 3 citations,
May 2010 in “Archives of dermatology”
3 citations,
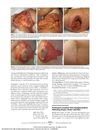
May 2010 in “Archives of dermatology” Herpes zoster infection can cause permanent hair color change in the affected area.
 3 citations,
January 2014 in “Middle East African Journal of Ophthalmology”
3 citations,
January 2014 in “Middle East African Journal of Ophthalmology” A woman lost her hair after taking acyclovir, but it grew back when she stopped the medication.
 1 citations,
April 2018 in “SLEEP”
1 citations,
April 2018 in “SLEEP” People with obstructive sleep apnea are more likely to get herpes zoster, but nightmares don't affect the risk.
2 citations,
December 2019 in “Chinese medical journal/Chinese Medical Journal” A woman with a scalp infection and herpes recovered fully after treatment.
 1 citations,
June 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy”
1 citations,
June 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy” People with Alopecia Areata have more herpes simplex infections but similar rates of cancer, blood clots, and heart disease compared to those without it.
 7 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology”
7 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology” Hair loss can be caused by stress, infections, drugs, and various diseases, with treatment depending on accurate diagnosis.
 10 citations,
February 2006 in “Archives of dermatology”
10 citations,
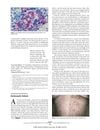
February 2006 in “Archives of dermatology” A man's chest hair turned white after a shingles infection, possibly due to virus-damaged pigment cells.
 28 citations,
April 2009 in “Annals of laboratory medicine”
28 citations,
April 2009 in “Annals of laboratory medicine” The dense fine speckled pattern in ANA tests is common in autoimmune diseases, challenging previous beliefs that it was unrelated.
 4 citations,
January 2009 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
4 citations,
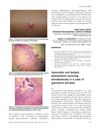
January 2009 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” A patient with granuloma annulare experienced both isotopic and isomorphic responses, with skin lesions responding to steroids but relapsing after stopping treatment.
 2 citations,
June 2016 in “Journal of skin and stem cell”
2 citations,
June 2016 in “Journal of skin and stem cell” Wet cupping blood has different components than regular venous blood, which might affect skin disorder treatments.
 March 2024 in “IP Indian journal of clinical and experimental dermatology”
March 2024 in “IP Indian journal of clinical and experimental dermatology” Elderly in South India commonly suffer from skin issues like wrinkles, dryness, and infections, needing better skin care education.
 January 2021 in “Erciyes medical journal”
January 2021 in “Erciyes medical journal” The COVID-19 pandemic changed the types of skin conditions seen at a clinic, with fewer patients and varying numbers of specific conditions.
 September 2015 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
September 2015 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Skin diseases are common in HIV patients and could help detect HIV early in Ethiopia.
 21 citations,
June 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
21 citations,
June 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy” The COVID-19 pandemic led to fewer dermatology visits and changed the types of skin conditions patients experienced.
 July 2017 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
July 2017 in “British Journal of Dermatology” The document concludes that scalp conditions have various causes and can present in many different ways.
 June 2015 in “Journal of the turkish academy of dermatology”
June 2015 in “Journal of the turkish academy of dermatology” Eating the right foods is important for skin health and can help treat some skin conditions.
 July 1988 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
July 1988 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Various dermatologic treatments were effective for skin conditions like acne, rosacea, hair loss, and psoriasis from December 1986 to December 1987.
 2 citations,
January 2014 in “Springer eBooks”
2 citations,
January 2014 in “Springer eBooks” The book details skin conditions in older adults, their link to mental health, cancer treatment importance, hair loss remedies, and managing autoimmune and itchy skin.
 2 citations,
September 2014 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences”
2 citations,
September 2014 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences” Most HIV patients in the study showed skin and mucous membrane issues, with oral thrush being the most common.
 August 2023 in “American Journal of Hospice and Palliative Medicine”
August 2023 in “American Journal of Hospice and Palliative Medicine” People in palliative care often have skin problems due to their main illness or other health issues, and treatments focus on comfort and quality of life.
 25 citations,
December 1995 in “Neurology”
25 citations,
December 1995 in “Neurology” The research found that chickenpox virus spreads in skin through blood then to skin cells, while shingles virus moves from nerves to hair follicle areas before infecting skin cells.
 2 citations,
April 2019 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
2 citations,
April 2019 in “Dermatologic Therapy” A patient with alopecia had hair regrowth with tofacitinib but developed a skin reaction, choosing to continue the treatment despite the side effect.
 January 2016 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2016 in “Springer eBooks” Cryotherapy may be an effective and simple treatment for mild hair loss with few side effects.
 222 citations,
September 2016 in “JCI insight”
222 citations,
September 2016 in “JCI insight” Tofacitinib is safe and effective for severe alopecia areata, but hair loss may return 2 months after stopping treatment.
 66 citations,
June 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
66 citations,
June 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Baricitinib is effective and safe for treating severe alopecia areata.
 65 citations,
November 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
65 citations,
November 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The document concludes that early recognition and treatment of primary cicatricial alopecia is crucial to prevent permanent hair loss.
 51 citations,
October 2002 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
51 citations,
October 2002 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Finasteride increases hair density in female androgenetic alopecia, but individual results may vary.
 23 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
23 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Permanent hair loss from cicatricial alopecia is treated by reducing inflammation and managing symptoms, but regrowth in scarred areas is unlikely.
 11 citations,
November 2021 in “BMJ Open”
11 citations,
November 2021 in “BMJ Open” People with alopecia areata have higher rates of mental health issues, autoimmune diseases, and infections.
 10 citations,
January 2023 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
10 citations,
January 2023 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Baricitinib and deuruxolitinib are effective for treating alopecia areata, but their efficacy depends on the dose.





























