 2 citations,
October 2017 in “Revista Da Associacao Medica Brasileira”
2 citations,
October 2017 in “Revista Da Associacao Medica Brasileira” Removing p16INK4a from skin cells can lead to faster and more clumped growth, which might help with hair growth.
 109 citations,
September 2011 in “Human molecular genetics online/Human molecular genetics”
109 citations,
September 2011 in “Human molecular genetics online/Human molecular genetics” New treatments targeting specific genes show promise for treating keratin disorders.
 84 citations,
June 2010 in “The Plant Cell”
84 citations,
June 2010 in “The Plant Cell” Phospholipase A2 is necessary for the correct placement of PIN proteins in plant roots, affecting root growth.
[object Object]  3 citations,
September 1980 in “Experientia”
3 citations,
September 1980 in “Experientia” Dobutamine does not mimic dopamine at therapeutic doses but may at very high concentrations; microfilaments, not microtubules, are important for wound healing in Xenopus embryos.
 10 citations,
January 2012 in “Journal of biomedical optics”
10 citations,
January 2012 in “Journal of biomedical optics” Melanin density affects hair color, and this method can help in cosmetic assessments and diagnosing hair diseases.
 2 citations,
August 2020 in “JCRPE”
2 citations,
August 2020 in “JCRPE” A girl with Denys-Drash syndrome was misdiagnosed due to biotin affecting her hormone test results.
 5 citations,
May 2019 in “Cureus”
5 citations,
May 2019 in “Cureus” Taking biotin supplements can cause incorrect thyroid test results, leading to wrong diagnoses.
124 citations,
July 1997 in “Journal of Biological Chemistry” Overexpressing a specific enzyme in mice causes hair loss and female infertility.
3 citations,
July 2022 in “BMC chemistry” The methods accurately measure finasteride and tadalafil in Entadfi™ capsules for quality control.
 43 citations,
October 1955 in “The journal of nutrition/The Journal of nutrition”
43 citations,
October 1955 in “The journal of nutrition/The Journal of nutrition” Germ-free rats need biotin for growth and have different vitamin metabolism compared to regular rats.
30 citations,
February 2010 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Plet-1 protein helps hair follicle cells move and stick to tissues.
68 citations,
January 2014 in “Dermatology research and practice” Skin side effects from cancer drugs targeting EGFR can affect treatment adherence but can be managed with antibiotics like tetracycline.
 1 citations,
June 2020 in “Journal of AOAC INTERNATIONAL”
1 citations,
June 2020 in “Journal of AOAC INTERNATIONAL” Two new methods accurately measure Aminexil, Pyridoxine, and Niacinamide in hair products.
 4 citations,
November 1968 in “Textile research journal”
4 citations,
November 1968 in “Textile research journal” Hair fibers may have a unique, non-protein sheath not previously identified.
 January 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
January 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Small molecule DMF improves psoriasis and multiple sclerosis, adult skin cells can be made to grow new hair, certain skin cells initiate hair growth, IL-17C controls gut health and can cause skin inflammation, and skin cells produce IL-17 that can lead to psoriasis.
 823 citations,
February 1998 in “Analytical Chemistry”
823 citations,
February 1998 in “Analytical Chemistry” Method detects finasteride in plasma at very low concentrations.
 September 2009 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association”
September 2009 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association” Hair loss significantly affects quality of life, wet combing is better than visual inspection for finding head lice, many with oral lichen planus have allergies, and wet wraps with steroids quickly improve itchy skin conditions.
 February 2023 in “Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology”
February 2023 in “Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology” Optical imaging and light therapy show promise for diagnosing and treating liver injury caused by surgery.
 29 citations,
April 2019 in “Acta neuropathologica communications”
29 citations,
April 2019 in “Acta neuropathologica communications” Stopping mitochondrial respiration can prevent brain cancer spread in skin cancer patients, and plant compound β-sitosterol could help achieve this.
 47 citations,
March 2019 in “Journal of immunology research”
47 citations,
March 2019 in “Journal of immunology research” Valproic Acid could potentially be used to treat immune-related conditions due to its ability to modify immune cell functions.
 1 citations,
March 2019 in “Journal of AOAC INTERNATIONAL”
1 citations,
March 2019 in “Journal of AOAC INTERNATIONAL” New method quickly and accurately measures dexpanthenol in hair products.
[object Object]  3 citations,
January 2019 in “Elsevier eBooks”
3 citations,
January 2019 in “Elsevier eBooks” Pharmacists should interpret lab data and perform physical exams to improve patient care.
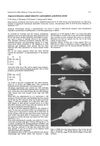 2 citations,
September 1980 in “Experientia”
2 citations,
September 1980 in “Experientia” Polyethylene alanine caused hair loss in young lab animals but not in adults, with hair regrowth occurring within 20 days.
5 citations,
March 2011 in “Journal of proteomics” Histone H4, released by cells exposed to colchicine, can cause hair loss by inhibiting cell growth and enzyme activity.
 November 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
November 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Oral JAK inhibitors help regrow hair in alopecia patients.
 April 1906 in “The American Journal of the Medical Sciences”
April 1906 in “The American Journal of the Medical Sciences” Keratosis Pilaris Atrophicans causes skin scarring and might be treated with a new synthetic retinoid.
 10 citations,
May 2012 in “PloS one”
10 citations,
May 2012 in “PloS one” Low ERCC3 gene activity is linked to non-pigmented hair growth.
 August 2022 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
August 2022 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” The authors agree they didn't discuss the risks of too much micronutrients and value the focus on biotin deficiency signs and treatment effectiveness.
 January 2025 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology”
January 2025 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology” Hox proteins help maintain keratinocyte identity by regulating miRNA expression.
 May 2021 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society”
May 2021 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society” A patient produced cortisol after adrenalectomy, possibly due to residual tissue or other body parts making steroids.

























