 2 citations,
April 2015 in “S. Karger AG eBooks”
2 citations,
April 2015 in “S. Karger AG eBooks” The document concludes that successful surgical repair of scalp and forehead issues requires careful planning and various techniques depending on the injury or defect size.
 23 citations,
March 2001 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
23 citations,
March 2001 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Hair restoration surgery techniques have evolved, with focus on patient selection and realistic goals, and future advancements may include cloning and gene therapy.
 3 citations,
December 1987 in “The Journal of Dermatologic Surgery and Oncology”
3 citations,
December 1987 in “The Journal of Dermatologic Surgery and Oncology” Understanding facial anatomy and aesthetics is key for good functional and cosmetic outcomes after tumor removal surgery on the forehead and eyebrow.
 20 citations,
February 1991 in “The Journal of Dermatologic Surgery and Oncology”
20 citations,
February 1991 in “The Journal of Dermatologic Surgery and Oncology” Scalp flaps are used for reconstruction, considering factors like inelasticity, hair growth, and blood supply, with techniques adapting to age-related changes in vascularity.
 December 2002 in “Operative Techniques in Otolaryngology-head and Neck Surgery”
December 2002 in “Operative Techniques in Otolaryngology-head and Neck Surgery” Manage hair loss from trauma with scalp expansion, advancement flaps, and hair transplantation.
 2 citations,
October 2010 in “Springer eBooks”
2 citations,
October 2010 in “Springer eBooks” Using cheek skin and cartilage grafts for nose reconstruction after skin cancer surgery can maintain shape and function but may require multiple surgeries and hair removal in men.
 10 citations,
January 2011 in “Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery”
10 citations,
January 2011 in “Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery” Surgical methods for hair loss are less common than hair transplants but still useful, especially for scarring hair loss.
 April 1981 in “Postgraduate Medicine”
April 1981 in “Postgraduate Medicine” In 1981, the punch graft technique was the main method for hair transplantation, and medical treatments for baldness were not very effective.
 2 citations,
May 2005 in “Seminars in Plastic Surgery”
2 citations,
May 2005 in “Seminars in Plastic Surgery” The Juri Temporo-Parieto-Occipital Flap is a good option for scalp reconstruction and hairline restoration with a natural look, despite some risk of necrosis and scarring.
 15 citations,
March 2000 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
15 citations,
March 2000 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Hair transplantation has evolved since 1822, with significant advancements by key figures and widespread international growth.
 3 citations,
December 2008 in “The American Journal of Cosmetic Surgery”
3 citations,
December 2008 in “The American Journal of Cosmetic Surgery” Hair transplantation has evolved to refined techniques like FUE and FUT, with Finasteride and Minoxidil as the only other proven treatments for hair loss.
 5 citations,
May 2005 in “Seminars in Plastic Surgery”
5 citations,
May 2005 in “Seminars in Plastic Surgery” The document concludes that correcting poor hair transplants requires a careful plan and a mix of techniques to achieve a natural look and address various challenges.
 17 citations,
May 2013 in “Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Clinics of North America”
17 citations,
May 2013 in “Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Clinics of North America” The document concludes that careful surgical methods and choosing the right materials are key for successful scalp, skull, and frontal sinus reconstruction.
 27 citations,
January 2008 in “Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery”
27 citations,
January 2008 in “Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery” Modern hair restoration techniques have evolved from punch grafting to methods like micro-grafting and follicular unit transplantation, but they are labor-intensive, expensive, and can lead to patient dissatisfaction. Future treatments may involve cloned hair follicles and drugs like finasteride.
 18 citations,
March 2018 in “Archives of Plastic Surgery”
18 citations,
March 2018 in “Archives of Plastic Surgery” The superficial temporal artery flap is a reliable method for reconstructing complex facial defects with minimal complications.
 5 citations,
July 1988 in “Facial Plastic Surgery”
5 citations,
July 1988 in “Facial Plastic Surgery” Tissue expansion is a useful method for reconstructive surgery with good results and room for further enhancement.
 19 citations,
February 2008 in “Facial Plastic Surgery”
19 citations,
February 2008 in “Facial Plastic Surgery” The article concludes that microvascular free flaps, especially the latissimus dorsi flap, are recommended for large scalp reconstructions, and hair transplantation offers high survival rates and excellent aesthetic results.
 5 citations,
January 1985 in “Facial Plastic Surgery”
5 citations,
January 1985 in “Facial Plastic Surgery” Flap surgery is effective for treating male baldness, offering immediate results with dense hair growth.
 September 2004 in “Atlas of the Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Clinics”
September 2004 in “Atlas of the Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Clinics” Hair restoration surgery techniques can effectively treat scalp deformities and have evolved to provide natural-looking results.
 1 citations,
January 2010 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2010 in “Elsevier eBooks” The document concludes that local flaps are effective for reconstructive surgery in the head and neck, offering good skin match and function.
 9 citations,
February 2013 in “Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery”
9 citations,
February 2013 in “Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery” The article explains how to rebuild parts of the head and face and how to transplant hair to cover scars, highlighting the need for careful planning and choosing the right method for each patient.
 57 citations,
July 2005 in “Clinics in Plastic Surgery”
57 citations,
July 2005 in “Clinics in Plastic Surgery” Reconstruct lips with proper planning, templates, and revisions for appearance and function.
 10 citations,
May 2009 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
10 citations,
May 2009 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Technique effectively reconstructs large scalp defects with minimal hair loss and visible scarring.
 10 citations,
July 1981 in “Archives of Otolaryngology-head & Neck Surgery”
10 citations,
July 1981 in “Archives of Otolaryngology-head & Neck Surgery” Short scalp flaps are easier but not good for severe baldness; Juri flaps are complex but better for density and coverage.
 May 1993 in “Medical Clinics of North America”
May 1993 in “Medical Clinics of North America” Surgical hair replacement is a viable option for male pattern baldness when done with proper planning and realistic expectations.

The conclusion is that closing scalp wounds is possible, but restoring hair without donor material is still a major challenge.
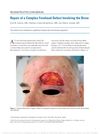 3 citations,
April 2016 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
3 citations,
April 2016 in “Dermatologic Surgery” A man's forehead and eyebrow were successfully reconstructed with a skin and hair graft that matched his other eyebrow, without needing frequent trimming.
 December 1994 in “The American Journal of Cosmetic Surgery”
December 1994 in “The American Journal of Cosmetic Surgery” Understanding the scalp's blood flow and using delay techniques can improve the success of hair restoration surgeries.
 17 citations,
March 2006 in “BJU international”
17 citations,
March 2006 in “BJU international” Using buccal mucosa for hypospadias repair in children is effective and reduces complications.
 26 citations,
July 2006 in “Current Opinion in Otolaryngology & Head and Neck Surgery”
26 citations,
July 2006 in “Current Opinion in Otolaryngology & Head and Neck Surgery” New techniques in scalp reconstruction have improved cosmetic results and reduced complications, especially for large defects.






























