 15 citations
,
April 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
15 citations
,
April 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Oral minoxidil can increase or maintain hair thickness in most people with lichen planopilaris, with mild side effects.
 3 citations
,
January 2018
3 citations
,
January 2018 A woman had an unusual allergic reaction to a hair loss treatment, which cleared up after stopping the treatment and using a different medication.
 14 citations
,
January 2015 in “Skin appendage disorders”
14 citations
,
January 2015 in “Skin appendage disorders” Minoxidil treatment for hair loss can cause scalp allergy and severe hair loss.
September 2014 in “DOAJ (DOAJ: Directory of Open Access Journals)” Rosemary is as effective as Minoxidil for treating alopecia areata.
71 citations
,
December 2013 in “The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings/The Journal of investigative dermatology symposium proceedings” There are no FDA-approved treatments for Alopecia Areata, and current options have varying success and relapse rates.
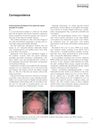 12 citations
,
November 2011 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
12 citations
,
November 2011 in “International Journal of Dermatology” A woman developed a scalp condition from using minoxidil, which improved with a different treatment but left scarring.
 7 citations
,
January 2009 in “International Journal of Trichology”
7 citations
,
January 2009 in “International Journal of Trichology” Dermoscopy can't help doctors identify scalp irritation caused by topical minoxidil.
12 citations
,
January 2006 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Topical 1% sildenafil is not recommended for treating alopecia areata in children.
 72 citations
,
January 2001 in “Drugs”
72 citations
,
January 2001 in “Drugs” Minoxidil and finasteride treat hair loss; more research needed for other options.
 19 citations
,
December 1985 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
19 citations
,
December 1985 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Minoxidil can cause scalp comedones and acne.








