TLDR Poliosis circumscripta is a patch of white hair caused by lack of melanin, linked to genetic and acquired conditions.
Poliosis circumscripta, marked by localized white hair patches due to reduced or absent melanin or melanocytes in hair follicles, could occur on any hairy body area. It was linked to genetic syndromes such as piebaldism, Waardenburg, and tuberous sclerosis, as well as acquired conditions like inflammatory diseases, neoplastic entities, and medication effects. The review aimed to assist clinicians in evaluating patients with poliosis by detailing the various conditions associated with it.
 532 citations
,
August 2011 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
532 citations
,
August 2011 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Vitiligo is a skin condition causing white spots, more common in women, often starts before age 20, and can affect mental health.
 391 citations
,
January 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
391 citations
,
January 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Half of people with Alopecia Areata may see hair regrowth within a year without treatment, but recovery is unpredictable.
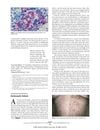 10 citations
,
February 2006 in “Archives of dermatology”
10 citations
,
February 2006 in “Archives of dermatology” A man's chest hair turned white after a shingles infection, possibly due to virus-damaged pigment cells.
51 citations
,
May 2004 in “American journal of ophthalmology” Using topical prostaglandin F2α for glaucoma may cause loss of eyelash or eyebrow pigment.

The woman has unexplained hair loss and it's unclear what her condition is or how to treat it.
 109 citations
,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
109 citations
,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Alopecia areata is a type of hair loss that can lead to complete baldness, often associated with other autoimmune conditions, and half of the cases may see hair return within a year.




