 53 citations,
August 2019 in “American journal of human genetics”
53 citations,
August 2019 in “American journal of human genetics” FOXN1 gene variants cause low T cells and immune issues from birth.
 3 citations,
May 2020 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
3 citations,
May 2020 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” The unique coat of lykoi cats is likely caused by new variants in the Hairless gene.
[object Object]  7 citations,
May 2019 in “European Journal of Human Genetics”
7 citations,
May 2019 in “European Journal of Human Genetics” BMP4-related anomalies can cause a wide range of eye, brain, and hand/foot problems, and new cases show this variability.
 December 2021 in “Molecular genetics and genomics”
December 2021 in “Molecular genetics and genomics” Cats with abnormal hair had DSG4 gene changes causing hair problems.
 3 citations,
January 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
3 citations,
January 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Different types of atopic dermatitis were linked to specific genetic and immune changes, suggesting that severe cases might need stronger immune-targeting treatments.
 336 citations,
August 2015 in “European Journal of Epidemiology”
336 citations,
August 2015 in “European Journal of Epidemiology” The Rotterdam Study found risk factors for elderly diseases, links between lifestyle and genetics with health conditions, and aimed to explore new areas like DNA methylation and sensory input effects on brain function.
 3 citations,
November 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
3 citations,
November 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The document suggests that more research is needed to confirm if baldness can indicate a higher risk of severe COVID-19 in men.
 11 citations,
March 2020 in “American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A”
11 citations,
March 2020 in “American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A” A mutation in the EDNRA gene causes Oro-Oto-Cardiac syndrome, affecting face and heart development.
9 citations,
July 2016 in “Genes” Genetic variants in PDE6H and LPAR6 cause vision impairment and hair loss in two Pakistani brothers.
 156 citations,
August 2016 in “Journal of controlled release”
156 citations,
August 2016 in “Journal of controlled release” Tight junctions are key for skin protection and controlling what gets absorbed or passes through the skin.
 9 citations,
February 2022 in “Nature communications”
9 citations,
February 2022 in “Nature communications” Rare changes in the KRT82 gene are linked to a higher risk of Alopecia Areata.
 40 citations,
January 2017 in “Intestinal Research”
40 citations,
January 2017 in “Intestinal Research” Genotyping for NUDT15 p.Arg139Cys can help predict thiopurine side effects in Japanese IBD patients.
122 citations,
April 2020 in “American Journal Of Pathology” Skin aging is a complex process influenced by various factors, leading to wrinkles and sagging, and should be considered a disease due to its health impacts.
 23 citations,
December 2017 in “Scientific Reports”
23 citations,
December 2017 in “Scientific Reports” ARL15 is important for fat cell development and the release of the hormone adiponectin.
1 citations,
May 2023 in “Frontiers in Pharmacology” Genetic screening for NUDT15 polymorphisms is crucial for patients taking azathioprine, especially in Asians.
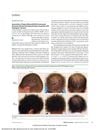 5 citations,
July 2020 in “JAMA Dermatology”
5 citations,
July 2020 in “JAMA Dermatology” Minoxidil solution applied twice daily improved hair growth in patients with Woolly Hair/Hypotrichosis due to LIPH gene issues, with mild side effects.
 25 citations,
March 2012 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
25 citations,
March 2012 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Genetic variants linked to ten skin diseases were found, showing both immune and non-immune factors play a role.
 14 citations,
April 2021 in “Biology”
14 citations,
April 2021 in “Biology” Thai rice bran extracts, especially from Tubtim Chumphae rice, can significantly reduce the activity of hair loss genes, with x-tocopherol showing potential as an anti-hair loss product.
 5 citations,
August 2019 in “iScience”
5 citations,
August 2019 in “iScience” Deleting the Trf1 protein in mice is safe and may help prevent cancer without major side effects.
 December 2023 in “American journal of medical genetics. Part A”
December 2023 in “American journal of medical genetics. Part A” A new syndrome was linked to two new genetic changes in the MBTPS1 gene in a 14-year-old girl.
 25 citations,
June 2019 in “Endocrine Related Cancer”
25 citations,
June 2019 in “Endocrine Related Cancer” Mutations in certain receptors can cause diseases and offer new treatment options.
 February 2022 in “International journal of KIU”
February 2022 in “International journal of KIU” Certain genes and nutrients like vitamin D, zinc, and omega fatty acids affect COVID-19 severity and infection risk.
 10 citations,
November 2018 in “Genetics in medicine”
10 citations,
November 2018 in “Genetics in medicine” Lack of cystatin M/E causes thin hair and dry skin.
 January 2023 in “Revista Paulista de Pediatria”
January 2023 in “Revista Paulista de Pediatria” A Brazilian male with IFAP syndrome has a unique genetic variant causing his condition.
 January 2023 in “Acta dermatovenerologica Alpina, Pannonica et Adriatica (Tiskana izd.)”
January 2023 in “Acta dermatovenerologica Alpina, Pannonica et Adriatica (Tiskana izd.)” The article concludes that schoolchildren and adolescents experienced various skin issues during the COVID-19 pandemic, including acne from masks and other skin reactions from the virus and vaccines.
 August 2022 in “Frontiers in genetics”
August 2022 in “Frontiers in genetics” A new genetic change in the DSC3 gene is linked to a rare condition causing hair loss and skin blisters in a child.
[object Object]  2 citations,
January 2019 in “Medizinische Genetik”
2 citations,
January 2019 in “Medizinische Genetik” The document reports findings on genetic research, including ethical concerns about genome editing, improved diagnosis of mitochondrial mutations, solving inherited eye diseases, confirming gene roles in epilepsy, linking a gene to aneurysms, and identifying genes associated with age-related macular degeneration.
 93 citations,
April 2012 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science”
93 citations,
April 2012 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” Improving skin barrier and using antifungal treatments can help manage dandruff.
 1 citations,
May 2023 in “European Journal of Human Genetics”
1 citations,
May 2023 in “European Journal of Human Genetics” Rare ULBP3 gene changes may raise the risk of Alopecia areata, a certain FAS gene deletion could cause a dysfunctional protein in an immune disorder, and having one copy of a specific genetic deletion is okay, but two copies cause sickle cell disease.
 144 citations,
March 2013 in “Circulation Research”
144 citations,
March 2013 in “Circulation Research” K_ATP channel gene mutations are linked to heart diseases, but more research is needed to understand the connection and treatment potential.



























