 1 citations,
May 2003 in “Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine”
1 citations,
May 2003 in “Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine” The boy had trichotillomania, causing hair loss, and treatment focused on habit reversal and support.
 3 citations,
January 2021 in “Skin appendage disorders”
3 citations,
January 2021 in “Skin appendage disorders” Trichoscopy is useful for correctly diagnosing tinea capitis in adults with unexplained hair loss.
 8 citations,
February 2007 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
8 citations,
February 2007 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Higher serum ferritin levels than currently used might be needed to rule out iron deficiency in women with hair loss.
[object Object] 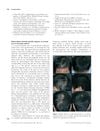 10 citations,
July 2012 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
10 citations,
July 2012 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Syphilis can cause hair loss and should be considered in unexplained cases.

The woman has unexplained hair loss and it's unclear what her condition is or how to treat it.
 7 citations,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Syphilis can cause hair loss without other symptoms and should be considered when diagnosing unexplained hair loss.
 4 citations,
July 2015 in “Case Reports in Dermatology”
4 citations,
July 2015 in “Case Reports in Dermatology” A woman with unexplained hair loss was found to have harmless skin tumors and a scarring hair loss condition, but the tumors didn't cause the hair loss.
 January 2022 in “Clinical Cases in Dermatology”
January 2022 in “Clinical Cases in Dermatology” Lack of certain nutrients may contribute to hair loss and proper diet or supplements could improve it.
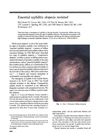 53 citations,
May 1995 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
53 citations,
May 1995 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Syphilis can cause hair loss that looks like other conditions, but it improves with treatment.
 24 citations,
September 1985 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
24 citations,
September 1985 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The report suggests a possible link between hair loss and hidden scalp tumors but states more evidence is needed to confirm this.
 13 citations,
January 2015 in “International Journal of Trichology”
13 citations,
January 2015 in “International Journal of Trichology” Higher lead and cadmium, and lower zinc and iron levels in the blood might be linked to chronic hair loss in women.
 32 citations,
July 2017 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual”
32 citations,
July 2017 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual” New hair and skin changes were found in a rare case of syphilis-related hair loss.
40 citations,
November 1966 in “Archives of Dermatology” Trichorrhexis nodosa is mainly caused by hair trauma and improves with gentler hair care.
 6 citations,
October 1993 in “The journal of the Royal Society of Health”
6 citations,
October 1993 in “The journal of the Royal Society of Health” Children's hair loss has many causes and requires careful diagnosis and personalized treatment, including emotional support.
 87 citations,
October 1997 in “JAMA”
87 citations,
October 1997 in “JAMA” Some vaccines might rarely cause hair loss, more research is needed.
 56 citations,
January 2008 in “Dermatology”
56 citations,
January 2008 in “Dermatology” Higher iron levels in the blood are not linked to increased hair loss in women.
4 citations,
March 1968 in “The Lancet” Avoiding aspirin may prevent hair loss.
 28 citations,
September 1998 in “Medical Clinics of North America”
28 citations,
September 1998 in “Medical Clinics of North America” Most hair loss can be diagnosed with patient history and physical exam, and a few common types make up most cases.
 10 citations,
June 2000 in “Primary Care”
10 citations,
June 2000 in “Primary Care” The document explains different hair loss types and treatments, emphasizing diagnosis through examination and tests, and specific treatments for each condition.
 7 citations,
October 2000 in “Allergo Journal”
7 citations,
October 2000 in “Allergo Journal” Stress may affect hair growth by influencing hair follicle development and could contribute to hair loss.
 April 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
April 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Some treatments work better for different types of hair loss, and nutrients like iron and L-lysine are important for preventing hair loss.
 January 2012 in “Vitamins & trace elements”
January 2012 in “Vitamins & trace elements” Smoking and drinking can lower vitamin levels and potentially trigger early hair loss, but overall vitamin levels don't seem to affect hair loss duration.
 95 citations,
February 2019 in “The New England Journal of Medicine”
95 citations,
February 2019 in “The New England Journal of Medicine” Mutations in the PADI3 gene are linked to a higher risk of scarring hair loss in women of African descent.
 January 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
January 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” The 2015 Hair Research Congress concluded that stem cells, maraviroc, and simvastatin could potentially treat Alopecia Areata, topical minoxidil, finasteride, and steroids could treat Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia, and PTGDR2 antagonists could also treat alopecia. They also found that low-level light therapy could help with hair loss, a robotic device could assist in hair extraction, and nutrition could aid hair growth. They suggested that Alopecia Areata is an inflammatory disorder, not a single disease, indicating a need for personalized treatments.
1 citations,
October 2018 in “Ukraïnsʹkij žurnal dermatologìï, venerologìï, kosmetologìï” Wolvit® (biotin 5 mg) is effective and safe for treating hair loss and scalp conditions in women.
 2 citations,
May 2023 in “JAAD Case Reports”
2 citations,
May 2023 in “JAAD Case Reports” The document concludes that early and accurate diagnosis of hair loss on the top of the scalp in Black men is important to distinguish CCCA from other types of hair loss.
[object Object]  February 2024 in “International neuropsychiatric disease journal”
February 2024 in “International neuropsychiatric disease journal” Alopecia areata severely impacts quality of life, mental health, and work productivity.
 December 2024 in “Nutrients”
December 2024 in “Nutrients” Skin, hair, and nail changes can help detect eating disorders early.
 15 citations,
March 2014 in “Body Image”
15 citations,
March 2014 in “Body Image” Wig users with alopecia do a lot of emotional and practical work to make their wigs look natural and manage how others see them.
 January 2016 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2016 in “Springer eBooks” The conclusion is that using the 5W1H method can improve diagnosis and management of childhood hair-pulling disorder.



























