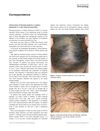
signaling protein that, when suppressed, may grow hair by reducing inflammation and stem cell loss
An essential vasodilator with some anti-androgenic effects, has excellent safety record
a synthetic cortisol used for anti-inflammatory effects
glycoprotein that inhibits TGF-β and promotes hair growth by antagonizing activin
much-hyped research compound targeting prolactin receptor in scalp