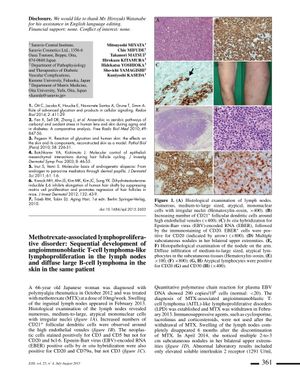
Methotrexate-Associated Lymphoproliferative Disorder: Sequential Development of Angioimmunoblastic T-Cell Lymphoma-Like Lymphoproliferation in the Lymph Nodes and Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma in the Skin in the Same Patient
July 2015
in “
European Journal of Dermatology
”
TLDR Stopping methotrexate might reverse lymphoma-like conditions in some patients.
A 66-year-old Japanese woman with polymyalgia rheumatica developed lymph node swelling and skin nodules after treatment with methotrexate (MTX). Histological examination showed angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma-like lymphoproliferative disorders in the lymph nodes and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the skin. The lymph node swelling and skin nodules regressed after discontinuing MTX, suggesting a potential link between MTX and the development of lymphoproliferative disorders. This case emphasizes the need for awareness of MTX-associated lymphoproliferative disorders and the possibility of a non-aggressive management approach.





