 73 citations,
March 2009 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
73 citations,
March 2009 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” The document concludes that accurate diagnosis of hair disorders is crucial and requires a range of diagnostic methods.
 14 citations,
January 1985 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
14 citations,
January 1985 in “International Journal of Dermatology” The cause of alopecia areata was unknown, and while various treatments existed, no best treatment was agreed upon.
 239 citations,
November 2000 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
239 citations,
November 2000 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Finasteride doesn't effectively treat hair loss in postmenopausal women.
 179 citations,
September 1998 in “BMJ”
179 citations,
September 1998 in “BMJ” Hair loss in men is common, treatable, but not curable.
 16 citations,
March 2013 in “JAMA Dermatology”
16 citations,
March 2013 in “JAMA Dermatology” A cancer drug called nilotinib might cause hair loss due to inflammation around hair follicles.
 6 citations,
June 2019 in “Skin Research and Technology”
6 citations,
June 2019 in “Skin Research and Technology” Finasteride works for hair loss by maintaining existing hair follicles, not reversing miniaturization.
 3 citations,
November 1999 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
3 citations,
November 1999 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Examining scalp biopsies in different ways helps better diagnose hair loss types.
 6 citations,
November 1988 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
6 citations,
November 1988 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” The document concludes that hair analysis is not good for assessing nutrition but can detect long-term heavy metal exposure.
 5 citations,
November 2017 in “Dermatologica Sinica”
5 citations,
November 2017 in “Dermatologica Sinica” Transverse scalp biopsies are more accurate for diagnosing non-cicatricial alopecia, but examining both types is best for accuracy.
 July 2024 in “Plastic and Aesthetic Research”
July 2024 in “Plastic and Aesthetic Research” Careful planning and accurate diagnosis are crucial for successful hair restoration surgery.
 December 2022 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
December 2022 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” MicroRNA-205 helps hair grow by changing the stiffness and contraction of hair follicle cells.
 6 citations,
October 2005 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology”
6 citations,
October 2005 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology” The document discusses male and female pattern hair loss, its diagnosis methods, FDA-approved treatments like finasteride and minoxidil, their side effects, and the role of lifestyle changes.
 November 2023 in “International Journal of Trichology”
November 2023 in “International Journal of Trichology” Trichoscopic features help diagnose and assess female pattern hair loss severity, with inflammation playing a key role.
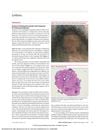 17 citations,
August 2019 in “JAMA Facial Plastic Surgery”
17 citations,
August 2019 in “JAMA Facial Plastic Surgery” Some men lost hair after deoxycholic acid treatment for neck fat, but most saw improvement or resolution.
 25 citations,
October 2018 in “PloS one”
25 citations,
October 2018 in “PloS one” Key genes regulate hair follicle phase changes in Inner Mongolia cashmere goats.
 2 citations,
January 2018 in “DOAJ (DOAJ: Directory of Open Access Journals)”
2 citations,
January 2018 in “DOAJ (DOAJ: Directory of Open Access Journals)” The most effective way to diagnose non-scarring hair loss is by transverse sectioning, and some cases, particularly in males with inflammation around hair follicles, might be curable.
 57 citations,
November 1987 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
57 citations,
November 1987 in “Pediatric Dermatology” Children's hair grows in different types from before birth through puberty, with growth rates and characteristics varying by age, sex, and race.
 43 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
43 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Recognizing the different stages of alopecia areata is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
 July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” Telogen Effluvium is a common, usually reversible hair loss condition, often improved by removing the trigger and possibly treated with various products, though their effectiveness is uncertain.
 67 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
67 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” Chronic Telogen Effluvium may resolve after years and is diagnosed by examining the patient's history and clinical signs, with treatment aimed at underlying causes and possibly minoxidil.
 1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks”
1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks” Telogen Effluvium is a common hair loss condition that can be short-term or long-lasting and is often caused by stress, illness, or nutritional issues.
 2 citations,
October 2015 in “Primary Care: Clinics in Office Practice”
2 citations,
October 2015 in “Primary Care: Clinics in Office Practice” Doctors should diagnose hair loss by examining the patient and possibly doing tests, and then treat it based on the type, which may prevent permanent hair loss.
 January 2016 in “Human & Experimental Toxicology”
January 2016 in “Human & Experimental Toxicology” A specific DNA sequence caused hair loss in male mice by activating immune cells and increasing a certain immune signal.
 83 citations,
May 1999 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
83 citations,
May 1999 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss that spreads out can often fix itself or be treated by finding and handling the cause.
 68 citations,
March 1965 in “The BMJ”
68 citations,
March 1965 in “The BMJ” Hormones and genetics affect hair growth and patterns, with some changes reversible and others not.
 13 citations,
July 2004 in “Skinmed”
13 citations,
July 2004 in “Skinmed” Common types of non-scarring hair loss have various causes and treatments, but more effective solutions are needed.
 August 2024 in “EMJ Dermatology”
August 2024 in “EMJ Dermatology” Non-scarring alopecia in females affects emotional well-being and requires accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment.
 78 citations,
February 2004 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
78 citations,
February 2004 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Melatonin helps hair growth in women with hair loss.
 1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks”
1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks” The document concludes that alopecia areata is an unpredictable autoimmune hair loss condition with no cure, but various treatments exist that require personalized approaches.
 43 citations,
July 1984 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
43 citations,
July 1984 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Antiandrogen therapy helped increase hair growth in women with hormonal imbalances related to baldness.






























