 1 citations,
January 2013 in “International Journal of Trichology”
1 citations,
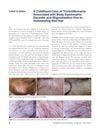
January 2013 in “International Journal of Trichology” A girl with red hair developed hair-pulling and body image disorders after being bullied for her hair color.
 December 2024 in “IntechOpen eBooks”
December 2024 in “IntechOpen eBooks” Trichoscopy helps diagnose and track alopecia areata by examining specific hair and scalp markers.
 February 2024 in “Skin research and technology”
February 2024 in “Skin research and technology” LC-OCT is a promising tool for diagnosing and monitoring Alopecia areata.
 June 2023 in “International journal of pharmaceutical quality assurance”
June 2023 in “International journal of pharmaceutical quality assurance” Videodermoscopy is effective for diagnosing different types of non-scarring hair loss.
 February 2023 in “Journal of vaccines and immunology”
February 2023 in “Journal of vaccines and immunology” Alopecia areata causes sudden hair loss, often on the scalp, and can be severe, especially with early onset or related health issues.
January 2023 in “Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research” Trichoscopic patterns often overlap in scalp disorders, so dermatologists need to stay updated.
 March 2021 in “CRC Press eBooks”
March 2021 in “CRC Press eBooks” The document concludes that different patterns of hair thickness and scalp changes can help diagnose types of non-scarring hair loss.
December 2020 in “Journal of Face Aesthetics” Trichoscopy effectively helps diagnose different types of hair loss in women.
 November 2014 in “Prescriber”
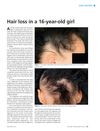
November 2014 in “Prescriber” The 16-year-old girl with hair loss was successfully treated for alopecia areata, leading to significant hair regrowth.
February 2013 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Follicular red dots can appear where alopecia areata and vitiligo overlap.
 January 2012 in “Yearbook of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery”
January 2012 in “Yearbook of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery” Alopecia areata is a hair loss condition that often starts before age 30 and can affect various body parts, with unpredictable hair regrowth chances.
14 citations,
April 2017 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual” Yellow dots are common in severe alopecia areata.
 26 citations,
September 2016 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
26 citations,
September 2016 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Trichoscopy is good for telling apart tinea capitis and alopecia areata in kids.
 42 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
42 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Trichoscopy is a useful tool for diagnosing different hair and scalp diseases without surgery.
 2 citations,
January 2008 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
2 citations,
January 2008 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Trichoscopy is a helpful and quick method to diagnose hair loss without shaving.

Non-invasive methods can effectively diagnose and manage alopecia areata.
 January 2008 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
January 2008 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Trichoscopy is a helpful and quick method to identify different types of hair loss in women.
 178 citations,
December 2011 in “Journal of Dermatological Case Reports”
178 citations,
December 2011 in “Journal of Dermatological Case Reports” Trichoscopy is a useful tool for diagnosing different hair and scalp diseases by their unique visual features.
 13 citations,
June 2012 in “Journal of Dermatological Case Reports”
13 citations,
June 2012 in “Journal of Dermatological Case Reports” An 8-year-old boy with hair-pulling disorder had a bald patch that was confirmed not to be a fungal infection and was treated with therapy.
 12 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
12 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic Clinics” A simplified method was introduced to diagnose most hair loss types by examining the patient's history and scalp, with some cases needing further tests.
 December 2024 in “Australian Journal of General Practice”
December 2024 in “Australian Journal of General Practice” The woman's hair loss pattern doesn't match typical conditions like alopecia areata or female pattern hair loss.
October 2015 in “CRC Press eBooks” Trichoscopy is a useful tool for examining and monitoring hair and scalp conditions.
April 2023 in “Media Dermato Venereologica Indonesiana” COVID-19 reinfection may trigger alopecia areata.
January 2022 in “Skin Appendage Disorders” Areata-like lupus can mimic alopecia areata but is a form of cutaneous lupus erythematosus.
 October 2021 in “International journal of research in dermatology”
October 2021 in “International journal of research in dermatology” No link between scalp patterns and alopecia severity in children, but more severe cases often had nail abnormalities.
 January 2015 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal”
January 2015 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal” The patient's hair loss is most likely due to diffuse alopecia areata.
 3 citations,
January 2021 in “Skin appendage disorders”
3 citations,
January 2021 in “Skin appendage disorders” Hair loss can occur about 4 weeks after scalp surgery but usually grows back within 3 months without treatment.
1 citations,
March 2022 in “Anais brasileiros de dermatologia/Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” Trichoscopy helps tell apart hair loss due to alopecia areata from trichotillomania in eyebrows.
 13 citations,
January 2014 in “Postępy Dermatologii i Alergologii”
13 citations,
January 2014 in “Postępy Dermatologii i Alergologii” Patchy alopecia areata can affect only pigmented hairs, leaving gray hairs untouched.
 5 citations,
November 2012 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
5 citations,
November 2012 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” Comma hairs are a new sign for identifying scalp fungal infections.






















