 3 citations,
January 2010 in “Elsevier eBooks”
3 citations,
January 2010 in “Elsevier eBooks” The document describes various skin conditions, their features, and treatments but lacks detailed study size information.

Diagnosing oral ulcers can be complex and requires careful examination and follow-up.
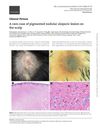
A man had a rare pigmented nodule on his scalp that developed from birthmarks.
 98 citations,
July 2014 in “Trends in Molecular Medicine”
98 citations,
July 2014 in “Trends in Molecular Medicine” Hair follicles are hormone-sensitive and involved in growth and other functions, with potential for new treatments, but more research is needed.
 42 citations,
March 2008 in “Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology”
42 citations,
March 2008 in “Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology” Hormones and neuroendocrine factors control hair growth and color, and more research could lead to new hair treatment options.
 24 citations,
May 2012 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
24 citations,
May 2012 in “International Journal of Dermatology” The document concludes that eyelash trichomegaly, which is the abnormal growth of eyelashes, can be present from birth, caused by diseases, or result from certain medications.
 23 citations,
May 2016 in “American Journal of Pathology”
23 citations,
May 2016 in “American Journal of Pathology” The research suggests that a specific skin gene can be controlled by signals within and between cells and is wrongly activated in certain skin diseases.
 19 citations,
April 2016 in “Experimental Dermatology”
19 citations,
April 2016 in “Experimental Dermatology” Melanoblasts migrate to the skin using various pathways, and understanding this process could help with skin disease research.
 13 citations,
January 2010 in “Advances in Biochemical Engineering / Biotechnology”
13 citations,
January 2010 in “Advances in Biochemical Engineering / Biotechnology” Understanding hair biology is key to developing better treatments for hair and scalp issues.
 43 citations,
August 2008 in “Regenerative Medicine”
43 citations,
August 2008 in “Regenerative Medicine” Scientists created early-stage hairs from mouse cells that grew into normal, pigmented hair when implanted into other mice.
 25 citations,
September 2006 in “Birth Defects Research”
25 citations,
September 2006 in “Birth Defects Research” Different processes create patterns in skin and things like hair and feathers.
 4 citations,
March 2017 in “Development”
4 citations,
March 2017 in “Development” Estrogen is important for keeping adult mouse nipple skin healthy by controlling certain cell signals.

The document concludes that Syndromes of Severe Insulin Resistance are rare disorders with limited treatment options.
 176 citations,
January 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
176 citations,
January 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Bone Morphogenetic Proteins (BMPs) help control skin health, hair growth, and color, and could potentially be used to treat skin and hair disorders.
 13 citations,
September 2017 in “Oncotarget”
13 citations,
September 2017 in “Oncotarget” A certain signaling pathway in mice, when increased, causes hair to gray by depleting the cells that give hair its color.
79 citations,
December 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Alopecia areata may be treated by restoring hair follicle immune privilege and adjusting immune responses.
33 citations,
July 2007 in “Journal of cell science” Miz1 is essential for proper hair structure and growth.
94 citations,
April 2018 in “Nature Genetics” New genetic locations explain much of hair color variation in Europeans.
34 citations,
January 2013 in “Frontiers in genetics” Stem cells can help other stem cells by producing supportive factors.
 30 citations,
April 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
30 citations,
April 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Radiation mainly affects keratinocyte stem cells, not melanocyte stem cells, causing hair to gray.
 84 citations,
April 2005 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
84 citations,
April 2005 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Treatments for melanin disorders exist, but more effective options needed.
 759 citations,
February 2009 in “Current Biology”
759 citations,
February 2009 in “Current Biology” Hair follicles are complex, dynamic mini-organs that help us understand cell growth, death, migration, and differentiation, as well as tissue regeneration and tumor biology.
 421 citations,
April 2012 in “The New England Journal of Medicine”
421 citations,
April 2012 in “The New England Journal of Medicine” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune condition causing hair loss with no cure and treatments that often don't work well.
 236 citations,
July 2001 in “Trends in Molecular Medicine”
236 citations,
July 2001 in “Trends in Molecular Medicine” Future hair loss treatments should aim to extend hair growth, reactivate resting follicles, reverse shrinkage, and possibly create new follicles, with gene therapy showing promise.
 163 citations,
March 2012 in “BMC biology”
163 citations,
March 2012 in “BMC biology” Stem cell niches support, regulate, and coordinate stem cell functions.
 66 citations,
May 2012 in “Scientific Reports”
66 citations,
May 2012 in “Scientific Reports” Scientists successfully created and transplanted bioengineered hair follicles that function like natural ones, suggesting a new treatment for hair loss.
 53 citations,
April 2014 in “Experimental Dermatology”
53 citations,
April 2014 in “Experimental Dermatology” Wnt10b makes hair follicles bigger, but DKK1 can reverse this effect.
 46 citations,
July 1988 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
46 citations,
July 1988 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Hormone imbalances can cause specific skin changes, which may help in early detection of endocrine disorders.
 41 citations,
October 2008 in “The American journal of pathology”
41 citations,
October 2008 in “The American journal of pathology” Blocking a specific protein signal can make hair grow on mouse nipples.
 31 citations,
April 1999 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
31 citations,
April 1999 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Nd:YAG laser can reduce hair with multiple treatments, but permanent removal isn't guaranteed.


























