 29 citations,
March 2001 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
29 citations,
March 2001 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Steven Kossard classified lymphocyte-related hair loss into four patterns, each linked to different types of baldness.
 23 citations,
September 2019 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual”
23 citations,
September 2019 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual” The study concluded that AAI and DAA are forms of the same disease, with different symptoms in men and women, and that corticosteroid treatment is effective.
22 citations,
January 2017 in “Acta Endocrinologica” A woman with multiple autoimmune diseases showed improvement in hair loss but not in skin discoloration after treatment.
 21 citations,
March 2006 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
21 citations,
March 2006 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Most hair loss disorders can be accurately diagnosed and treated in an outpatient setting.
 20 citations,
July 1990 in “Pediatrics in Review”
20 citations,
July 1990 in “Pediatrics in Review” The four main causes of hair loss in children are fungal infections, pulling out hair, autoimmune hair loss, and stress-related hair shedding.
 19 citations,
September 2014 in “JAMA Dermatology”
19 citations,
September 2014 in “JAMA Dermatology” Eosinophilic infiltrate is not a reliable indicator for diagnosing chronic alopecia areata.
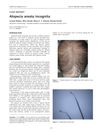 19 citations,
January 2011 in “Clinics”
19 citations,
January 2011 in “Clinics” A young woman with a rare hair loss condition improved with steroid and biotin treatment.
 16 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology”
16 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune hair loss condition that needs more research for better treatments.
 14 citations,
July 1987 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
14 citations,
July 1987 in “Dermatologic Clinics” The document concludes that treating female hair loss should target reducing excess androgen and blocking its effects on hair follicles, with the best treatments being hormonal therapy, adrenal suppression, and topical minoxidil.
 8 citations,
June 2016 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
8 citations,
June 2016 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” Two women were diagnosed with a rare melanoma that looked like hair loss but was actually a type of skin cancer.
 7 citations,
January 2011 in “Veterinary Pathology”
7 citations,
January 2011 in “Veterinary Pathology” A horse with severe hair loss was diagnosed with alopecia areata and a yeast infection.
 5 citations,
January 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders”
5 citations,
January 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders” The conclusion is that it's important to tell apart alopecia areata from lipedematous alopecia for proper treatment, as alopecia areata can be reversed.
 4 citations,
February 2021 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology”
4 citations,
February 2021 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology” Trichoscopy is a quick and reliable way to diagnose hair loss in women.
 3 citations,
June 2020 in “Cureus”
3 citations,
June 2020 in “Cureus” A woman's hair loss led to discovering she had lupus.
 3 citations,
July 2013 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
3 citations,
July 2013 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” A woman's hair loss, resembling an autoimmune condition, improved after treatment, but requires ongoing checks due to potential serious associations.
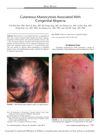 3 citations,
February 2012 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
3 citations,
February 2012 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” A 3-year-old girl with skin mast cell buildup and congenital baldness improved with treatment, suggesting a rare link between these conditions.
 3 citations,
January 1989 in “PubMed”
3 citations,
January 1989 in “PubMed” The review found that specific changes in scalp tissue can help diagnose different types of hair loss.
 2 citations,
May 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
2 citations,
May 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Hypothyroidism patients with hair loss typically have thinning hair, smaller hair follicles, and normal hair shedding.
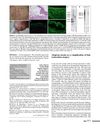 2 citations,
November 2012 in “European Journal of Dermatology”
2 citations,
November 2012 in “European Journal of Dermatology” Hair transplant surgery may cause alopecia areata, a new possible complication.
 1 citations,
June 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy”
1 citations,
June 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy” People with Alopecia Areata have more herpes simplex infections but similar rates of cancer, blood clots, and heart disease compared to those without it.
 1 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune hair loss condition, with various treatments showing mixed effectiveness and no guaranteed cure.
 1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks”
1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks” The document concludes that alopecia areata is an unpredictable autoimmune hair loss condition with no cure, but various treatments exist that require personalized approaches.
1 citations,
September 2016 in “Veterinary dermatology” A combination of ciclosporin and ketoconazole can effectively treat severe hair loss in dogs.
 1 citations,
January 2008 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2008 in “Elsevier eBooks” The document concludes that various disorders can cause hair loss in dogs, each requiring different treatments, and some may heal on their own.
 January 2025 in “TURKDERM”
January 2025 in “TURKDERM” Alopecia areata incognito in children can be effectively treated with triamcinolone acetonide and supplements, leading to full hair regrowth.
 April 2024 in “Journal of cutaneous pathology”
April 2024 in “Journal of cutaneous pathology” Skin conditions like seborrheic dermatitis can make it harder to correctly diagnose hair loss because they can cause the oil glands in the skin to shrink.
 December 2023 in “Portuguese journal of dermatology and venereology”
December 2023 in “Portuguese journal of dermatology and venereology” Trichoscopy can reliably distinguish between alopecia areata and trichotillomania.
 June 2023 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
June 2023 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Congenital alopecia areata may have genetic links and topical corticosteroids are an effective treatment.

A 12-year-old girl was misdiagnosed with alopecia areata but actually had a nevus sebaceus with a genetic mutation.
 December 2022 in “Rossijskij žurnal kožnyh i veneričeskih boleznej”
December 2022 in “Rossijskij žurnal kožnyh i veneričeskih boleznej” New treatments for child hair loss due to immune issues are effective but not yet officially approved.




























