 January 2021 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences”
January 2021 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences” Prolactin levels and gene polymorphism are not linked to vitiligo severity but are related to BMI.
 22 citations,
July 2014 in “Hormones”
22 citations,
July 2014 in “Hormones” Metformin may help treat neuroendocrine tumors.
 July 2018 in “Nasza Dermatologia Online”
July 2018 in “Nasza Dermatologia Online” Frontal fibrosing alopecia and ulerythema ophryogenes may be related and can evolve from one to the other.
 6 citations,
January 2020 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
6 citations,
January 2020 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” New topical treatment using spherical nucleic acids shows promise in reducing psoriasis inflammation.
 33 citations,
October 2013 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
33 citations,
October 2013 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Pioglitazone usually doesn't effectively treat or cure lichen planopilaris.
12 citations,
January 2018 in “Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis” Certain IL-18 gene variations may increase the risk of alopecia areata.
 May 2020 in “JAAD case reports”
May 2020 in “JAAD case reports” Using anthralin and calcipotriene together might help treat tough cases of alopecia areata, but more research is needed to understand how it works.
 March 2024 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology”
March 2024 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology” Tofacitinib successfully treated vitiligo in a patient with lupus without side effects.
1 citations,
March 2022 in “Dermatology Research and Practice” Higher CD70 and CD27 gene expression in alopecia areata lesions predicts disease severity and activity.
 7 citations,
August 2023 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
7 citations,
August 2023 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” JAK inhibitors offer new hope for treating severe alopecia areata.
 26 citations,
January 2017 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
26 citations,
January 2017 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Antidepressants might help with skin inflammation and improve conditions like psoriasis and eczema.
 31 citations,
May 2021 in “Journal of endocrinological investigation”
31 citations,
May 2021 in “Journal of endocrinological investigation” APS-1 in Italy shows diverse AIRE mutations and various autoimmune issues.

Better models and evaluation methods for alopecia areata are needed.
 1 citations,
July 2022 in “Functional foods in health and disease/Journal of functional foods in health & disease”
1 citations,
July 2022 in “Functional foods in health and disease/Journal of functional foods in health & disease” Taking a probiotic supplement twice a day improved hair growth, skin hydration, and metabolic health in adults at risk of metabolic syndrome.
April 2023 in “Media Dermato Venereologica Indonesiana” COVID-19 reinfection may trigger alopecia areata.
1 citations,
January 2017 in “International journal of trichology” Diphenylcyclopropenone (DPCP) effectively treated both alopecia areata and verruca vulgaris.
 2 citations,
February 2018 in “InTech eBooks”
2 citations,
February 2018 in “InTech eBooks” TNF-alpha inhibitors can cause various immune-related skin issues.
56 citations,
March 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” 17β-estradiol can reduce inflammation in the skin.
 1 citations,
January 2024 in “Curēus”
1 citations,
January 2024 in “Curēus” Upadacitinib significantly improved a man's severe scalp condition when other treatments failed.
 52 citations,
October 2010 in “Antiviral Therapy”
52 citations,
October 2010 in “Antiviral Therapy” New treatments for Hepatitis C show promise but need more research to confirm their safety and effectiveness for clinical use.
October 2021 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Herpes simplex virus infections should be considered in pemphigus patients to avoid unnecessary changes in treatment.
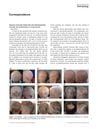 1 citations,
November 2019 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
November 2019 in “International Journal of Dermatology” A 6-year-old girl with alopecia universalis regrew most of her hair after treatment with simvastatin/ezetimibe, minoxidil, and prednisolone.
 6 citations,
September 2017 in “Multiple Sclerosis and Related Disorders”
6 citations,
September 2017 in “Multiple Sclerosis and Related Disorders” Nail loss may be a side effect of the MS drug teriflunomide.
 4 citations,
May 2021 in “Biomedicines”
4 citations,
May 2021 in “Biomedicines” Targeting the protein Caveolin-1 might help treat a type of scarring hair loss called Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia.
 15 citations,
April 2022 in “Immunology”
15 citations,
April 2022 in “Immunology” Men and women get COVID-19 at similar rates, but men tend to get sicker and have a higher risk of dying, while women usually have stronger immune responses and vaccine reactions.
 March 2023 in “Revista română de reumatologie”
March 2023 in “Revista română de reumatologie” Skin problems are common in lupus, often appearing first, with various types and treatments, and careful monitoring is important for diagnosis and management.
 1 citations,
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Tofacitinib may slow hair loss in scarring alopecias but is unlikely to regrow significant hair.
 52 citations,
January 2022 in “Current Research in Pharmacology and Drug Discovery”
52 citations,
January 2022 in “Current Research in Pharmacology and Drug Discovery” New treatments for COVID-19 show promise, but more effective antiviral drugs are needed.
1 citations,
June 2016 in “FEBS open bio” Fish oil increased cell growth and macrophages in the skin but didn't affect COX-2 expression.
 January 2025 in “Journal of Personalized Medicine”
January 2025 in “Journal of Personalized Medicine” People with Alopecia Areata are more likely to have prediabetes and obesity.























