 57 citations,
October 2013 in “international journal of endocrinology and metabolism”
57 citations,
October 2013 in “international journal of endocrinology and metabolism” Female pattern hair loss is common, linked to polycystic ovarian syndrome, and treated with topical Minoxidil.
 43 citations,
August 2016 in “International Journal of Nanomedicine”
43 citations,
August 2016 in “International Journal of Nanomedicine” Eupafolin nanoparticles help protect skin cells from damage caused by air pollution.
 39 citations,
April 2001 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
39 citations,
April 2001 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Latanoprost, a glaucoma medication, caused excessive eyelid hair growth in many patients.
 36 citations,
June 2012 in “PubMed”
36 citations,
June 2012 in “PubMed” There are potential treatments for pattern baldness, but more research is needed to confirm their effectiveness.
 36 citations,
November 2005 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
36 citations,
November 2005 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Topical latanoprost doesn't effectively regrow hair in severe eyebrow alopecia areata cases.
 35 citations,
May 2012 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy”
35 citations,
May 2012 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy” The document concludes that there are various treatments for different types of alopecia, but more research is needed for evidence-based treatments.
34 citations,
October 2015 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Scientists don't fully understand eyelash hair follicle biology, including growth and color, and suggest more research is needed.
 33 citations,
November 2006 in “Survey of Ophthalmology”
33 citations,
November 2006 in “Survey of Ophthalmology” Madarosis is the loss of eyelashes and eyebrows due to various health issues and requires thorough examination to diagnose and treat the underlying cause.
 29 citations,
March 2010 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
29 citations,
March 2010 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Wnt3a activates certain genes in hair follicle cells, including a newly discovered one, EP2, which may affect hair growth.
 22 citations,
September 2004 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
22 citations,
September 2004 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Bimatoprost can cause longer, thicker, darker eyelashes and eyebrows.
 22 citations,
April 2003 in “Eye”
22 citations,
April 2003 in “Eye” Applying latanoprost on skin can stimulate hair growth with minimal side effects.
 21 citations,
January 2015 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
21 citations,
January 2015 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Latanoprost may cause scalp inflammation and delayed healing.
 20 citations,
November 2009 in “European Journal of Dermatology”
20 citations,
November 2009 in “European Journal of Dermatology” Latanoprost, a glaucoma treatment, was found ineffective in treating hair loss in eyebrows and eyelashes.
 19 citations,
May 1992 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
19 citations,
May 1992 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Some alternative vitiligo treatments show promise, but none are as effective as psoralens and UVA.
 16 citations,
January 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders”
16 citations,
January 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders” Intralesional corticosteroids work best for mild alopecia areata, and DPCP works best for moderate to severe cases.
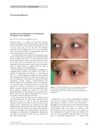 15 citations,
November 2009 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
15 citations,
November 2009 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Bimatoprost helped a girl grow her eyelashes back quickly and without serious side effects.
14 citations,
September 2015 in “PubMed” Alopecia areata can be managed with various treatments, and severe cases should be referred to dermatologists.
 11 citations,
July 2015 in “Gene”
11 citations,
July 2015 in “Gene” DHT affects bone growth by altering gene activity in osteoblasts, potentially complicating steroid use.
 11 citations,
January 2013 in “Ocular Surface”
11 citations,
January 2013 in “Ocular Surface” The document concludes that modern ocular cosmetics enhance beauty and eyelash health, with safe practices and regulations being important.
 9 citations,
December 2017 in “The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology”
9 citations,
December 2017 in “The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology” New targeted therapies for hair loss from alopecia areata show promise, with personalized treatment expected in the future.
9 citations,
March 2015 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” The symposium concluded that understanding the molecular mechanisms of skin aging could lead to better clinical practices and treatments.
7 citations,
March 1990 in “Pigment Cell Research” Certain chemicals cause hair graying in black mice but not yellow mice.
 7 citations,
October 2006 in “Medical hypotheses”
7 citations,
October 2006 in “Medical hypotheses” UV light might cause excessive hair growth by increasing PGE2 in the skin.
 5 citations,
July 2014 in “Actas dermo-sifiliográficas/Actas dermo-sifiliográficas”
5 citations,
July 2014 in “Actas dermo-sifiliográficas/Actas dermo-sifiliográficas” Latanoprost eye drops caused excessive hair growth and eyelash whitening in a woman.
5 citations,
July 2011 in “PubMed” Injected bimatoprost 0.03% solution did not effectively treat female-pattern hair loss.
5 citations,
July 2010 in “Archives of Internal Medicine” Prostaglandins may protect hair follicles during chemotherapy.
 5 citations,
October 1988 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
5 citations,
October 1988 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Minoxidil promotes hair growth but exact mechanism is unknown.
 4 citations,
March 2023 in “Current Oncology”
4 citations,
March 2023 in “Current Oncology” Scalp cooling is the only FDA-approved method to prevent hair loss from chemotherapy, but other treatments like minoxidil and PRP are being tested.
 4 citations,
August 2013 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
4 citations,
August 2013 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Updated treatments for female hair loss include minoxidil, antiandrogens, hair transplants, and light therapy.
 3 citations,
June 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
3 citations,
June 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” The conclusion suggests that focusing on certain cellular pathways may improve the prevention and repair of hair loss caused by radiotherapy.
























