 1 citations,
March 2023 in “Science Translational Medicine”
1 citations,
March 2023 in “Science Translational Medicine” Blocking a certain signal in the gp130 receptor can improve tissue healing and lessen osteoarthritis symptoms.
 55 citations,
January 2002 in “Journal of liposome research”
55 citations,
January 2002 in “Journal of liposome research” New liposomal formulations may improve delivery of treatments to hair follicles, potentially helping with hair loss.
 41 citations,
August 2015 in “The FASEB Journal”
41 citations,
August 2015 in “The FASEB Journal” Blocking the Wnt/β‐catenin pathway can speed up wound healing, reduce scarring, and improve cartilage repair.
 94 citations,
June 2016 in “The FASEB Journal”
94 citations,
June 2016 in “The FASEB Journal” The Wnt/β-catenin pathway helps tissue regeneration but can also cause fibrosis, and drugs that inhibit this pathway may aid in healing skin and heart tissues.
 19 citations,
October 2011 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
19 citations,
October 2011 in “Clinics in Dermatology” New chemotherapy drugs cause skin side effects, but treatments like minocycline and tetracycline can help reduce them.
 April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Blocking JAK-STAT5 signaling in mice leads to hair growth.
 112 citations,
January 2014 in “Molecular and cellular therapies”
112 citations,
January 2014 in “Molecular and cellular therapies” Blocking the Wnt pathway could lead to new treatments for cancer and tissue repair but requires careful development to avoid side effects.
 70 citations,
October 2020 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology”
70 citations,
October 2020 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology” Janus kinase inhibitors are promising drugs for treating autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.
 40 citations,
August 2022 in “Frontiers in immunology”
40 citations,
August 2022 in “Frontiers in immunology” Blocking JAK/STAT pathways can help treat hair loss from alopecia areata.
 7 citations,
October 2019 in “Annals of palliative medicine”
7 citations,
October 2019 in “Annals of palliative medicine” New targeted cancer drugs can cause skin side effects, and managing them requires patient education and timely care.
 51 citations,
June 2021 in “Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy”
51 citations,
June 2021 in “Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy” The document concludes that while there are promising methods to control CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing, more research is needed to overcome challenges related to safety and effectiveness for clinical use.
 411 citations,
April 2010 in “Gastroenterology”
411 citations,
April 2010 in “Gastroenterology” Targeting colon cancer stem cells might lead to better treatment results.
 3 citations,
September 2020 in “Molecular Brain”
3 citations,
September 2020 in “Molecular Brain” The anti-viral drug Elvitegravir may protect brain cells from damage related to neurodegenerative diseases.
 1 citations,
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” SM04554 may increase hair growth as a topical treatment for androgenetic alopecia.
 113 citations,
September 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
113 citations,
September 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Applying a special compound can promote hair growth without harmful side effects.

The treatment was ineffective in humans.
24 citations,
March 2020 in “Cells” Natural small molecules can help treat diseases by activating or inhibiting the Wnt pathway.

The new hydrogel helps heal burn wounds better than current options by reducing bacteria and inflammation.
July 2024 in “European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry” New small molecule drugs could help treat hair loss.
 February 2022 in “Journal of Biomedical Nanotechnology”
February 2022 in “Journal of Biomedical Nanotechnology” Shikonin, a small molecule, speeds up burn wound healing and hair growth by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway.
 7 citations,
March 2021 in “Molecular Medicine Reports”
7 citations,
March 2021 in “Molecular Medicine Reports” A mix of specific inhibitors and a growth factor helps keep hair growth cells from losing their properties in the lab.
 16 citations,
March 2018 in “Seminars in Oncology”
16 citations,
March 2018 in “Seminars in Oncology” The document concludes that pregnancy and cancer share immune evasion tactics, but more research is needed before using checkpoint blockade immunotherapy in pregnant cancer patients to avoid harm to the placenta.
2 citations,
December 2023 in “Pharmaceutics” Inhaling medicine may reduce side effects and improve treatment for a major lung cancer type.
 April 2018 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
April 2018 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Certain small molecules can help regrow hair by turning on the body's cell cleanup process.
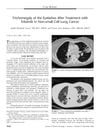 12 citations,
November 2006 in “Journal of thoracic oncology”
12 citations,
November 2006 in “Journal of thoracic oncology” A cancer patient's eyelashes grew excessively without other common side effects after taking the cancer drug erlotinib.

Chemicals and stem cells combined have advanced regenerative medicine with few safety concerns, focusing on improving techniques and treatment effectiveness.
 45 citations,
April 2019 in “International Immunology”
45 citations,
April 2019 in “International Immunology” The study concluded that immune cells attacking hair follicles cause hair loss in alopecia, with genetics and environment also playing a role, and highlighted the potential of certain treatments.
 April 2023 in “Medizinische Genetik”
April 2023 in “Medizinische Genetik” New research has found 14 genes linked to the risk of developing alopecia areata, improving understanding and treatment options.
 17 citations,
December 2019 in “Stem Cells International”
17 citations,
December 2019 in “Stem Cells International” Bioactive molecules show promise for improving skin repair and regeneration by overcoming current challenges with further research.
 16 citations,
July 2017 in “Rheumatology and Therapy”
16 citations,
July 2017 in “Rheumatology and Therapy” Tofacitinib, a medication for arthritis, showed potential for treating severe hair loss in a small Brazilian case series, but more research is needed.



























