 November 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
November 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Most Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa patients with a specific mutation likely have Sephardic ancestry from about 500 years ago.
11 citations,
December 2013 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology” A child with skin and heart issues had rare genetic mutations affecting skin and heart cell cohesion.
14 citations,
May 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” A rare gene mutation causes skin fragility and itching without affecting hair or nails.
 8 citations,
December 2009 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
8 citations,
December 2009 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Researchers found a new mutation in the FERMT1 gene in a Spanish family with Kindler syndrome.
 9 citations,
March 2012 in “Experimental dermatology”
9 citations,
March 2012 in “Experimental dermatology” Natural gene therapy shows promise for treating skin disorders like epidermolysis bullosa.
 16 citations,
October 2014 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
16 citations,
October 2014 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Oral retinoids may help some patients with hard-to-treat lichen planopilaris, but more research is needed.
May 2020 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” BIVV009 is a safe treatment for bullous pemphigoid that reduces C3 deposition without harmful side effects.
 May 2012 in “Nature Genetics”
May 2012 in “Nature Genetics” Blond hair in Solomon Islanders is due to a unique genetic variant, not European ancestry.
 3 citations,
July 1997 in “The Lancet”
3 citations,
July 1997 in “The Lancet” Finasteride may increase hair growth and prevent baldness in men, but can cause sexual side effects.
 1 citations,
July 1997 in “The Lancet”
1 citations,
July 1997 in “The Lancet” Scientists found a new protein, AMY117, common in Alzheimer's patients, which could be important for treatment and diagnosis.
 July 1997 in “The Lancet”
July 1997 in “The Lancet” A new protein linked to Alzheimer's was discovered, and a hair loss treatment showed effectiveness but had some sexual side effects.
 July 1997 in “The Lancet”
July 1997 in “The Lancet” Finasteride increased hair count and regrowth in men with hair loss but also caused more sexual side effects than placebo.
 October 2023 in “Pediatric dermatology”
October 2023 in “Pediatric dermatology” Middle Eastern patients with epidermolysis bullosa show specific genetic mutations linked to different types of the disease.
June 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Plucked hair can help diagnose pemphigus vulgaris early.
 4 citations,
April 1999 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
4 citations,
April 1999 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Long-pulsed ruby lasers effectively reduce hair for up to 2 years with minimal pain.
 20 citations,
December 2003 in “Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy”
20 citations,
December 2003 in “Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy” An 800nm diode laser safely and effectively reduces hair for about 8 months, with most patients satisfied and few side effects.
24 citations,
September 2011 in “Autoimmunity” Natural killer cells play a key role in autoimmune skin diseases like pemphigus vulgaris.
11 citations,
March 2012 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Most patients with dark skin were satisfied with laser hair removal and had few complications.
294 citations,
August 1999 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Laser hair removal is safe with the right settings, but side effects like pain and skin changes are more common in darker or tanned skin.
 4 citations,
November 2012 in “Dermatitis”
4 citations,
November 2012 in “Dermatitis” A man got severe skin irritation after using marking nut sap for hair loss.
 September 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
September 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Scientists used stem cells to create a model of the skin disease Epidermolysis Bullosa simplex, which helped them understand its molecular mechanisms and could aid in finding treatments.
 8 citations,
September 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
8 citations,
September 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Some diets and supplements might help with skin disorders, but their effectiveness varies and more research is needed.
52 citations,
June 1998 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Ruby laser treatment is effective and well-tolerated for reducing hair growth.
 7 citations,
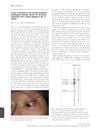
February 2010 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
February 2010 in “British Journal of Dermatology” A woman with a rare autoimmune disorder had a blister on her eye and unique immune reaction, which was effectively treated with medication.
1 citations,
September 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Anti-Desmocollin 3 antibodies can cause pemphigus-like symptoms in mice.
 19 citations,
October 2008 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
19 citations,
October 2008 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Anti-cancer treatments can cause reversible hair loss, skin sensitivity, pigmentation changes, nail damage, and skin reactions, with a need for more research on managing these side effects.
 3 citations,
May 2011 in “Practice nursing”
3 citations,
May 2011 in “Practice nursing” As skin ages, it gets thinner, paler, and more wrinkled, and protection and care like sunblock and moisturizers are important.
 May 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
May 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology” The 1891 epidemic skin disease was likely caused by arsenic poisoning, possibly from beer or fish.
 31 citations,
April 2019 in “Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine”
31 citations,
April 2019 in “Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine” β-blockers can cause skin problems like psoriasis and vitiligo, and doctors should tell patients about these risks.
 14 citations,
May 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology”
14 citations,
May 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology” Fat tissue extract may help treat vitiligo by reducing cell stress and promoting skin repair.




















