy” Combining triamcinolone acetonide with immunotherapy can help regrow hair in some alopecia totalis patients.
 41 citations,
August 2007 in “European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology”
41 citations,
August 2007 in “European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology” A woman's total hair loss from hepatitis C treatment grew back after stopping the medication.
 27 citations,
April 2005 in “Journal of Chemotherapy”
27 citations,
April 2005 in “Journal of Chemotherapy” Some patients may experience temporary total hair loss from hepatitis C treatment with PEG-interferon and ribavirin.
 3 citations,
August 2020 in “Case Reports in Dermatology”
3 citations,
August 2020 in “Case Reports in Dermatology” Tofacitinib treatment significantly improved a patient's psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and alopecia universalis.
 9 citations,
January 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy”
9 citations,
January 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy” A 14-year-old girl with severe hair loss regrew her hair using upadacitinib.
 3 citations,
July 2021 in “International journal of environmental research and public health/International journal of environmental research and public health”
3 citations,
July 2021 in “International journal of environmental research and public health/International journal of environmental research and public health” Two patients developed complete hair loss after Alemtuzumab treatment for MS, with no regrowth after two years.
 February 2024 in “Journal of cutaneous and aesthetic surgery”
February 2024 in “Journal of cutaneous and aesthetic surgery” The combined treatment helps improve severe hair loss and reduces the need for other medications.
 1 citations,
January 2023 in “IDCases”
1 citations,
January 2023 in “IDCases” A patient experienced severe hair loss after getting an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine.
16 citations,
April 2014 in “Anais brasileiros de dermatologia/Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” A patient lost all their hair while on rheumatoid arthritis medication.
 19 citations,
January 2018
19 citations,
January 2018 Most people with alopecia areata have nail changes, which are common but don't greatly affect their quality of life.
 February 2023 in “International Journal of Medical Arts”
February 2023 in “International Journal of Medical Arts” Trichloroacetic acid is a safe and effective treatment for hair loss in alopecia areata patients.
 16 citations,
April 2007 in “Journal of Medical Primatology”
16 citations,
April 2007 in “Journal of Medical Primatology” The monkey's hair loss was due to an autoimmune disease, not genetics.
 78 citations,
April 1984 in “Archives of Dermatology”
78 citations,
April 1984 in “Archives of Dermatology” Minoxidil can help regrow hair in alopecia areata patients.
 70 citations,
February 2015 in “Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery”
70 citations,
February 2015 in “Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery” Topical drugs and near-infrared light therapy show potential for treating alopecia.
 40 citations,
September 2018 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
40 citations,
September 2018 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Tofacitinib helped some young children with severe hair loss grow their hair back without bad side effects.
 295 citations,
January 2006 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
295 citations,
January 2006 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Alopecia areata, a common autoimmune hair loss condition, often runs in families.
 185 citations,
August 2005 in “Autoimmunity Reviews”
185 citations,
August 2005 in “Autoimmunity Reviews” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition causing hair loss due to the immune system attacking hair follicles, often influenced by genetics and stress.
 62 citations,
June 2015 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
62 citations,
June 2015 in “The Journal of Dermatology” People with alopecia areata have more Th17 cells and fewer Treg cells, which may be key to the condition's development.
 20 citations,
June 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology”
20 citations,
June 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology” The research suggests that autophagy-related genes might play a role in causing alopecia areata.
 20 citations,
August 2018 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
20 citations,
August 2018 in “Clinics in Dermatology” The conclusion is that understanding and addressing the psychological effects of alopecia areata is important for effective treatment.




























