7 citations,
January 2017 in “Neuromuscular Disorders” A rare autoimmune condition, Satoyoshi syndrome, can start in adults and improve with immunosuppressive treatment.
 14 citations,
August 2006 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
14 citations,
August 2006 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” A girl with no hair neglect developed plica neuropathica in the hospital, lost all her hair, but it grew back.
 September 1997 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
September 1997 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Alopecia linked to higher anxiety and personality disorders.
 64 citations,
March 2017 in “Nature communications”
64 citations,
March 2017 in “Nature communications” Researchers found 63 genes linked to male-pattern baldness, which could help in understanding its biology and developing new treatments.
 31 citations,
April 2010 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
31 citations,
April 2010 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Frontal fibrosing alopecia can cause sudden hair loss on limbs, similar to scalp hair loss.
September 2013 in “Canadian Medical Association Journal” Alopecia areata causes sudden hair loss, often resolves within a year, but can recur.
 4 citations,
March 1989 in “The BMJ”
4 citations,
March 1989 in “The BMJ” Naproxen is not the cause of hair loss in a child; it's due to a toxic event with expected hair regrowth.
 30 citations,
March 2010 in “European Journal of Dermatology”
30 citations,
March 2010 in “European Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss in elderly women is often caused by various factors, including hormonal changes after menopause.
 12 citations,
May 1989 in “Postgraduate Medicine”
12 citations,
May 1989 in “Postgraduate Medicine” The document concludes that hair loss is common and can be treated with medications like minoxidil or surgical options, and it significantly affects people's psychological well-being.
 48 citations,
March 1997 in “Veterinary Dermatology”
48 citations,
March 1997 in “Veterinary Dermatology” Some cats with sudden hair loss and tiredness might have cancer-related alopecia.
 December 2023 in “EPRA international journal of multidisciplinary research”
December 2023 in “EPRA international journal of multidisciplinary research” Alopecia areata causes sudden hair loss, has genetic links, and can be managed but not cured.
 1 citations,
March 2010 in “Internal medicine journal”
1 citations,
March 2010 in “Internal medicine journal” A 72-year-old man with sudden taste issues and hair growth was diagnosed with a severe stomach cancer and died within 5 months.

The patient with total hair loss did not regrow hair despite treatment, indicating a poor outlook for this type of hair loss.
 124 citations,
August 1994 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
124 citations,
August 1994 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Dexamethasone speeds up hair loss in mice, while cyclosporin A slows it down.
 24 citations,
March 1995 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
24 citations,
March 1995 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Etretinate therapy can cause hair loss by disrupting the hair growth cycle.
 13 citations,
November 2015 in “Blood Pressure”
13 citations,
November 2015 in “Blood Pressure” Hair loss may indicate higher heart risk and metabolic issues.
 14 citations,
April 2021 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
14 citations,
April 2021 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” COVID-19 may trigger sudden temporary hair loss.
 109 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
109 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Alopecia areata is a type of hair loss that can lead to complete baldness, often associated with other autoimmune conditions, and half of the cases may see hair return within a year.
 14 citations,
February 2021 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
14 citations,
February 2021 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” A COVID-19 patient with severe hair loss did not improve with hair loss medication after stopping and restarting it due to the infection.
 45 citations,
January 1992 in “Dermatology”
45 citations,
January 1992 in “Dermatology” Half of the patients treated with a specific drug for skin cancer experienced hair loss not related to the drug's dosage.
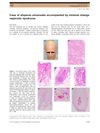 2 citations,
August 2015 in “Journal of dermatology”
2 citations,
August 2015 in “Journal of dermatology” A possible link exists between minimal change nephrotic syndrome and complete hair loss.
 January 2016 in “Journal of The Korean Medical Association”
January 2016 in “Journal of The Korean Medical Association” The document says how to diagnose and treat hair loss from alopecia areata, but there's no cure and treatments vary.
 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Alopecia areata is a common autoimmune condition causing varying hair loss, diagnosed by specific patterns of inflammation around hair follicles, with several treatment options available.
 48 citations,
May 1999 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
48 citations,
May 1999 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Alopecia areata is an unpredictable autoimmune hair loss condition, treated based on severity, with half of patients regrowing hair within a year without treatment.
 8 citations,
August 2016 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
8 citations,
August 2016 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Timolol eye-drops can cause hair loss.
 5 citations,
April 2002 in “The American Journal of Medicine”
5 citations,
April 2002 in “The American Journal of Medicine” Hair loss can be an early sign of HIV infection.
 1 citations,
January 2001 in “American Journal of Kidney Diseases”
1 citations,
January 2001 in “American Journal of Kidney Diseases” Hair loss in three Southeast Asian women with kidney failure may be linked to their anemia treatment with erythropoietin.
 1 citations,
July 2014 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
July 2014 in “International Journal of Dermatology” A cancer patient developed a type of hair loss after starting a cancer drug called vandetanib.
 5 citations,
February 2014 in “PubMed”
5 citations,
February 2014 in “PubMed” Hair loss in Telogen effluvium is often chronic, linked to stress, and lacks a confirmed treatment, but topical corticosteroids may be used.
 16 citations,
April 2011 in “Recent Patents on Inflammation & Allergy Drug Discovery”
16 citations,
April 2011 in “Recent Patents on Inflammation & Allergy Drug Discovery” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune disease causing hair loss in patches, often starting before age 20, and while some cases recover on their own, treatments include topical corticosteroids, minoxidil, and promising new methods like IL-31 antibodies and 308-nm Excimer laser therapy.



























