Cells to Surgery Quiz: December 2017
November 2017
in “
The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology
”
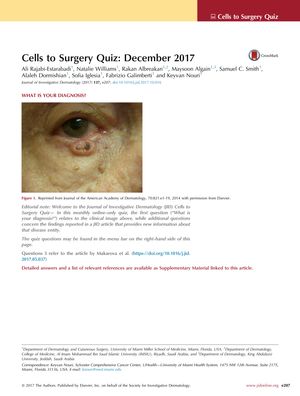
TLDR Mohs micrographic surgery is effective for treating basal cell carcinoma on the eyelid, while radiotherapy has higher recurrence rates, and topical vitamin D3 may reduce and delay BCC formation in mice.
The document provided information on the diagnosis and treatment of basal cell carcinoma (BCC), including the efficacy of Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) for a 55-year-old female patient with BCC on the eyelid. It also discussed the side effects of various treatments such as vismodegib, radiotherapy, and imiquimod (IMQ). Additionally, a study by Makarova et al. was summarized, which found that topical vitamin D3 could reduce visible BCC formation and delay its appearance in mice, and that ultraviolet radiation (UVR) increases circulating vitamin D3 levels in female mice, potentially diminishing UVR's pro-carcinogenic effects. However, oral vitamin D3 supplements were not found to prevent BCC carcinogenesis. Radiotherapy was noted to have higher recurrence rates for BCC compared to surgery (7.5% vs. 0.7%).





