 9 citations,
March 2011 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology”
9 citations,
March 2011 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology” The document concludes that anticonvulsants like phenytoin may cause skin reactions by affecting tryptophan metabolism and suggests researching vitamin levels in patients with drug reactions.
 March 2005 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
March 2005 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Two cosmetic lotions used day and night may be a good alternative to minoxidil for hair loss treatment with better cosmetic effects and tolerance.
 March 2005 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
March 2005 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The two lotions used day and night may be a good alternative to minoxidil for hair loss treatment with better cosmetic effects and tolerance.
 March 2005 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
March 2005 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Two cosmetic lotions improved hair growth and had better cosmetic effects than 2% minoxidil.
2 citations,
September 2019 in “Neurology Neuroimmunology & Neuroinflammation” IVIg treatment improved symptoms but caused permanent dark hair loss.
 1 citations,
January 2020 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal”
1 citations,
January 2020 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal” Pigtail hair is a sign of new hair growth and should be recognized in hair loss conditions like acute telogen effluvium.
 May 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine”
May 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” New understanding and treatments for hair loss are improving, but more research is needed.
 3 citations,
August 2020 in “PubMed”
3 citations,
August 2020 in “PubMed” Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is effective in treating various skin conditions and improving hair density, thickness, and patient satisfaction, with lower relapse rates for Alopecia Areata.
 1 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical research in dermatology”
1 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical research in dermatology” Hair loss, known as Androgenetic Alopecia, is often caused by hormones and can be diagnosed using noninvasive techniques. Treatments include topical minoxidil and oral finasteride, with new treatments being explored. There may also be a link between this type of hair loss and heart disease risk.
 December 2024 in “Journal of Skin and Stem Cell”
December 2024 in “Journal of Skin and Stem Cell” Trichoscopy helps diagnose and manage different types of hair loss in the Indian population.

New treatments for hair loss should target eight main causes and use specific plant compounds and peptides for better results.
 December 2020 in “Our Dermatology Online”
December 2020 in “Our Dermatology Online” Skin biopsies are recommended for confirming alopecia diagnosis due to variability in clinical assessments; the link between vitamin D levels and alopecia is unclear.
 42 citations,
January 2008 in “Dermatology”
42 citations,
January 2008 in “Dermatology” Dermoscopy effectively distinguishes between acute total hair loss and other types of female hair loss.
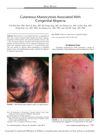 3 citations,
February 2012 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
3 citations,
February 2012 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” A 3-year-old girl with skin mast cell buildup and congenital baldness improved with treatment, suggesting a rare link between these conditions.
 October 2023 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual”
October 2023 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual” Many patients experienced hair loss after COVID-19, with women affected more, starting on average 49 days post-infection.
 196 citations,
June 2008 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
196 citations,
June 2008 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Dermoscopy helps diagnose and manage alopecia areata by showing specific hair changes.
 29 citations,
December 2017 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
29 citations,
December 2017 in “International Journal of Dermatology” People with alopecia areata often have lower vitamin D levels, which are linked to more severe and longer-lasting hair loss, but vitamin D receptor levels in the skin don't show the same pattern and don't predict treatment success.
 20 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
20 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Researchers created a fast, accurate computer program to measure hair loss in alopecia areata patients.
 July 2023 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine ”
July 2023 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine ” Alopecia areata is a hair loss condition caused by immune factors and can be treated with JAK inhibitors.
 5 citations,
October 2012 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
5 citations,
October 2012 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Trichoscopy is a useful tool for diagnosing hair and scalp diseases without needing skin biopsies.
10 citations,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Trichology” Mesalazine may help treat extensive alopecia areata effectively.
 November 2023 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
November 2023 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Trichoscopy helps tell apart other hair loss conditions from common hair loss.
Accurate diagnosis of hair loss types is crucial for effective treatment.
4 citations,
January 2018 in “Indian dermatology online journal” Trichoscopy helped diagnose and cure a child's hair loss caused by a fungal infection.
 June 2023 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
June 2023 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” A woman's rare hair loss condition improved on its own, suggesting this type might recover like common cases.
 60 citations,
January 1987 in “Dermatology”
60 citations,
January 1987 in “Dermatology” Alopecia areata may appear differently depending on the individual's type of hair loss and scalp condition.
 March 2024 in “Case Reports in Dermatology”
March 2024 in “Case Reports in Dermatology” A woman's hair loss was misdiagnosed as alopecia areata but was actually lichen planopilaris, needing immediate and ongoing treatment.
 66 citations,
December 2018 in “Dermatology”
66 citations,
December 2018 in “Dermatology” Both ruxolitinib and tofacitinib are effective and safe for treating severe alopecia areata, but relapses are common.
 47 citations,
September 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
47 citations,
September 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Ludwig pattern hair loss in women results from varying sensitivity in hair follicles, causing fewer visible hairs.
 35 citations,
November 2010 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
35 citations,
November 2010 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” Dilated follicular infundibula and increased catagen/telogen follicles are key indicators for diagnosing alopecia areata.

























