 3 citations,
December 2022 in “Cells”
3 citations,
December 2022 in “Cells” Cannabinoids like CBD and THC may help treat non-cancer skin diseases, but more research is needed.
 December 2022 in “BMC women's health”
December 2022 in “BMC women's health” The CNC® prosthetic system improved body image in breast cancer patients with hair loss from chemotherapy but did not significantly change their psychological wellbeing.
 5 citations,
October 2018 in “Research in psychotherapy”
5 citations,
October 2018 in “Research in psychotherapy” The Italian version of a relationship scale was adapted for cancer patients, showing some differences from the original and suggesting its use could improve therapy and treatment adherence.
 August 2024 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
August 2024 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Using 5-alpha reductase inhibitors may lower the risk of breast cancer in females.
 36 citations,
May 2017 in “The journal of sexual medicine”
36 citations,
May 2017 in “The journal of sexual medicine” Cyproterone acetate treatment is safe and causes mild feminization, which increases with added estrogen.
 25 citations,
August 2006 in “Human Reproduction”
25 citations,
August 2006 in “Human Reproduction” Oral contraceptives lower testosterone levels in women, especially those with certain genetic traits, and may be linked to increased breast cancer risk.
 11 citations,
February 2016 in “Current Medicinal Chemistry”
11 citations,
February 2016 in “Current Medicinal Chemistry” New treatments for prostate cancer and BPH show promise, including novel compounds that target hormone synthesis and response.
 April 2024 in “Dermatovenerologiâ, kosmetologiâ”
April 2024 in “Dermatovenerologiâ, kosmetologiâ” Actinic keratosis is a sun-induced skin condition that can potentially turn into skin cancer and requires treatment to prevent malignancy.
 2 citations,
March 2005 in “Cancer biology & therapy”
2 citations,
March 2005 in “Cancer biology & therapy” Bexxar treatment led to a high response rate in patients with advanced-stage, treatment-resistant follicular lymphoma.
 January 2023 in “Applied sciences”
January 2023 in “Applied sciences” Gefitinib and Sasam-Kyeongokgo together significantly reduce cancer growth and improve immune response in mice.
 38 citations,
July 1998 in “Journal of surgical oncology”
38 citations,
July 1998 in “Journal of surgical oncology” A woman with breast cancer developed a rare condition causing excessive fine hair growth on her face and body.
12 citations,
December 2010 in “Journal of thoracic oncology” New treatments for non-small cell lung cancer are being tested, with some already in use, focusing on immune response and targeting cancer cells, but side effects vary.
 3 citations,
June 2011 in “Korean Journal of Clinical Oncology”
3 citations,
June 2011 in “Korean Journal of Clinical Oncology” The document concluded that there were no effective ways to prevent hair loss from chemotherapy but treatments were being explored.
 15 citations,
May 1966 in “The Journal of Urology”
15 citations,
May 1966 in “The Journal of Urology” A woman developed severe bladder inflammation after cancer treatment with Cytoxan.
3 citations,
August 2017 in “Springer eBooks” The document explains breast development, common breast conditions, and their treatments.
 April 2024 in “Dermatovenerologiâ, kosmetologiâ”
April 2024 in “Dermatovenerologiâ, kosmetologiâ” Actinic keratosis is a sun-induced skin condition that can potentially turn into skin cancer and requires various treatments to prevent this.
 March 2024 in “BMC cancer”
March 2024 in “BMC cancer” High levels of ST14 and TMEFF1 proteins in ovarian cancer are linked to worse patient outcomes and may be a new treatment target.
 81 citations,
February 2000 in “Anti-cancer drugs”
81 citations,
February 2000 in “Anti-cancer drugs” Doxil showed some effectiveness against advanced prostate cancer but caused severe side effects at higher doses.
 61 citations,
May 2010 in “Integrative Cancer Therapies”
61 citations,
May 2010 in “Integrative Cancer Therapies” There is no clear recommendation for using selenium in cancer patients; it may be beneficial to correct low selenium levels before treatment.
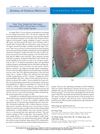 35 citations,
May 2008 in “Journal of Clinical Oncology”
35 citations,
May 2008 in “Journal of Clinical Oncology” A cancer patient died from a severe skin reaction after taking the drug cetuximab.
 20 citations,
March 2005 in “Current Medicinal Chemistry”
20 citations,
March 2005 in “Current Medicinal Chemistry” New compounds show promise for treating hair loss, enlarged prostate, and prostate cancer, with some being more effective and having different side effects than current treatments.
 3 citations,
July 2014 in “Indian Journal of Surgery”
3 citations,
July 2014 in “Indian Journal of Surgery” Sex hormones might influence bladder cancer development, and aromatase inhibitors could increase risk in postmenopausal women.
 113 citations,
July 2020 in “Communications biology”
113 citations,
July 2020 in “Communications biology” Men, especially older ones with health issues like prostate cancer, may have worse COVID-19 outcomes and could benefit from therapies targeting male hormones.
 88 citations,
July 2014 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
88 citations,
July 2014 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Targeted cancer therapies often cause skin reactions, so dermatologists must manage these effects.
 13 citations,
January 2017 in “Molecules”
13 citations,
January 2017 in “Molecules” Compounds from Alpinia zerumbet may help with hair regrowth and cancer treatment by targeting PAK1.
 4 citations,
August 2018 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
4 citations,
August 2018 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” There is an urgent need for better treatments for hair loss caused by chemotherapy.
 2 citations,
July 1998 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
2 citations,
July 1998 in “Dermatologic Clinics” European dermatologic treatments focus on lifestyle and psychosocial factors, use diverse methods like baths and climate therapy, and emphasize the importance of diet and supplements for skin health.

Hair follicles can be used to quickly assess drug effects in cancer treatment.
 141 citations,
August 2018 in “Nature Reviews Microbiology”
141 citations,
August 2018 in “Nature Reviews Microbiology” Some viruses can cause cancer by changing cell processes and avoiding the immune system; vaccines and targeted treatments help reduce these cancers.
 114 citations,
March 2002 in “Current opinion in oncology/Current opinion in oncology, with cancerlit”
114 citations,
March 2002 in “Current opinion in oncology/Current opinion in oncology, with cancerlit” Cancer therapy can cause various skin problems, including hair loss, skin darkening, painful hand-foot syndrome, and severe skin damage.




























