November 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
November 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Oral minoxidil is more convenient but topical minoxidil improves hair density better.

There are many treatments for common hair loss, but more trials are needed to decide which are best.
1 citations
,
January 2022 in “Dermatologic therapy” Topical minoxidil can cause tingling or pricking sensations.
 16 citations
,
June 2021 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
16 citations
,
June 2021 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Minoxidil effectively treats hair loss, especially androgenetic alopecia, but needs more research for better understanding.
4 citations
,
December 2020 in “Giornale italiano di dermatologia e venereologia” Italian guidelines recommend using trichoscopy for diagnosis and treatments like minoxidil for hair loss.
 August 2019 in “DOAJ (DOAJ: Directory of Open Access Journals)”
August 2019 in “DOAJ (DOAJ: Directory of Open Access Journals)” Minoxidil is a primary treatment for hair loss but its exact working method is unknown.
 8 citations
,
April 2019 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
8 citations
,
April 2019 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Tretinoin boosts minoxidil's effect on hair loss by increasing enzyme activity.
 43 citations
,
July 2018 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
43 citations
,
July 2018 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Finasteride and minoxidil mix works better for hair growth than minoxidil alone, with similar safety.
 3 citations
,
January 2018 in “Annals of Dermatology”
3 citations
,
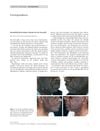
January 2018 in “Annals of Dermatology” A woman developed facial hair cysts after using a 3% minoxidil solution for hair loss, which disappeared after stopping the treatment and removing the cysts surgically.
 24 citations
,
October 2016 in “Oncotarget”
24 citations
,
October 2016 in “Oncotarget” Finasteride has a higher risk of reproductive side effects than minoxidil.
 6 citations
,
May 2012 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology”
6 citations
,
May 2012 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology” Oral minoxidil can cause inflamed, ingrown hairs in the beard area.
 269 citations
,
August 2002 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
269 citations
,
August 2002 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” 5% minoxidil works better for hair growth and density, with minor irritation.
 19 citations
,
December 1985 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
19 citations
,
December 1985 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Minoxidil can cause scalp comedones and acne.