3 citations,
January 2020 in “International journal of trichology” Congenital triangular alopecia is a hair loss condition present from birth or early childhood with no effective treatment needed.
[object Object] 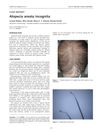 19 citations,
January 2011 in “Clinics”
19 citations,
January 2011 in “Clinics” A young woman with a rare hair loss condition improved with steroid and biotin treatment.

A woman regrew her hair after receiving injections of special cell-derived vesicles.
 2 citations,
October 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
2 citations,
October 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Focal atrichia helps diagnose female pattern hair loss.
 6 citations,
August 2006 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
6 citations,
August 2006 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” Two teenage brothers had a rare, treatment-resistant form of female-pattern hair loss with unusual scalp changes.
 4 citations,
March 2013 in “The American Journal of Cosmetic Surgery”
4 citations,
March 2013 in “The American Journal of Cosmetic Surgery” Melanin absorbing light is necessary but not enough for effective hair removal by light treatment.
 170 citations,
December 2009 in “Histopathology”
170 citations,
December 2009 in “Histopathology” The conclusion is that accurate diagnosis of different types of hair loss requires good teamwork between skin doctors and lab experts.
 75 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
75 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Chronic Telogen Effluvium is a hair loss condition in middle-aged women that usually doesn't lead to complete baldness.
 59 citations,
August 1998 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
59 citations,
August 1998 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Genetics and hormones cause hair loss; finasteride treats it safely.
 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
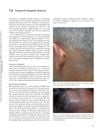
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Temporal triangular alopecia is a lifelong condition with hairless patches on the side of the head that may be present from birth.
 January 2019 in “SAGE Open Medical Case Reports”
January 2019 in “SAGE Open Medical Case Reports” A scalp biopsy revealed systemic amyloidosis in a woman who initially seemed to have a common hair loss condition.
 1 citations,
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
1 citations,
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Some medications for inflammation can cause a condition with scalp rashes and hair loss, often linked to Crohn's disease, and may require treatment changes to prevent permanent hair loss.
 49 citations,
February 2019 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism”
49 citations,
February 2019 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism” Use "female pattern hair loss" term, assess androgen excess, treat with minoxidil and other medications if needed.
 13 citations,
March 2016 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
13 citations,
March 2016 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” Some people's hair loss is caused by multiple factors, with the most common being a mix of AGA and CCCA.
 17 citations,
December 2004 in “The Journal of Men's Health & Gender”
17 citations,
December 2004 in “The Journal of Men's Health & Gender” Male pattern baldness involves hormone-related hair thinning, shorter hair, and inflammation.
 19 citations,
December 2008 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
19 citations,
December 2008 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The authors suggest that a new type of hair loss exists, which is different from alopecia areata.
 88 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
88 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” Minoxidil and finasteride effectively treat hair loss.
 19 citations,
February 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
19 citations,
February 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” CD3+ T-cell presence is a reliable marker to tell apart alopecia areata from pattern hair loss.
 2 citations,
January 2013 in “Hair therapy & transplantation”
2 citations,
January 2013 in “Hair therapy & transplantation” Hair transplants can be a treatment for scarring hair loss if there's good blood flow and no active disease.
 July 2021 in “Journal Für Ästhetische Chirurgie”
July 2021 in “Journal Für Ästhetische Chirurgie” Effective hair loss treatments require medical diagnosis and realistic expectations, with hair transplants offering improved, natural-looking results.
 14 citations,
September 2016 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
14 citations,
September 2016 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” The document concludes that new methods improve the accuracy of diagnosing scalp alopecia and challenges the old way of classifying it.
 1 citations,
January 2017 in “Expert opinion on orphan drugs”
1 citations,
January 2017 in “Expert opinion on orphan drugs” Adalimumab is the most effective treatment for severe hidradenitis suppurativa, but more research is needed to improve treatment options.
 1 citations,
May 2021 in “Journal Für Ästhetische Chirurgie”
1 citations,
May 2021 in “Journal Für Ästhetische Chirurgie” Doctors should thoroughly inform hair transplant patients about the procedure, risks, and costs to prevent dissatisfaction and legal issues.
[object Object]  1 citations,
December 2017 in “JAMA Facial Plastic Surgery”
1 citations,
December 2017 in “JAMA Facial Plastic Surgery” Artificial hair implantation using scaffolds is possible and PHDPE is more biocompatible than ePTFE.
 6 citations,
July 2015 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
6 citations,
July 2015 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Trichoepitheliomas can be hard to distinguish from other skin conditions and often start in teenage years.
 January 2022 in “International journal of zoology and animal biology”
January 2022 in “International journal of zoology and animal biology” Dogs with dermatomyositis, especially Collies and Shetland Sheepdogs, need better treatments for their skin and muscle inflammation.
 January 2023 in “Karger Kompass. Dermatologie”
January 2023 in “Karger Kompass. Dermatologie” Scientists are still unsure what triggers the immune system to attack hair follicles in Alopecia areata.
 1 citations,
August 2021 in “Canadian journal of neurological sciences”
1 citations,
August 2021 in “Canadian journal of neurological sciences” Woodhouse-Sakati syndrome can cause writer's cramp and other varied symptoms, highlighting the importance of genetic testing for diagnosis.
 2 citations,
December 2019 in “Veterinary Dermatology”
2 citations,
December 2019 in “Veterinary Dermatology” Microneedling with platelet-rich plasma helps dog hair regrow faster than microneedling alone.
 179 citations,
September 1998 in “BMJ”
179 citations,
September 1998 in “BMJ” Hair loss in men is common, treatable, but not curable.




























