37 citations,
January 2005 in “Clinics in dermatology” Recent progress has been made in understanding inherited hair and nail disorders.
[object Object] 
A genetic mutation in the EDA gene causes hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia in cats.
 August 2020 in “International Journal of Research in Dermatology”
August 2020 in “International Journal of Research in Dermatology” Clouston's syndrome is a rare disorder affecting nails, hair, teeth, and skin, caused by a gene mutation, and currently has no treatment, only supportive care.
 6 citations,
August 2022 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
6 citations,
August 2022 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” EDA signaling is linked to skin disorders, various cancers, and liver disease.
 November 2019 in “Harper's Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology”
November 2019 in “Harper's Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology” The document is a detailed medical reference on skin and genetic disorders.
 April 2023 in “Medizinische Genetik”
April 2023 in “Medizinische Genetik” New gene discoveries have improved diagnosis and treatment for skin and hair disorders, but more research is needed to fully understand them.
25 citations,
September 2005 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Rapp-Hodgkin syndrome, AEC, and EEC are different expressions of the same genetic disorder caused by TP63 gene mutations.
 15 citations,
February 2015 in “Cell & tissue research/Cell and tissue research”
15 citations,
February 2015 in “Cell & tissue research/Cell and tissue research” P-cadherin is important for hair growth and health, and its problems can cause hair and skin disorders.
 June 1997 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
June 1997 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Researchers found new hair and nail genes, how hair reacts to UV, differences in white and pigmented hair growth, nerve changes in alopecia, treatments for baldness and alopecia, a toenail condition linked to a genetic disorder, and that nail fungus is more common in people with psoriasis.
 April 2024 in “Diagnostics”
April 2024 in “Diagnostics” Most orthodontic patients with missing teeth also have hair disorders.
 November 2023 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
November 2023 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Mutations in the WNT10A gene cause Short Anagen Hair syndrome and increase the risk of male pattern hair loss.
4 citations,
December 2021 in “Journal of clinical laboratory analysis” A new mutation in the DCAF17 gene was found to cause Woodhouse-Sakati syndrome in a large family.
 9 citations,
January 2017 in “Journal of the Egyptian Women's Dermatologic Society (Print)”
9 citations,
January 2017 in “Journal of the Egyptian Women's Dermatologic Society (Print)” Fungal infection was the main cause of hair loss in Egyptian children studied.
 1 citations,
February 2013 in “InTech eBooks”
1 citations,
February 2013 in “InTech eBooks” Genetic mutations cause various hair diseases, and whole genome sequencing may reveal more about these conditions.
 September 2023 in “International journal of science and healthcare research”
September 2023 in “International journal of science and healthcare research” Genetic testing is crucial for diagnosing congenital atrichia, a rare condition causing irreversible hair loss.
 3 citations,
March 2017 in “International journal of women’s dermatology”
3 citations,
March 2017 in “International journal of women’s dermatology” Some domesticated animals have the same genetic skin diseases as humans, which can help doctors understand human genetic mutations.
2 citations,
August 2022 in “World Journal of Clinical Cases” Albumin and prednisone improved symptoms in a woman with Cronkhite-Canada syndrome, revealing potential genetic causes.
 January 2023 in “The Keio Journal of Medicine”
January 2023 in “The Keio Journal of Medicine” Certain gene variants can cause inherited hair diseases, which are important to diagnose and understand for patient care.
 3 citations,
June 2022 in “European journal of human genetics”
3 citations,
June 2022 in “European journal of human genetics” A new type of pachyonychia congenita linked to a specific keratin gene mutation was found in two Pakistani families.
 June 2021 in “International journal of research in dermatology”
June 2021 in “International journal of research in dermatology” A boy and his father with hereditary hypotrichosis simplex were treated for hair loss, but the treatment result is unknown.
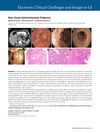 August 2013 in “Gastroenterology”
August 2013 in “Gastroenterology” A 60-year-old man with Cronkhite-Canada syndrome improved with treatment, but the condition has a high mortality rate and a risk of colorectal cancer.
 January 2024 in “Archives of pharmacy practice”
January 2024 in “Archives of pharmacy practice” The skin is vital for protection, temperature control, fluid balance, immunity, and sensing, with damage affecting daily life and mental health.
 6 citations,
August 1993 in “Archives of Dermatology”
6 citations,
August 1993 in “Archives of Dermatology” A woman's hair changed to a dry, tangled texture that's hard to comb after treatment with spironolactone, suggesting the medication might cause such hair changes.
[object Object]  1 citations,
February 2017 in “International journal of anatomy and research”
1 citations,
February 2017 in “International journal of anatomy and research” Understanding fetal skin development helps diagnose congenital skin diseases.
 31 citations,
August 2005 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
31 citations,
August 2005 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” The study concluded that PKP1 is essential for skin integrity and hair growth, and its dysfunction causes the symptoms of ectodermal dysplasia/skin fragility syndrome.
 4 citations,
August 2016 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
4 citations,
August 2016 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Using cetirizine on the skin and taking vitamin D can help increase hair growth in children with hair loss from ectodermal dysplasia.
 197 citations,
June 2009 in “American journal of human genetics”
197 citations,
June 2009 in “American journal of human genetics” WNT10A mutations often cause ectodermal dysplasias, with males showing more tooth issues than females.
 30 citations,
June 2016 in “Journal of Human Genetics”
30 citations,
June 2016 in “Journal of Human Genetics” Researchers found genetic mutations causing hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia in 88% of studied patients and identified new mutations and genetic variations affecting the disease.
 5 citations,
September 2015 in “BMC Medical Genetics”
5 citations,
September 2015 in “BMC Medical Genetics” The EDAR gene mutation leads to thinner and more deformed hair shafts.
 November 2019 in “Harper's Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology”
November 2019 in “Harper's Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology” Understanding normal hair growth and loss in children is key to diagnosing and treating hair disorders.

























