January 2017 in “대한피부과학회지” Minoxidil effectively improved hair loss in a teenage girl with androgenetic alopecia.
[object Object] 
The document concludes that Loose Anagen Hair Syndrome is a benign condition where hair is thin and easily pulled out, often improving with age.
 72 citations,
July 2008 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
72 citations,
July 2008 in “Dermatologic Therapy” CCCA is a scarring hair loss condition mainly in African descent women, possibly caused by genetics and hairstyling, treated with gentle hair care and medications.
 12 citations,
June 2017 in “Cell Cycle”
12 citations,
June 2017 in “Cell Cycle” Minoxidil foam helps hair growth by increasing good proteins and decreasing bad pathways in men with hair loss.
 3 citations,
March 2014 in “Turkderm”
3 citations,
March 2014 in “Turkderm” Hair loss in men can be slowed or reversed with treatments like minoxidil and finasteride, but it resumes if treatment stops. It may also indicate early heart disease and obesity.
 1 citations,
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
1 citations,
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” The conclusion is that detailed clinical descriptions help pathologists diagnose hair loss conditions more accurately.
 1 citations,
October 2006 in “Journal of Family Planning and Reproductive Health Care”
1 citations,
October 2006 in “Journal of Family Planning and Reproductive Health Care” The contraceptive implant Implanon may be linked to hair loss, but the reported case of alopecia could be unrelated to the implant.
 December 2024 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology Venereology and Leprology”
December 2024 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology Venereology and Leprology” Atypical male hair loss may not respond to usual treatments.
 November 2024 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences”
November 2024 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences” Reduced alpha smooth muscle actin may cause hair loss in androgenetic alopecia.
 February 2024 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
February 2024 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” This type of hair loss is probably often missed and treatments reducing inflammation might work well.
 September 2023 in “Medicine”
September 2023 in “Medicine” Herbal extract spray improved hair growth in a man with hair loss.
 July 2023 in “International journal of trichology”
July 2023 in “International journal of trichology” Cellcurin therapy with microneedling increases hair density and thickness in treating hair loss in men and women.
 January 2023 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2023 in “Springer eBooks” Most older adults experience pattern hair loss due to shrinking hair follicles, with men and women showing different balding patterns.
Cellcurin serum significantly increased hair growth in people with androgenetic alopecia.
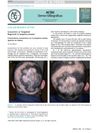 April 2016 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
April 2016 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” The document concludes that a unique target-like hair regrowth pattern in alopecia areata may be more common than thought and should be properly identified.
January 2009 in “Revista de Ciências Médicas” Male pattern baldness is a genetic condition causing hair loss, with limited but improving treatment options.
May 2022 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual” Trichoscopy is crucial for diagnosing and managing androgenetic alopecia, showing increased vellus hairs, empty follicles, and fibrosis with severity.
 June 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
June 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Microneedling with PRP and minoxidil (5%) improves hair growth more than minoxidil (5%) alone.

Male androgenetic alopecia (MAA) is a common, hereditary hair loss condition in men, linked to heart disease, and can be treated with minoxidil, finasteride, or hair transplantation.
[object Object]  12 citations,
June 2006 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia”
12 citations,
June 2006 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” The study found average numbers for different types of hair follicles in the scalp and observed differences between men and women, suggesting reasons for more common hair shedding in women.
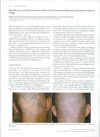 10 citations,
January 2010 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
10 citations,
January 2010 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Light therapy can effectively treat vitiligo and hair loss caused by a specific medication.
 4 citations,
October 2011 in “Pediatric dermatology”
4 citations,
October 2011 in “Pediatric dermatology” Head lice can cause unusual patchy hair loss.
3 citations,
June 2015 in “CRC Press eBooks” Male pattern hair loss affects up to 80% of men due to genetics and hormone sensitivity.
 2 citations,
July 2021 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
2 citations,
July 2021 in “Dermatologic Therapy” A woman's hair loss after COVID-19 was likely due to a mix of pressure-induced alopecia and acute telogen effluvium.
 2 citations,
January 2007 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
2 citations,
January 2007 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Red and infrared light therapy improves hair growth in balding patients.
 September 2024 in “LUTS Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms”
September 2024 in “LUTS Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms” People with hair loss may have worse urinary symptoms due to an enlarged prostate.

Minoxidil and finasteride are the only FDA-approved treatments for hair loss caused by genetic and hormonal factors, but their effectiveness is often doubted, indicating a need for new treatments.
 July 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
July 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The research found that male pattern hair loss is mostly genetic and involves hair thinning due to hormonal effects and changes in gene expression.
 May 2015 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
May 2015 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Oral minoxidil effectively increases hair growth in male baldness but can cause side effects like excessive hair growth and swelling.
Androgenetic alopecia is a common type of hair loss in men and women, caused by a testosterone byproduct affecting hair follicles, with sensitivity determined by genetics.
























