 10 citations,
January 2010 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
10 citations,
January 2010 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Light therapy can effectively treat vitiligo and hair loss caused by a specific medication.
 2 citations,
August 2013 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America”
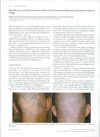
2 citations,
August 2013 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America” Treat the front and middle scalp before the vertex in hair transplants, aim for good density, use non-surgical options for young people, and customize treatment for natural results.
 4 citations,
December 1992 in “The American Journal of Cosmetic Surgery”
4 citations,
December 1992 in “The American Journal of Cosmetic Surgery” The modified S pattern for scalp reduction is effective for removing more bald scalp and hiding scars in hair restoration.
 53 citations,
January 2014 in “Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery”
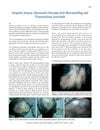
53 citations,
January 2014 in “Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery” Microneedling combined with triamcinolone can safely stimulate faster hair regrowth in people with Alopecia Areata.
 July 2007 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature”
July 2007 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature” The BASP classification is a detailed system for categorizing hair loss in both men and women, but it may be complex for beginners and not fully suitable for grading female hair loss.
 4 citations,
May 2002 in “Aesthetic Surgery Journal”
4 citations,
May 2002 in “Aesthetic Surgery Journal” A new hair loss classification for women improves treatment, but careful patient selection is crucial for successful hair transplantation.
 September 2023 in “Medicina-lithuania”
September 2023 in “Medicina-lithuania” The study suggests that analyzing DNA can help treat hair loss, but more research is needed.
 32 citations,
April 2019 in “JAAD case reports”
32 citations,
April 2019 in “JAAD case reports” JAK inhibitors helped treat hair loss in two people with Down syndrome.
 June 2024 in “Skin Appendage Disorders”
June 2024 in “Skin Appendage Disorders” Both PRP and MZT treatments can significantly improve hair growth in patients with androgenetic alopecia.
 13 citations,
May 2004 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
13 citations,
May 2004 in “Dermatologic Surgery” The paper concludes that copying the natural direction and angle of hair in transplants is key for a natural look and doesn't harm hair survival.
 February 2021 in “International journal of research in dermatology”
February 2021 in “International journal of research in dermatology” A boy's hair, nails, and skin improved after 6 months of steroid treatment.
 17 citations,
January 1996 in “Aesthetic Plastic Surgery”
17 citations,
January 1996 in “Aesthetic Plastic Surgery” The tumescent technique improves hair micrografting by providing lasting anesthesia, reducing bleeding, and increasing patient comfort.
 April 2024 in “JAMA dermatology”
April 2024 in “JAMA dermatology” Oral minoxidil is as effective as topical minoxidil for male hair loss but has more side effects like excessive hair growth and headaches.
 January 2010 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2010 in “Elsevier eBooks” Hair transplantation is a treatment for hair loss mainly caused by genetics, with various techniques and potential complications, and results visible after 8-12 months.
 5 citations,
July 2020 in “JAMA Dermatology”
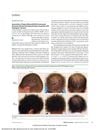
5 citations,
July 2020 in “JAMA Dermatology” Minoxidil solution applied twice daily improved hair growth in patients with Woolly Hair/Hypotrichosis due to LIPH gene issues, with mild side effects.
 12 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
12 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Low-Level Laser Therapy and other light treatments for hair growth lack strong evidence and need more research.
 6 citations,
December 2013 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
6 citations,
December 2013 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” Certain immune cells are more common on the top of the head and might help predict or treat common hair loss.
 June 2004 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
June 2004 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Dr. Walter P. Unger suggests that copying a person's natural hair direction and angle during transplants leads to a more natural and fuller appearance.
 September 2021 in “Medical lasers”
September 2021 in “Medical lasers” Laser treatment followed by a special hair growth solution increased hair count and thickness without side effects.
 30 citations,
September 2017 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
30 citations,
September 2017 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Men with common hair loss may have a higher risk of heart disease and diabetes, and should be checked for these conditions.
 January 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
January 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” The 2015 Hair Research Congress concluded that stem cells, maraviroc, and simvastatin could potentially treat Alopecia Areata, topical minoxidil, finasteride, and steroids could treat Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia, and PTGDR2 antagonists could also treat alopecia. They also found that low-level light therapy could help with hair loss, a robotic device could assist in hair extraction, and nutrition could aid hair growth. They suggested that Alopecia Areata is an inflammatory disorder, not a single disease, indicating a need for personalized treatments.
 90 citations,
June 2006 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
90 citations,
June 2006 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” The document concludes that accurate diagnosis of different types of hair loss requires careful examination of hair and scalp tissue, considering both clinical and microscopic features.
 5 citations,
January 2012 in “Hair therapy & transplantation”
5 citations,
January 2012 in “Hair therapy & transplantation” Hair mesotherapy might help with certain types of hair loss but lacks strong scientific proof and has some risks.
 165 citations,
August 2013 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine”
165 citations,
August 2013 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine” Low-Level Laser Therapy is effective and safe for hair growth with minimal side effects.
 3 citations,
October 1993 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
3 citations,
October 1993 in “The Journal of Dermatology” The review suggests limited treatments for common hair loss conditions, with potential for future improvements.
 20 citations,
July 1990 in “Pediatrics in Review”
20 citations,
July 1990 in “Pediatrics in Review” The four main causes of hair loss in children are fungal infections, pulling out hair, autoimmune hair loss, and stress-related hair shedding.
 9 citations,
April 1986 in “Postgraduate Medicine”
9 citations,
April 1986 in “Postgraduate Medicine” Hair loss has many causes and treatments, and losing some hair daily is normal; proper diagnosis is key, and minoxidil can help treat it.
 3 citations,
October 1982 in “Postgraduate Medicine”
3 citations,
October 1982 in “Postgraduate Medicine” Most types of hair loss can regrow naturally, but there are no effective cures for male pattern or age-related hair loss, and only limited options for females.
 33 citations,
April 1990 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
33 citations,
April 1990 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Minoxidil effectively treats hair loss, with better results in women.
 September 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
September 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Lower vitamin D levels are linked to higher CRP levels in people with a type of hair loss called alopecia areata.






























