 33 citations,
August 2018 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America”
33 citations,
August 2018 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America” The document explains hair biology, the causes of hair loss, and reviews various hair loss treatments.
[object Object]  11 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology”
11 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology” Taking Propecia might lead to the development of cataracts.
 January 2016 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2016 in “Springer eBooks” The conclusion is that using the 5W1H method can improve diagnosis and management of childhood hair-pulling disorder.
 23 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology”
23 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology” A boy with chromosome 13q deletion syndrome developed eye cancer, a woman with breast cancer lost vision due to a rare side-effect of her treatment, a man's vision worsened after using a hair loss drug, and two rare disorders were discussed. Optical Coherence Tomography is useful for diagnosing and monitoring these conditions.
 45 citations,
April 2019 in “International Immunology”
45 citations,
April 2019 in “International Immunology” The study concluded that immune cells attacking hair follicles cause hair loss in alopecia, with genetics and environment also playing a role, and highlighted the potential of certain treatments.
 30 citations,
January 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
30 citations,
January 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Fibrosing alopecia in a pattern distribution is a hair loss condition often confused with other types, requiring early treatment but usually not resulting in significant hair regrowth.
 29 citations,
January 2007 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
29 citations,
January 2007 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Eyebrow loss has many causes and requires accurate diagnosis for proper treatment.
July 2024 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” The inhibitor DPP can promote hair growth.
 19 citations,
August 2019 in “Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets”
19 citations,
August 2019 in “Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets” New treatments for hair loss may target specific pathways and generate new hair follicles.
 8 citations,
July 2012 in “Cambridge University Press eBooks”
8 citations,
July 2012 in “Cambridge University Press eBooks” Androgens can both increase body hair and cause scalp hair loss.
 January 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” The document concludes that alopecia has various forms, each with specific treatments, but no definitive cure for certain types like CCCA has been proven.
 47 citations,
October 2014 in “Expert Opinion on Emerging Drugs”
47 citations,
October 2014 in “Expert Opinion on Emerging Drugs” New alopecia treatments aim for better results and fewer side effects.
[object Object]  6 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology”
6 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology” The document concludes that careful diagnosis is crucial for chromosome 13q deletion syndrome, tamoxifen can cause reversible eye damage, finasteride may be linked to cataracts, and OCT is useful for diagnosing macular diseases.
 42 citations,
March 2006 in “Drug Discovery Today: Therapeutic Strategies”
42 citations,
March 2006 in “Drug Discovery Today: Therapeutic Strategies” The conclusion is that we need more effective hair loss treatments than the current ones, and these could include new drugs, gene and stem cell therapy, hormones, and scalp cooling, but they all need thorough safety testing.
 7 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology”
7 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology” Hair loss can be caused by stress, infections, drugs, and various diseases, with treatment depending on accurate diagnosis.
 288 citations,
June 2009 in “Human reproduction update”
288 citations,
June 2009 in “Human reproduction update” The modified Ferriman-Gallwey method is a useful tool for diagnosing hirsutism.
 55 citations,
July 2016 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
55 citations,
July 2016 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Multiple treatments work best for hair loss.
 13 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology”
13 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology” A baby boy with 13q deletion syndrome had eye cancer, a woman's vision improved after stopping a breast cancer drug, a man developed cataracts from using Propecia, and a rare skin disorder called Lipoid Proteinosis was discussed. Also, a tool called OCT is useful for diagnosing macular diseases.
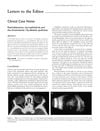 7 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology”
7 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology” Finasteride, often used for hair loss, can potentially cause cataracts.
 20 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology”
20 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology” Eye exams are crucial for kids with 13q deletion syndrome, tamoxifen can cause vision loss, Propecia may lead to cataracts, Lipoid Proteinosis causes skin bumps, and OCT is useful for diagnosing macular diseases.
 8 citations,
September 2021 in “Skin appendage disorders”
8 citations,
September 2021 in “Skin appendage disorders” Trichotillomania treatment is most successful with a mix of behavioral therapy, medication, and social support.
 1 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical research in dermatology”
1 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical research in dermatology” Hair loss, known as Androgenetic Alopecia, is often caused by hormones and can be diagnosed using noninvasive techniques. Treatments include topical minoxidil and oral finasteride, with new treatments being explored. There may also be a link between this type of hair loss and heart disease risk.
83 citations,
August 2020 in “Resources” Macroalgae compounds offer sustainable, effective benefits for cosmetics.
 33 citations,
March 2006 in “Seminars in cutaneous medicine and surgery”
33 citations,
March 2006 in “Seminars in cutaneous medicine and surgery” The document explains how to identify different hair problems using a microscope.
 8 citations,
January 2015 in “Scars, burns & healing”
8 citations,
January 2015 in “Scars, burns & healing” Hair transplantation effectively treats burn scar alopecia, improving self-esteem and confidence.
 59 citations,
June 2008 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
59 citations,
June 2008 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The article explains the genetic causes and symptoms of various hair disorders and highlights the need for more research to find treatments.
 53 citations,
March 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine”
53 citations,
March 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine” The document explains different types of hair loss, their causes, and treatments, and suggests future research areas.
 51 citations,
January 2012 in “Annals of Dermatology”
51 citations,
January 2012 in “Annals of Dermatology” Asian hair loss differs from Europeans; consider individual needs and psychological well-being for treatment.
 11 citations,
September 2010 in “American Journal of Medical Genetics - Part A”
11 citations,
September 2010 in “American Journal of Medical Genetics - Part A” A Turkish family with sparse hair and eyebrow loss has a mutation in the U2HR gene linked to Marie Unna hereditary hypotrichosis.
 49 citations,
January 2003 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
49 citations,
January 2003 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Effective management of children's hair loss involves accurate diagnosis, various treatments, and supportive care.




























