 23 citations
,
November 2018 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
23 citations
,
November 2018 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” The study concluded that severity of Frontal fibrosing alopecia is not linked to how long someone has it, can start before menopause, and eyebrow loss may be an early sign.
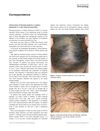 13 citations
,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
13 citations
,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology” The study found that treatment improved hair condition in patients with Fibrosing Alopecia in a Pattern Distribution in Chile.
 24 citations
,
September 2015 in “JAAD case reports”
24 citations
,
September 2015 in “JAAD case reports” Finasteride helps hair regrowth in frontal fibrosing alopecia.
 339 citations
,
February 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
339 citations
,
February 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Most patients with frontal fibrosing alopecia are postmenopausal women, and treatments like finasteride and dutasteride can improve or stabilize the condition.
220 citations
,
June 2013 in “The Journal of Pathology” Lichen planopilaris may be an autoimmune disease causing hair loss due to immune system issues in hair follicles.
 64 citations
,
June 2009 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
64 citations
,
June 2009 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Oral dutasteride can potentially treat frontal fibrosing alopecia in postmenopausal women, with some patients showing disease arrest and hair regrowth.
 25 citations
,
January 2006 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
25 citations
,
January 2006 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Finasteride lowers scalp and blood DHT levels, potentially treating male-pattern baldness.
 73 citations
,
November 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
73 citations
,
November 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Some women with common hair loss may develop permanent hair loss.
 179 citations
,
December 2004 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
179 citations
,
December 2004 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Some postmenopausal women with frontal fibrosing alopecia stopped losing hair with finasteride treatment, hinting at a possible hormonal cause.
 158 citations
,
February 2000 in “Archives of dermatology”
158 citations
,
February 2000 in “Archives of dermatology” Some people with pattern hair loss may also have scalp inflammation and scarring similar to lichen planopilaris.










