
The document is a detailed guide on skin conditions and treatments for dermatologists.
 86 citations,
August 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
86 citations,
August 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” To diagnose hair loss, use a systematic approach including history, exams, and tests.
 68 citations,
May 2012 in “Annals of Oncology”
68 citations,
May 2012 in “Annals of Oncology” Some breast cancer chemotherapy can cause permanent hair loss.
 53 citations,
November 1992 in “Mayo Clinic Proceedings”
53 citations,
November 1992 in “Mayo Clinic Proceedings” HIV can cause unusual and severe skin problems that are hard to treat.
 39 citations,
April 2001 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
39 citations,
April 2001 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Latanoprost, a glaucoma medication, caused excessive eyelid hair growth in many patients.
 37 citations,
June 2002 in “The Laryngoscope”
37 citations,
June 2002 in “The Laryngoscope” Ectodermal dysplasia causes various symptoms and early treatment is important for eye, dental, and skin issues.
 27 citations,
January 2020 in “Experimental Dermatology”
27 citations,
January 2020 in “Experimental Dermatology” Immune cells affect hair growth and could lead to new hair loss treatments.
 22 citations,
February 2002 in “Clinics in Geriatric Medicine”
22 citations,
February 2002 in “Clinics in Geriatric Medicine” Many elderly women experience unwanted facial hair and various hair loss conditions, with treatments available for each condition.
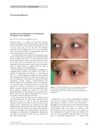 15 citations,
November 2009 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
15 citations,
November 2009 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Bimatoprost helped a girl grow her eyelashes back quickly and without serious side effects.
 10 citations,
February 2011 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
10 citations,
February 2011 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” The document concludes that proper diagnosis and evidence-based treatments are crucial for managing hair diseases, and psychological support for patients is important.
 8 citations,
July 2012 in “Cambridge University Press eBooks”
8 citations,
July 2012 in “Cambridge University Press eBooks” Androgens can both increase body hair and cause scalp hair loss.
 March 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
March 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Mycophenolic acid may help hair growth, a combination treatment improves hair thickness in male hair loss, and early treatment of frontal fibrosing alopecia is important.
 January 2014 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
January 2014 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Proteins like aPKC and PDGF-AA, substances like adenosine and ATP, and adipose-derived stem cells all play important roles in hair growth and health, and could potentially be used to treat hair loss and skin conditions.
 January 2012 in “Yearbook of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery”
January 2012 in “Yearbook of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery” Alopecia areata is a hair loss condition that often starts before age 30 and can affect various body parts, with unpredictable hair regrowth chances.
1 citations,
January 2015 in “International Journal of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine” Cyclosporine-A can cause excessive hair growth, which usually stops after discontinuing the drug.
 April 2024 in “Canadian Journal of Ophthalmology”
April 2024 in “Canadian Journal of Ophthalmology” A woman with advanced eye cancer went into complete remission using a combination of immunotherapy and topical treatments.
 October 2023 in “Case reports in dermatological medicine”
October 2023 in “Case reports in dermatological medicine” A Jordanian family with Clouston syndrome has a common GJB6 gene mutation.
December 2022 in “Molecular Pharmaceutics” Latanoprost-loaded nanotransfersomes could help treat hair loss by promoting hair growth.
 185 citations,
June 2014 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
185 citations,
June 2014 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” A man with severe hair loss and skin disease regrew his hair with no side effects after taking tofacitinib.
 2 citations,
January 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
2 citations,
January 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” Targeted therapies for lung cancer are effective but require careful management of side effects to benefit patients.
 October 2022 in “IntechOpen eBooks”
October 2022 in “IntechOpen eBooks” Hair loss due to scarring can be treated by reducing inflammation, removing scar tissue, and transplanting hair. The Follicular Unit Extraction technique is effective but requires skill and time. Future focus should be on scar-less healing methods.
14 citations,
September 2015 in “PubMed” Alopecia areata can be managed with various treatments, and severe cases should be referred to dermatologists.
26 citations,
February 2015 in “Pediatric blood & cancer” Targeted anticancer therapies in children often cause skin side effects like rash and dry skin.
2 citations,
April 2008 in “Advances in therapy” Proper diagnosis and treatment of childhood hair loss require distinguishing between alopecia and trichotillomania.
 January 2023 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
January 2023 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Baricitinib helped most teenagers with severe hair loss regrow hair and had mild side effects.

A man wrongly believed he had parasites, showing that delusional infestation can affect men and is often linked with other psychiatric issues, but can be treated with antipsychotics.
 January 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
January 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” The 2015 Hair Research Congress concluded that stem cells, maraviroc, and simvastatin could potentially treat Alopecia Areata, topical minoxidil, finasteride, and steroids could treat Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia, and PTGDR2 antagonists could also treat alopecia. They also found that low-level light therapy could help with hair loss, a robotic device could assist in hair extraction, and nutrition could aid hair growth. They suggested that Alopecia Areata is an inflammatory disorder, not a single disease, indicating a need for personalized treatments.
 4 citations,
March 2023 in “Current Oncology”
4 citations,
March 2023 in “Current Oncology” Scalp cooling is the only FDA-approved method to prevent hair loss from chemotherapy, but other treatments like minoxidil and PRP are being tested.
 9 citations,
January 2020 in “Postepy Dermatologii I Alergologii”
9 citations,
January 2020 in “Postepy Dermatologii I Alergologii” Frontal fibrosing alopecia is a poorly understood condition with increasing cases and unclear treatment effectiveness.
 13 citations,
September 2017 in “Skin appendage disorders”
13 citations,
September 2017 in “Skin appendage disorders” Some women with Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia also have Lichen Planopilaris, which can lead to more symptoms and affect hair outside the scalp.

























