 October 2022 in “Journal for Research in Applied Sciences and Biotechnology”
October 2022 in “Journal for Research in Applied Sciences and Biotechnology” Certain changes in the SHBG gene may increase the risk of PCOS in Iraqi women.
The balance between cell renewal and differentiation controls the growth of cancerous cells in mouse skin.
578 citations,
April 1993 in “Cell” TGFα gene mutation in mice causes abnormal skin, wavy hair, curly whiskers, and sometimes eye inflammation.
 56 citations,
March 2015 in “Cell death and differentiation”
56 citations,
March 2015 in “Cell death and differentiation” Older skin has higher cancer risk due to inflammation and stem cell issues.
44 citations,
August 2008 in “Plant journal” D'orenone stops root hair growth by disrupting auxin transport, but adding auxin can reverse this.
14 citations,
April 2013 in “Journal of dermatological science” Hairless protein reduces Msx2 gene activity, affecting hair follicle development.
 November 2023 in “Journal of plant nutrition and soil science”
November 2023 in “Journal of plant nutrition and soil science” Boron deficiency in maize affects leaf boron levels and nutrient uptake differently depending on root hair presence and soil type.
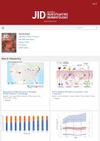 November 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
November 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Neutrophils quickly respond to skin injury.
 December 2021 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
December 2021 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Neutrophils quickly move to the site of skin injury.
12 citations,
July 2004 in “Molecular genetics and genomics” A new mouse mutation causes skin and hair defects due to a gene change.
 277 citations,
July 2002 in “Molecular Endocrinology”
277 citations,
July 2002 in “Molecular Endocrinology” Removing part of the vitamin D receptor stops vitamin D from working properly.
 48 citations,
March 2022 in “Nano Letters”
48 citations,
March 2022 in “Nano Letters” The document explains how to make antibacterial microneedles inspired by lamprey teeth to help heal infected wounds.
 September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” The protein aPKCλ is crucial for keeping hair follicle stem cells inactive and for hair growth and regeneration.
50 citations,
February 2004 in “Genomics” A gene mutation causes lanceolate hair in rats by disrupting hair shaft integrity.
36 citations,
March 2014 in “Cell death and differentiation” Disrupting β-catenin signaling in certain cells causes anorectal malformations.
May 2014 in “The journal of immunology/The Journal of immunology” Early over-expression of FoxN1 harms immune and skin development.
 195 citations,
April 2005 in “Journal of biological chemistry/The Journal of biological chemistry”
195 citations,
April 2005 in “Journal of biological chemistry/The Journal of biological chemistry” The ZIP7 gene helps control zinc levels in cells by moving zinc from the Golgi apparatus to the cytoplasm.
 165 citations,
September 2001 in “Genes & development”
165 citations,
September 2001 in “Genes & development” CDP is crucial for lung and hair follicle cell development.
37 citations,
February 2010 in “Psychoneuroendocrinology” Androgen self-administration might be controlled by membrane receptors, not nuclear ones.
37 citations,
June 2000 in “Experimental dermatology” The Lanceolate hair-J mutation in mice mimics human hair disorders like Netherton's syndrome.
36 citations,
October 2015 in “Cell reports” Gab1 protein is crucial for hair growth and stem cell renewal, and Mapk signaling helps maintain these processes.
 31 citations,
July 2004 in “Molecular Medicine”
31 citations,
July 2004 in “Molecular Medicine” Certain defective glucocorticoid receptor mutants move faster inside cell nuclei and work less effectively.
 30 citations,
October 2014 in “PLOS ONE”
30 citations,
October 2014 in “PLOS ONE” BAF200 is essential for proper heart and coronary artery formation.
29 citations,
October 2019 in “Journal of dermatological science” Studying premature aging syndromes helps understand human aging and suggests potential treatments.
 28 citations,
December 2008 in “Laboratory investigation”
28 citations,
December 2008 in “Laboratory investigation” Activin activation in skin cells speeds up wound healing without affecting scar quality.
 25 citations,
June 2022 in “Developmental cell”
25 citations,
June 2022 in “Developmental cell” Overactivating Hedgehog signaling makes hair follicle cells in mice grow hair faster and create more follicles.
22 citations,
December 2015 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” A mouse gene mutation increases the risk of skin cancer.
12 citations,
December 2011 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” The C-terminal tail of AHF/trichohyalin is essential for organizing keratin filaments in keratinocytes.
 11 citations,
January 2012 in “Journal of cell science”
11 citations,
January 2012 in “Journal of cell science” Rac1 is essential for proper hair structure and color.
9 citations,
May 2002 in “PubMed” Retinoic acid affects skin and hair health by working with specific receptors, and its absence can lead to hair loss and skin changes.















