 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Alopecia areata is a common autoimmune condition causing varying hair loss, diagnosed by specific patterns of inflammation around hair follicles, with several treatment options available.
 32 citations,
June 2003 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
32 citations,
June 2003 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” Lipedematous scalp is mainly caused by an increase in fat tissue under the skin and is different from lipedematous alopecia.
January 2025 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” Male pattern baldness worsens with age and can be treated with medications like minoxidil and finasteride, but side effects and personalized care are important.
 August 2024 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy”
August 2024 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy” New regenerative therapies show promise for treating hair loss.
 1 citations,
July 2024 in “Skin Research and Technology”
1 citations,
July 2024 in “Skin Research and Technology” High-frequency ultrasound can effectively visualize and assess hair loss.

A girl with Crohn's disease developed hair loss due to her increased medication, a rare side effect seen in some children.
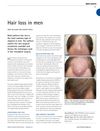 May 2013 in “Trends in Urology & Men's Health”
May 2013 in “Trends in Urology & Men's Health” Male-pattern hair loss is normal, often involves hormone effects on hair follicles, and can be treated with medication or surgery, but new treatments are being researched.
 32 citations,
April 2015 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
32 citations,
April 2015 in “British Journal of Dermatology” The hair shedding scale accurately identifies abnormal hair shedding in women with long hair, with grades 5 and 6 indicating excessive shedding.
 179 citations,
March 2005 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
179 citations,
March 2005 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Oral antiandrogens effectively treat female hair loss, with better results in higher hair loss grades.
 7 citations,
January 2009 in “International Journal of Trichology”
7 citations,
January 2009 in “International Journal of Trichology” Dermoscopy can't help doctors identify scalp irritation caused by topical minoxidil.
 80 citations,
December 2017 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
80 citations,
December 2017 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Low-dose oral minoxidil and spironolactone combo effectively reduces hair loss and improves hair density in women.
 53 citations,
February 2020 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy”
53 citations,
February 2020 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy” Finasteride and minoxidil work best together for hair loss.
 16 citations,
February 2017 in “Dermatology and Therapy”
16 citations,
February 2017 in “Dermatology and Therapy” The new visual scale is a quick and effective way to measure hair loss in women.
 3 citations,
January 2016 in “Skin appendage disorders”
3 citations,
January 2016 in “Skin appendage disorders” Possible causes of female hair loss include androgenetic alopecia, telogen effluvium, cicatricial alopecia, and alopecia areata incognita; diagnosis and treatment require dermoscopy and histopathology.
 30 citations,
May 2004 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
30 citations,
May 2004 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” The document concludes that early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for children with hair loss to prevent permanent damage, although not all conditions can be effectively treated.
 18 citations,
March 2003 in “PubMed”
18 citations,
March 2003 in “PubMed” Hair loss in women can be due to abnormal hair growth cycles or damaged hair follicles, with the most common type being androgenetic alopecia; treatment varies by cause, and the psychological impact is significant.
 16 citations,
July 2002 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
16 citations,
July 2002 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” A woman with lupus experienced skin death due to a blood clotting disorder after stopping a blood thinner, which healed with treatment.
 35 citations,
January 2002 in “Dermatology”
35 citations,
January 2002 in “Dermatology” A woman's hair loss during treatment with specific hepatitis C drugs grew back after stopping the medication.
 6 citations,
March 1999 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
6 citations,
March 1999 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Scalp biopsies are essential for accurately diagnosing alopecia areata.
 36 citations,
August 2009 in “PubMed”
36 citations,
August 2009 in “PubMed” The review suggests seeing a dermatologist for scarring hair loss and using treatments like minoxidil or finasteride for common male and female pattern hair loss.
 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Trichotillomania is a disorder where people compulsively pull out their hair, treated with drugs and behavior therapy.
 35 citations,
January 1993 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
35 citations,
January 1993 in “International Journal of Dermatology” People with HIV and low T cell counts have more hair and scalp problems.
76 citations,
October 2000 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Follicular mucinosis can be an early sign of aggressive mycosis fungoides.
 5 citations,
September 1986 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
5 citations,
September 1986 in “Pediatric Dermatology” A family showed a new condition with inherited hair loss and skin changes, possibly due to one genetic disorder.
 5 citations,
December 1981 in “PubMed”
5 citations,
December 1981 in “PubMed” Metoprolol, a blood pressure medication, was linked to reversible hair loss.
 22 citations,
June 1980 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
22 citations,
June 1980 in “International Journal of Dermatology” The document concludes that correct diagnosis of alopecia types is crucial, scalp biopsies are important, and more research is needed.
 8 citations,
March 1979 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
8 citations,
March 1979 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Dr. Vera H. Price's 1979 work emphasizes the importance of accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment for hair loss.
 5 citations,
October 2014 in “Scottish medical journal”
5 citations,
October 2014 in “Scottish medical journal” Nitrofurantoin may cause sub-acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus.
 33 citations,
December 2013 in “Journal of cutaneous pathology”
33 citations,
December 2013 in “Journal of cutaneous pathology” A fungal infection can look like a different scalp condition in teens, leading to wrong treatment until proper tests are done.
 2 citations,
April 2015 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual”
2 citations,
April 2015 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual” Daily use of antifungal shampoo can hide symptoms and make it hard to diagnose fungal scalp infections.



























