April 2020 in “International journal of reproduction, contraception, obstetrics and gynecology” A postmenopausal woman with hair loss and hirsutism improved after surgery to remove an ovarian tumor.
 May 2023 in “The journal of sexual medicine”
May 2023 in “The journal of sexual medicine” Ovarian Hyperthecosis caused hypersexuality in an older woman and was successfully treated with surgery.
 1 citations,
February 2016 in “European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology”
1 citations,
February 2016 in “European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology” An 84-year-old woman's hair loss was due to a rare condition called Leydig cell hyperplasia, which was treated with surgery.
 November 2018 in “Endocrine Abstracts”
November 2018 in “Endocrine Abstracts” A woman's high testosterone levels were caused by a rare ovarian tumor, not the initially diagnosed condition.
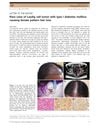 August 2019 in “Journal of Dermatology”
August 2019 in “Journal of Dermatology” Woman with diabetes had hair loss due to rare ovarian tumor; surgery improved hair growth.
 20 citations,
October 2017 in “Clinical Endocrinology”
20 citations,
October 2017 in “Clinical Endocrinology” The conclusion is that removing both ovaries is the best treatment for excess male hormones in postmenopausal women, with medication as another option, and managing insulin resistance is important for diagnosis and treatment.
 2 citations,
May 2018 in “Diagnosis”
2 citations,
May 2018 in “Diagnosis” A 68-year-old woman developed male traits due to a tumor in her ovary, which was removed, returning her hormone levels to normal.
 1 citations,
December 1998 in “PubMed”
1 citations,
December 1998 in “PubMed” Surgery on a 68-year-old woman with an ovarian tumor led to reduced hirsutism and normal testosterone levels.
 December 2021 in “Aegean journal of obstetrics and gynecology”
December 2021 in “Aegean journal of obstetrics and gynecology” A woman's male-like physical changes were caused by two rare ovarian conditions.
 April 2023 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
April 2023 in “Research Square (Research Square)” A 24-year-old woman had a rare ovarian tumor that caused male-pattern hair growth and was hard to diagnose and treat.
 April 2023 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
April 2023 in “Research Square (Research Square)” A young woman had a rare, aggressive ovarian tumor that was hard to diagnose and treat, leading to disease progression despite treatment.
 February 2021 in “Endocrinology, diabetes & metabolism case reports”
February 2021 in “Endocrinology, diabetes & metabolism case reports” A postmenopausal woman's excessive hair growth and hair loss were due to a non-cancerous ovarian condition, treated successfully with surgery.
 1 citations,
January 2018 in “Journal of Gynecologic Surgery”
1 citations,
January 2018 in “Journal of Gynecologic Surgery” Removing both ovaries can treat increased testosterone and related symptoms in postmenopausal women with ovarian hyperthecosis.
 May 2021 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society”
May 2021 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society” A woman's severe hormone imbalance after menopause led to finding a rare ovarian tumor, treated by surgery.
 13 citations,
August 2020 in “Mayo Clinic proceedings”
13 citations,
August 2020 in “Mayo Clinic proceedings” Women with lichen planopilaris often have thyroid disease, depression, anxiety, and may respond to treatment with slowed disease progression.
 2 citations,
October 2015 in “Obstetrics and gynaecology cases - reviews”
2 citations,
October 2015 in “Obstetrics and gynaecology cases - reviews” Removing both ovaries may better treat increased male hormone levels and related symptoms in postmenopausal women when hormone therapy doesn't work.
 December 2013 in “Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences”
December 2013 in “Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences” Ovarian steroid cell tumors should be considered in adults with hirsutism and high testosterone, with surgery as the main treatment.
 April 2020 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society”
April 2020 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society” An ovarian tumor caused a woman's male-like symptoms, which improved after surgery.
 251 citations,
October 2014 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism”
251 citations,
October 2014 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism” The guidelines advise against using testosterone and DHEA in women for most conditions due to safety and effectiveness concerns, but suggest considering testosterone for postmenopausal women with low sexual desire.
 4 citations,
June 2005 in “Andrology”
4 citations,
June 2005 in “Andrology” A woman's diabetes improved after removing ovarian tumors that caused high testosterone levels.
 3 citations,
May 2011 in “Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology”
3 citations,
May 2011 in “Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology” A woman's pelvic pain and bleeding led to finding and successfully treating a rare benign tumor in her reproductive system.
 1 citations,
November 2023 in “American journal of clinical pathology”
1 citations,
November 2023 in “American journal of clinical pathology” Transgender men on testosterone therapy need ongoing gynecologic care due to potential cancer risks.
 5 citations,
November 2018 in “Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology”
5 citations,
November 2018 in “Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology” Ovarian Leydig cell tumors are hard to diagnose with just advanced imaging; expert ultrasound and clinical evaluation are essential.
 254 citations,
September 2014 in “Menopause”
254 citations,
September 2014 in “Menopause” The NAMS 2014 recommendations guide healthcare providers on treating health issues in midlife women, emphasizing individualized care and informed decision-making.
 238 citations,
July 2003 in “British Journal of Plastic Surgery”
238 citations,
July 2003 in “British Journal of Plastic Surgery” Hidradenitis suppurativa, a chronic skin disease, can be managed with antibiotics, lifestyle changes, and in severe cases, surgery. Early diagnosis and careful planning are key, and laser treatment can be an efficient solution for mild to severe cases.
 86 citations,
May 2013 in “American journal of obstetrics and gynecology”
86 citations,
May 2013 in “American journal of obstetrics and gynecology” Gynecologists should provide comprehensive care for transgender patients, including mental health evaluation, hormone therapy, and surgical options, while monitoring for side effects and ensuring patient safety.
 61 citations,
January 2017 in “Human Reproduction Open”
61 citations,
January 2017 in “Human Reproduction Open” The review recommends hormone replacement therapy for women with premature ovarian insufficiency to manage symptoms and protect health, with specific approaches for different groups.
 57 citations,
December 2018 in “JAMA Surgery”
57 citations,
December 2018 in “JAMA Surgery” Hormone treatment for transgender patients may not need to be stopped before surgery, but more research is needed, especially on estrogen.
 45 citations,
March 2015 in “Clinical Endocrinology”
45 citations,
March 2015 in “Clinical Endocrinology” Testosterone therapy is generally safe for transmen, improves sexual function, and has manageable health risks with proper monitoring.
 26 citations,
December 2016 in “Psychiatric Clinics of North America”
26 citations,
December 2016 in “Psychiatric Clinics of North America” Testosterone therapy and surgeries like mastectomy improve transgender men's lives and mental health with low risks and high satisfaction.




























