Rapidly Progressive Alopecia Areata Totalis in a COVID-19 Patient, Unresponsive to Tofacitinib
February 2021
in “
Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology
”

TLDR A COVID-19 patient with severe hair loss did not improve with hair loss medication after stopping and restarting it due to the infection.
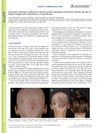
The document reports a case of a 24-year-old female patient with alopecia areata totalis (AAT) who experienced a sudden and intense anagen effluvium (rapid hair loss) after testing positive for COVID-19. Despite having complete hair regrowth while using tofacitinib, an oral JAK 1/3 inhibitor, for the last 12 months, the patient's condition worsened after discontinuing the medication due to the COVID-19 infection. The reintroduction of tofacitinib after 14 days did not improve her hair loss even after 3 months. The case suggests that the withdrawal of tofacitinib may lead to persistent anagen effluvium in patients with AA and COVID-19, and the virus may directly affect the hair follicle immune privilege. The exact role of COVID-19 in postinfection hair loss is still unclear, and the authors recommend testing all patients with anagen or telogen effluvium for COVID-19. The document concludes that the continuous use of JAK inhibitors in AA patients who develop COVID-19 infection is controversial and the real effect of the virus on hair follicles needs further investigation.