TLDR Photodynamic therapy improved skin issues from sorafenib when other treatments failed.
Sorafenib, used for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma, was linked to significant skin toxicity, including rare follicular involvement. A 55-year-old man developed painful nodular-cystic lesions during treatment. Traditional treatments failed, but photodynamic therapy (PDT) led to clinical improvement without systemic side effects. While PDT did not prevent new lesions, it reduced symptoms and improved the patient's quality of life, allowing continued cancer treatment. This case suggested PDT as a potential option for managing severe skin toxicity when standard therapies were ineffective.
 192 citations
,
January 2015 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
192 citations
,
January 2015 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Targeted cancer therapies often cause serious skin problems that need careful management.
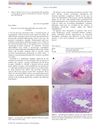 5 citations
,
August 2014 in “Australasian journal of dermatology”
5 citations
,
August 2014 in “Australasian journal of dermatology” Sorafenib can cause delayed skin problems, so patients need careful monitoring.
11 citations
,
December 2013 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Sorafenib often causes skin side effects, indicating effective cancer treatment.
 March 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
March 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The document lists various dermatology topics, treatments, and diagnostic methods.
 2 citations
,
October 2018 in “Springer eBooks”
2 citations
,
October 2018 in “Springer eBooks” Cancer treatments can cause skin-related side effects that may affect patient quality of life and require changes in treatment.
 6 citations
,
April 2013 in “Current Dermatology Reports”
6 citations
,
April 2013 in “Current Dermatology Reports” Dermatologists are crucial for managing skin side effects in metastatic melanoma patients using vemurafenib and ipilimumab.
278 citations
,
May 2013 in “Ca” Targeted anticancer therapies can cause severe side effects similar to traditional chemotherapy, but with different types.
 26 citations
,
August 2018 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
26 citations
,
August 2018 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Hair loss in cancer patients can be related to the cancer itself, treatment, or other conditions, and understanding it is important for diagnosis and patient care.





