 1 citations,
March 2024 in “BioDrugs”
1 citations,
March 2024 in “BioDrugs” Biologics for severe asthma have known side effects, but some new risks need more study.
 1 citations,
October 2023
1 citations,
October 2023 Syntax-based neural networks can match Transformers in handling unseen sentences.
 1 citations,
April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Patients with autoimmune blistering diseases experience a reduced quality of life, with the need for better measurement tools, especially for those with mucous membrane pemphigoid.
 1 citations,
September 2017 in “Textual Practice”
1 citations,
September 2017 in “Textual Practice” The document concludes that Hilary Mantel's memoir shows how childhood experiences affect adult health, criticizing modern medicine for ignoring the mental aspects of physical illness.
 1 citations,
June 2017 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
1 citations,
June 2017 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) is a hair transplant method with less scarring and discomfort but requires skilled surgeons and has limitations on graft numbers per session.
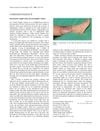 1 citations,
May 2002 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
May 2002 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss caused by longer latent hair cycle and sudden miniaturization, not gradual follicle size reduction.
 1 citations,
November 1995 in “Postgraduate medical journal”
1 citations,
November 1995 in “Postgraduate medical journal” A Saudi individual initially identified as a girl had a genetic disorder affecting gender development.
 March 2024 in “World Journal Of Advanced Research and Reviews”
March 2024 in “World Journal Of Advanced Research and Reviews” Educators who survived COVID-19 faced physical, psychological, and social challenges but overcame them with resilience and support, highlighting the need for schools to provide better health and psychological care.
 March 2024 in “Journal of medicinal plants studies”
March 2024 in “Journal of medicinal plants studies” Hibiscus has medicinal benefits but can be toxic in high doses and is unsafe for pregnant women and infants.

Black hair's diversity in patterns and textures is influenced by follicle shape and keratin, and it holds cultural, artistic, and mathematical significance.

Pre-trained Transformers need extreme retraining to perform well on DarkNet data.
 January 2021 in “Middle East journal of applied sciences”
January 2021 in “Middle East journal of applied sciences” Zinc is essential for plant growth and human health, but many soils lack enough zinc, affecting crops and potentially leading to health problems.
 April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The research found that certain characteristics like age, sex, race, marital status, and education level can influence whether alopecia patients stick to their hair loss treatment with topical minoxidil.
 July 2018 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
July 2018 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Mindfulness reduces anxiety and depression in skin disease patients; dermatologists and psychiatrists often lack confidence in treating psychodermatological conditions.
 January 2017 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2017 in “Elsevier eBooks” The document concludes that choosing the right forehead and brow lifting technique based on individual patient characteristics is crucial to prevent complications and achieve desired results.
 May 2002 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
May 2002 in “British Journal of Dermatology” A pregnant woman's skin condition improved after giving birth, possibly due to high estrogen levels during pregnancy.
 May 2002 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
May 2002 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss caused by longer latent hair cycle and sudden miniaturization, not gradual follicle size reduction.
 855 citations,
June 2009 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism”
855 citations,
June 2009 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism” The guideline recommends mental health involvement in diagnosing gender identity disorder and outlines hormone and surgical treatment protocols, emphasizing safety, informed consent, and long-term monitoring.
 359 citations,
September 2017 in “European Journal of Epidemiology”
359 citations,
September 2017 in “European Journal of Epidemiology” The Rotterdam Study updated findings on elderly health, focusing on heart disease, genetics, lifestyle effects, and disease understanding.
 336 citations,
August 2015 in “European Journal of Epidemiology”
336 citations,
August 2015 in “European Journal of Epidemiology” The Rotterdam Study found risk factors for elderly diseases, links between lifestyle and genetics with health conditions, and aimed to explore new areas like DNA methylation and sensory input effects on brain function.
 266 citations,
November 2013 in “European Journal of Epidemiology”
266 citations,
November 2013 in “European Journal of Epidemiology” The Rotterdam Study aims to understand disease causes in the elderly and has found new risk factors and genetic influences on various conditions.
 247 citations,
August 2011 in “European Journal of Epidemiology”
247 citations,
August 2011 in “European Journal of Epidemiology” The Rotterdam Study updated its design and objectives in 2012, providing insights into various diseases in the elderly, including skin cancer, bone health, liver disease, neurological and psychiatric conditions, and respiratory issues.
 237 citations,
January 2010 in “The Journal of Sexual Medicine”
237 citations,
January 2010 in “The Journal of Sexual Medicine” The report recommends personalized treatment for women's sexual dysfunctions and more research on effective therapies.
 219 citations,
September 2009 in “European journal of epidemiology”
219 citations,
September 2009 in “European journal of epidemiology” The Rotterdam Study aims to understand various diseases in older adults.
 212 citations,
September 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
212 citations,
September 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The document provides a method to classify human hair growth stages using a model with human scalp on mice, aiming to standardize hair research.
 205 citations,
July 2009 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
205 citations,
July 2009 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Male and female skin differ in many ways, which could lead to gender-specific skin treatments.
 193 citations,
January 2015 in “International journal of trichology”
193 citations,
January 2015 in “International journal of trichology” Dermatologists need to understand hair products to treat hair and scalp issues better.
 177 citations,
July 2004 in “The Journal of Sexual Medicine”
177 citations,
July 2004 in “The Journal of Sexual Medicine” Experts recommend thorough medical, sexual, and psychosocial assessments for women's sexual dysfunctions, and suggest individualized treatment plans with regular check-ups. They also mention potential use of estrogen and androgen therapy, but with caution due to safety concerns.
 170 citations,
September 2019 in “Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine”
170 citations,
September 2019 in “Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine” Some medicinal plants can help heal wounds and may lead to new treatments.
 162 citations,
April 2016 in “The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology”
162 citations,
April 2016 in “The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology” Testosterone therapy in transgender men has both desired effects like increased muscle mass and potential health risks such as higher cardiovascular risk.






























