 97 citations,
September 2006 in “Pharmaceutical Research”
97 citations,
September 2006 in “Pharmaceutical Research” No treatment fully prevents hair loss from chemotherapy yet.
 41 citations,
June 2003 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
41 citations,
June 2003 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Long-term minoxidil use can cause pseudoacromegaly, but stopping it improves symptoms.
 19 citations,
November 2018 in “Nutrients”
19 citations,
November 2018 in “Nutrients” Annurca apple extract may protect mouse hair from damage by chemotherapy and could help treat hair loss without promoting cancer growth.
 103 citations,
December 2011 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
103 citations,
December 2011 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Chemotherapy often causes temporary hair loss, which is distressing and needs better treatment and support.
 43 citations,
June 2012 in “Lasers in Medical Science”
43 citations,
June 2012 in “Lasers in Medical Science” Low-level laser treatment helped rats regrow hair faster after chemotherapy.
 21 citations,
January 2005 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
21 citations,
January 2005 in “Pediatric Dermatology” An 8-year-old girl with vitiligo developed extra hair growth on her knee after using tacrolimus ointment.
 9 citations,
April 2018 in “JAMA Dermatology”
9 citations,
April 2018 in “JAMA Dermatology” Topical minoxidil improves hair loss in 80% of women with breast cancer undergoing endocrine therapy.
 1 citations,
May 2006 in “Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents”
1 citations,
May 2006 in “Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents” No FDA-approved treatments for chemotherapy-induced hair loss existed in 2006; more research was needed.
 59 citations,
September 2008 in “Experimental dermatology”
59 citations,
September 2008 in “Experimental dermatology” Both mouse and rat models are effective for testing alopecia areata treatments.
 38 citations,
July 1998 in “Journal of surgical oncology”
38 citations,
July 1998 in “Journal of surgical oncology” A woman with breast cancer developed a rare condition causing excessive fine hair growth on her face and body.
 20 citations,
January 2018 in “Expert Opinion on Drug Safety”
20 citations,
January 2018 in “Expert Opinion on Drug Safety” Personalized treatment with inhibitors, minoxidil, and laser therapy helps hair loss.
 14 citations,
March 2007 in “Pediatric pulmonology”
14 citations,
March 2007 in “Pediatric pulmonology” Inhaled steroids in children may cause excessive hair growth and not always go away after stopping the medication.
 10 citations,
April 2016 in “Research and reports in transdermal drug delivery”
10 citations,
April 2016 in “Research and reports in transdermal drug delivery” Transfollicular drug delivery is promising but needs more research to improve and understand it better.
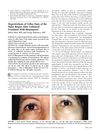 23 citations,
April 2004 in “American Journal of Ophthalmology”
23 citations,
April 2004 in “American Journal of Ophthalmology” Using bimatoprost on one side of the face caused increased cheek hair growth in a patient.
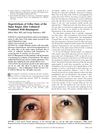 15 citations,
March 2004 in “American Journal of Ophthalmology”
15 citations,
March 2004 in “American Journal of Ophthalmology” Using bimatoprost on one side of the face caused increased cheek hair growth in a patient.
 8 citations,
May 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
8 citations,
May 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” UV light does not significantly affect minoxidil's ability to treat male pattern baldness.
 7 citations,
January 2020 in “Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
January 2020 in “Journal of Dermatology” Cantu syndrome, which causes excessive hair growth and skin issues, is due to a mutation in the ABCC9 gene, and understanding this could help develop new treatments for hair diseases.
 69 citations,
April 2010 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
69 citations,
April 2010 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Bimatoprost is a safe and effective treatment for making eyelashes longer, thicker, and darker.
 19 citations,
September 2020 in “Pharmaceutics”
19 citations,
September 2020 in “Pharmaceutics” Sodium Valproate nanospanlastics could be a safe and effective treatment for Androgenic Alopecia, with fewer side effects than minoxidil.
 9 citations,
December 2017 in “The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology”
9 citations,
December 2017 in “The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology” New targeted therapies for hair loss from alopecia areata show promise, with personalized treatment expected in the future.
 October 2021 in “International journal of basic and clinical pharmacology”
October 2021 in “International journal of basic and clinical pharmacology” Excessive eyelash growth from erlotinib may indicate positive tumor response and help treat madarosis.
 1 citations,
June 2017 in “International Journal of Toxicology”
1 citations,
June 2017 in “International Journal of Toxicology” Most drugs fail to reach the market, but understanding their properties and using strategies like early toxicity tests and drug repurposing can help advance their development.
 110 citations,
August 2016 in “Drugs”
110 citations,
August 2016 in “Drugs” Minoxidil is the only FDA-approved topical drug for treating male or female pattern hair loss, and other medications like finasteride and dutasteride can also increase hair growth.
 45 citations,
January 1981 in “Annals of Internal Medicine”
45 citations,
January 1981 in “Annals of Internal Medicine” Minoxidil controls blood pressure effectively, but may cause side effects like hypertrichosis.
 33 citations,
January 2002
33 citations,
January 2002 Latanoprost, a glaucoma drug, showed potential for promoting hair growth in bald monkeys, especially at higher doses.
 2 citations,
October 2018 in “Springer eBooks”
2 citations,
October 2018 in “Springer eBooks” Cancer treatments can cause skin-related side effects that may affect patient quality of life and require changes in treatment.
 18 citations,
August 2019 in “Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy”
18 citations,
August 2019 in “Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy” Quercetin-loaded nanoparticles can penetrate skin, minimize hair loss, and promote hair regrowth, showing slightly better results than a marketed product.
 5 citations,
January 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
5 citations,
January 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Low-dose oral minoxidil is an effective and safe treatment for hair loss.
 72 citations,
January 2001 in “Drugs”
72 citations,
January 2001 in “Drugs” Minoxidil and finasteride treat hair loss; more research needed for other options.
 31 citations,
May 2008 in “Drug Discovery Today: Disease Mechanisms”
31 citations,
May 2008 in “Drug Discovery Today: Disease Mechanisms” Different hair growth problems are caused by genetic issues or changes in hair growth cycles, and new treatments are being developed.






























